Wimax Network Simulation With Opnet Modeler 2 31o
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Wimax Network Simulation With Opnet Modeler 2 as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 399
- Pages: 1
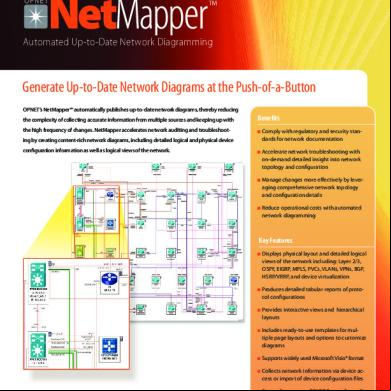
Model Overview OPNET Technologies, Inc.
WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) Specialized Model WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) is a last-mile broadband wireless technology for fixed and mobile wireless connectivity. The OPNET WiMAX specialized model is available for OPNET Modeler® Wireless Suite and OPNET Modeler® Wireless Suite for Defense. It s the IEEE 802.16-2004 and IEEE 802.16e2005 standards. It was developed by OPNET with guidance from prominent industry leaders such as Motorola, Samsung, Alcatel-Lucent, and Telecom.
Key Features MAC n IP convergence sub-layer n Service flow configuration and mapping
traffic to service flows
Network equipment manufacturers, telecom service providers, and defense organizations use the model to design WiMAX networks and devices. Studies include:
n Bandwidth request and grant mecha-
n Evaluating custom scheduling algorithms for WiMAX base and subscriber stations
n BS scheduler for uplink and downlink
n Optimizing application performance by leveraging WiMAX QoS policies n Predicting network performance for different MAC and PHY layer profiles n Visualizing live application performance over a simulated
nisms connections n Scheduling service for UGS, ertPS, rtPS,
nrtPS, BE n Adaptive modulation and coding n MSDU packing and fragmentation
WiMAX network infrastructure
n ARQ
• In-order SDU delivery • Cumulative ACKs • Fragmentation and packing n HARQ n Scanning-based BS selection n Handoff mechanisms for mobility n ASN based mobility n Power saving mode n Multihop relay (based on IEEE 802.16j)
Framing Predict application response times in a WiMAX network
n DL/UL AP generation n Grant consolidation per basic CID n Burst rectangulation
Calculate the inter-cell interference in a 19-cell WiMAX scenario
Design and evaluate WiMAX networks
www.opnet.com
Application and Network Performance
PHY n TDD n OFDMA, SOFDMA
• Preset values for SOFDMA (FFT 128, 512, 1024, 2048) n Co-channel interference • Perm-base • Sub-carrier overlap computation n MIMO STC n Multi-path fading • ITU models (Pedestrian A, Pedestrian B, Vehicular A, Vehicular B) • Finite state Markov channel models n Path-loss modeling • ITU (Pedestrian, Vehicular) • Erceg (terrains A, B, C) n Ranging (initial and periodic) n Uplink power control
Network features n Multiple cell networks n Multi-sector base station
OPNET Technologies, Inc. 7255 Woodmont Avenue, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, USA • phone: +1 (240) 497-3000 • email: [email protected] © 2010 OPNET Technologies, Inc. OPNET is a ed trademark of OPNET Technologies, Inc. All trademarks are the properly of their respective owners and used herein for identification purposes only.
n IP connectivity n IPv6
WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) Specialized Model WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) is a last-mile broadband wireless technology for fixed and mobile wireless connectivity. The OPNET WiMAX specialized model is available for OPNET Modeler® Wireless Suite and OPNET Modeler® Wireless Suite for Defense. It s the IEEE 802.16-2004 and IEEE 802.16e2005 standards. It was developed by OPNET with guidance from prominent industry leaders such as Motorola, Samsung, Alcatel-Lucent, and Telecom.
Key Features MAC n IP convergence sub-layer n Service flow configuration and mapping
traffic to service flows
Network equipment manufacturers, telecom service providers, and defense organizations use the model to design WiMAX networks and devices. Studies include:
n Bandwidth request and grant mecha-
n Evaluating custom scheduling algorithms for WiMAX base and subscriber stations
n BS scheduler for uplink and downlink
n Optimizing application performance by leveraging WiMAX QoS policies n Predicting network performance for different MAC and PHY layer profiles n Visualizing live application performance over a simulated
nisms connections n Scheduling service for UGS, ertPS, rtPS,
nrtPS, BE n Adaptive modulation and coding n MSDU packing and fragmentation
WiMAX network infrastructure
n ARQ
• In-order SDU delivery • Cumulative ACKs • Fragmentation and packing n HARQ n Scanning-based BS selection n Handoff mechanisms for mobility n ASN based mobility n Power saving mode n Multihop relay (based on IEEE 802.16j)
Framing Predict application response times in a WiMAX network
n DL/UL AP generation n Grant consolidation per basic CID n Burst rectangulation
Calculate the inter-cell interference in a 19-cell WiMAX scenario
Design and evaluate WiMAX networks
www.opnet.com
Application and Network Performance
PHY n TDD n OFDMA, SOFDMA
• Preset values for SOFDMA (FFT 128, 512, 1024, 2048) n Co-channel interference • Perm-base • Sub-carrier overlap computation n MIMO STC n Multi-path fading • ITU models (Pedestrian A, Pedestrian B, Vehicular A, Vehicular B) • Finite state Markov channel models n Path-loss modeling • ITU (Pedestrian, Vehicular) • Erceg (terrains A, B, C) n Ranging (initial and periodic) n Uplink power control
Network features n Multiple cell networks n Multi-sector base station
OPNET Technologies, Inc. 7255 Woodmont Avenue, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, USA • phone: +1 (240) 497-3000 • email: [email protected] © 2010 OPNET Technologies, Inc. OPNET is a ed trademark of OPNET Technologies, Inc. All trademarks are the properly of their respective owners and used herein for identification purposes only.
n IP connectivity n IPv6