Generative Approach Under Computer Aided Process Planning ( 2l3258
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Generative Approach Under Computer Aided Process Planning ( as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 886
- Pages: 14
GENERATIVE APPROACH UNDER COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS PLANNING (CAPP)
PROCESS PLANNING Is concerned with determining the sequence of individual machining operations needed to produce a given part or product. The resulting operation sequence is documented on a form typically referred to as a route sheet. This is a manual process, mainly dependent on experience and judgement of the planer. Here, there are differences among operation sequences developed by various planners, thus often leads to disputes
Cont..
There are various other difficulties in traditional process planning procedure, for example:
•
New machine tools in the factory make the old routings less optimal
Hence the need for a program which automatically generates the manufacturing operation sequence in order to eliminate these difficulties (CAPP)
CAPP incorporates logic, experience and judgement into a computer system
Introduction to: COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS PLANNING (CAPP)
The use of computer technology to aid in the process planning of a part or product in manufacturing.
CAPP works as the interface between CAD and CAM.
It takes CAD data, converts it to production data.
The production data is then fed to a production system.
CAPP has 2 alternative approaches:
Variant Systems and Generative Process Planning systems
GENERATIVE PROCESS PLANNING
It generates process plans utilizing decision logic, formulas, manufacturing rules, geometry based data to determine the processes required to convert the raw materials into finished parts. GPP involves the use of the computer to create an individual process plan from scratch, automatically and without human assistance. The computer would employ a set of algorithms through the various technical and logical decisions to determine the final plan for manufacturing
Generative CAPP cont..
Inputs to the system would include a comprehensive description of the workpart, such as:
•
part code number to summarize the workpart data.
Generative process plan mainly consists of two major components :
(i) Geometry based coding scheme.
(ii) Knowledge Based
Generative CAPP cont..
Geometry-based Coding Scheme:
All the geometric features for all process such as related surfaces, feature dimension, locations, on the features are defined by geometry based coding scheme.
The level of detail is much greater in generative system than a variant system
Knowledge Based:
Process knowledge in the form of decision logic and data are used for matching of part geometry requirement with the manufacturing capabilities.
Generative CAPP: Ingredients required in fully generative process planning system 1.The first ingredient is the technical knowledge of manufacturing and the logic that is used by successful process planners must be captured and coded into a computer program. In an expert system as it would be applied to process planning, the knowledge and logic of the human process planners is incorporated into a "knowledge base". The generative CAPP system would then use that knowledge base to solve process planning problems (i.e., create route sheet).
Generative CAPP cont.. 2.The second ingredient in generative process planning is a computer-compatible description of the part to be produced.
This description contains all of the pertinent data and information needed to plan the process sequence.
Two possible ways of providing this description are:
The geometric model of the part that is developed on a CAD system during product design.
A GT code number of the part that defines the part features in significant detail.
Generative CAPP cont.. 3.The third ingredient in a generative CAPP system is the capability to apply the process knowledge and planning logic contained in the knowledge base to a given part description.
The problem-solving procedure is referred to as the "inference engine" in the terminology of expert system. By using its knowledge base and inference engine, the CAPP system synthesizes a new process plan from scratch for each new part it is presented.
-Other planning functions, such as machine selection, tool selection, and process optimization, can also be automated using generative planning techniques.
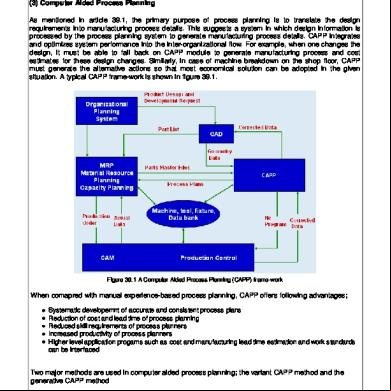
Block Diagram for Generative CAPP
Examples of the Generative CAPP Systems
Advantages of Generative CAPP
1) Process rationalization: In CAPP the same software carries out the process planning and its procedure remains the same whoever uses it. Thus the process planning becomes logical, consistent and rationalized as it does not depends on the individualistic experience or judgment.
2) Higher productivity of the process planners: With CAPP the amount of the clerical work is greatly reduced for the process engineers and there are fewer chances of errors. The planners can invest their time on more skilled jobs and also attain the better process plan that is eventually translated into their higher productivity.
3) Faster planning: With CAPP system the engineers can make the routing sheets for the jobs faster resulting in lesser lead times for the manufacturing process.
