Nptel Computer Aided Process Planning 3qq4h
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Nptel Computer Aided Process Planning as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 658
- Pages: 2
Module G:Computer Aided Process Planning
1 of 2
http://nptel.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-Delhi/Computer Aided ...
Module G (6) : Computer Aided Process Planning
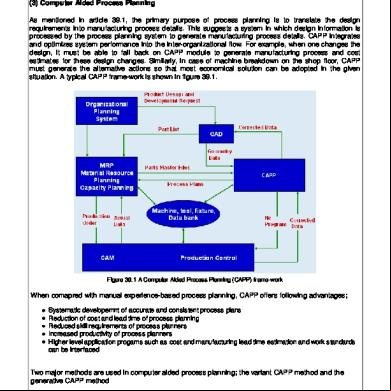
(3) Computer Aided Process Planning As mentioned in article 39.1, the primary purpose of process planning is to translate the design requirements into manufacturing process details. This suggests a system in which design information is processed by the process planning system to generate manufacturing process details. CAPP integrates and optimizes system performance into the inter-organizational flow. For example, when one changes the design, it must be able to fall back on CAPP module to generate manufacturing process and cost estimates for these design changes. Similarly, in case of machine breakdown on the shop floor, CAPP must generate the alternative actions so that most economical solution can be adopted in the given situation. A typical CAPP frame-work is shown in figure 39.1.
Figure 39.1 A Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP) frame-work
When comapred with manual experience-based process planning, CAPP offers following advantages; Systematic developemnt of accurate and consistent process plans Reduction of cost and lead time of process planning Reduced skill requirements of process planners Increased productivity of process planners Higher level application progams such as cost and manufacturing lead time estimation and work standards can be interfaced
Two major methods are used in computer aided process planning; the variant CAPP method and the generative CAPP method (3.1) The variant CAPP method In variant CAPP approach, a process plan for a new part is created by recalling, identifying and
7/3/2014 8:31 PM
Module G:Computer Aided Process Planning
2 of 2
http://nptel.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-Delhi/Computer Aided ...
retrieving an existing plan for a similar part and making necessary modifications for the new part. Sometimes, the process plans are developed for parts representing a fmily of parts called 'master parts'. The similiarities in design attributes and manufacturing methods are exploited for the purpose of formation of part families. A number of methods have been developed for part family formation using coding and classification schemes of group technology (GT), similiarity-coefficient based algorithms and mathematical programming models. The variant process planning approach can be realized as a four step process; 1. 2. 3. 4.
Definition of coding scheme Grouping parts into part families Development of a standard process plan Retrieval and modification of standard process plan
A number of variant process planning schemes have been developed and are in use. One of the most widely used CAPP system is CAM-I developed by McDonnell-Douglas Automation Company. This system can be used to generate process plan for rotational, prismatic and sheet-metal parts. 3.2 The generative CAPP method The next stage of evolution is towards generative CAPP. In the generative CAPP, process plans are generated by means of decision logic, formulas, technology algorithms and geometry based data to perform uniquely many processing decisions for converting part from raw material to finished state. There are two major components of generative CAPP; a geometry based coding scheme and process knowledge in form of decision logic data. The geometry based coding scheme defines all geometric features for process related surfaces together with feature dimensions, locations, tolerances and the surface finish desired on the features. The level of detail is much greater in a generative system than a variant system. For example, details such as rough and finished states of the parts and process capability of machine tools to transform these parts to the desired states are provided. Process knowledge in form of in the form of decision logic and data matches the part geometry requirements with the manufacturing capabilities using knowledge base. It includes selection of processes, machine tools, jigs or fixtures, tools, inspection equipments and sequencing operations. Development of manufacturing knowledge base is backbone of generative CAPP. The tools that are widely used in development of this database are flow-charts, decision tables, decision trees, iterative algorithms, concept of unit machined surfaces, pattern recognition techniques and artificial intelligence techniques such as expert system shells. < PREV
NEXT >
Prof.Madhusudan Rao
7/3/2014 8:31 PM
1 of 2
http://nptel.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-Delhi/Computer Aided ...
Module G (6) : Computer Aided Process Planning
(3) Computer Aided Process Planning As mentioned in article 39.1, the primary purpose of process planning is to translate the design requirements into manufacturing process details. This suggests a system in which design information is processed by the process planning system to generate manufacturing process details. CAPP integrates and optimizes system performance into the inter-organizational flow. For example, when one changes the design, it must be able to fall back on CAPP module to generate manufacturing process and cost estimates for these design changes. Similarly, in case of machine breakdown on the shop floor, CAPP must generate the alternative actions so that most economical solution can be adopted in the given situation. A typical CAPP frame-work is shown in figure 39.1.
Figure 39.1 A Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP) frame-work
When comapred with manual experience-based process planning, CAPP offers following advantages; Systematic developemnt of accurate and consistent process plans Reduction of cost and lead time of process planning Reduced skill requirements of process planners Increased productivity of process planners Higher level application progams such as cost and manufacturing lead time estimation and work standards can be interfaced
Two major methods are used in computer aided process planning; the variant CAPP method and the generative CAPP method (3.1) The variant CAPP method In variant CAPP approach, a process plan for a new part is created by recalling, identifying and
7/3/2014 8:31 PM
Module G:Computer Aided Process Planning
2 of 2
http://nptel.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-Delhi/Computer Aided ...
retrieving an existing plan for a similar part and making necessary modifications for the new part. Sometimes, the process plans are developed for parts representing a fmily of parts called 'master parts'. The similiarities in design attributes and manufacturing methods are exploited for the purpose of formation of part families. A number of methods have been developed for part family formation using coding and classification schemes of group technology (GT), similiarity-coefficient based algorithms and mathematical programming models. The variant process planning approach can be realized as a four step process; 1. 2. 3. 4.
Definition of coding scheme Grouping parts into part families Development of a standard process plan Retrieval and modification of standard process plan
A number of variant process planning schemes have been developed and are in use. One of the most widely used CAPP system is CAM-I developed by McDonnell-Douglas Automation Company. This system can be used to generate process plan for rotational, prismatic and sheet-metal parts. 3.2 The generative CAPP method The next stage of evolution is towards generative CAPP. In the generative CAPP, process plans are generated by means of decision logic, formulas, technology algorithms and geometry based data to perform uniquely many processing decisions for converting part from raw material to finished state. There are two major components of generative CAPP; a geometry based coding scheme and process knowledge in form of decision logic data. The geometry based coding scheme defines all geometric features for process related surfaces together with feature dimensions, locations, tolerances and the surface finish desired on the features. The level of detail is much greater in a generative system than a variant system. For example, details such as rough and finished states of the parts and process capability of machine tools to transform these parts to the desired states are provided. Process knowledge in form of in the form of decision logic and data matches the part geometry requirements with the manufacturing capabilities using knowledge base. It includes selection of processes, machine tools, jigs or fixtures, tools, inspection equipments and sequencing operations. Development of manufacturing knowledge base is backbone of generative CAPP. The tools that are widely used in development of this database are flow-charts, decision tables, decision trees, iterative algorithms, concept of unit machined surfaces, pattern recognition techniques and artificial intelligence techniques such as expert system shells. < PREV
NEXT >
Prof.Madhusudan Rao
7/3/2014 8:31 PM