4) Good visibility: The documents made from the computer are neat, clean and clear, which makes reading the routing sheets easier.
5) Operate with other software: The CAPP software can be easily integrated with the other software like deg and manufacturing software. This makes the whole process of deg, planning and manufacturing an integrated process.
Disadvantages
Drawbacks is complex and very difficult to develop
Generative process plan design requires long term investments of people, machinery, and time.
PROCESS PLANNING Is concerned with determining the sequence of individual machining operations needed to produce a given part or product. The resulting operation sequence is documented on a form typically referred to as a route sheet. This is a manual process, mainly dependent on experience and judgement of the planer. Here, there are differences among operation sequences developed by various planners, thus often leads to disputes
Cont..
There are various other difficulties in traditional process planning procedure, for example:
•
New machine tools in the factory make the old routings less optimal
Hence the need for a program which automatically generates the manufacturing operation sequence in order to eliminate these difficulties (CAPP)
CAPP incorporates logic, experience and judgement into a computer system
Introduction to: COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS PLANNING (CAPP)
The use of computer technology to aid in the process planning of a part or product in manufacturing.
CAPP works as the interface between CAD and CAM.
It takes CAD data, converts it to production data.
The production data is then fed to a production system.
CAPP has 2 alternative approaches:
Variant Systems and Generative Process Planning systems
GENERATIVE PROCESS PLANNING
It generates process plans utilizing decision logic, formulas, manufacturing rules, geometry based data to determine the processes required to convert the raw materials into finished parts. GPP involves the use of the computer to create an individual process plan from scratch, automatically and without human assistance. The computer would employ a set of algorithms through the various technical and logical decisions to determine the final plan for manufacturing
Generative CAPP cont..
Inputs to the system would include a comprehensive description of the workpart, such as:
•
part code number to summarize the workpart data.
Generative process plan mainly consists of two major components :
(i) Geometry based coding scheme.
(ii) Knowledge Based
Generative CAPP cont..
Geometry-based Coding Scheme:
All the geometric features for all process such as related surfaces, feature dimension, locations, on the features are defined by geometry based coding scheme.
The level of detail is much greater in generative system than a variant system
Knowledge Based:
Process knowledge in the form of decision logic and data are used for matching of part geometry requirement with the manufacturing capabilities.
Generative CAPP: Ingredients required in fully generative process planning system 1.The first ingredient is the technical knowledge of manufacturing and the logic that is used by successful process planners must be captured and coded into a computer program. In an expert system as it would be applied to process planning, the knowledge and logic of the human process planners is incorporated into a "knowledge base". The generative CAPP system would then use that knowledge base to solve process planning problems (i.e., create route sheet).
Generative CAPP cont.. 2.The second ingredient in generative process planning is a computer-compatible description of the part to be produced.
This description contains all of the pertinent data and information needed to plan the process sequence.
Two possible ways of providing this description are:
The geometric model of the part that is developed on a CAD system during product design.
A GT code number of the part that defines the part features in significant detail.
Generative CAPP cont.. 3.The third ingredient in a generative CAPP system is the capability to apply the process knowledge and planning logic contained in the knowledge base to a given part description.
The problem-solving procedure is referred to as the "inference engine" in the terminology of expert system. By using its knowledge base and inference engine, the CAPP system synthesizes a new process plan from scratch for each new part it is presented.
-Other planning functions, such as machine selection, tool selection, and process optimization, can also be automated using generative planning techniques.
Block Diagram for Generative CAPP
Examples of the Generative CAPP Systems
Advantages of Generative CAPP
1) Process rationalization: In CAPP the same software carries out the process planning and its procedure remains the same whoever uses it. Thus the process planning becomes logical, consistent and rationalized as it does not depends on the individualistic experience or judgment.
2) Higher productivity of the process planners: With CAPP the amount of the clerical work is greatly reduced for the process engineers and there are fewer chances of errors. The planners can invest their time on more skilled jobs and also attain the better process plan that is eventually translated into their higher productivity.
3) Faster planning: With CAPP system the engineers can make the routing sheets for the jobs faster resulting in lesser lead times for the manufacturing process.
4) Good visibility: The documents made from the computer are neat, clean and clear, which makes reading the routing sheets easier.
5) Operate with other software: The CAPP software can be easily integrated with the other software like deg and manufacturing software. This makes the whole process of deg, planning and manufacturing an integrated process.
Disadvantages
Drawbacks is complex and very difficult to develop
Generative process plan design requires long term investments of people, machinery, and time.