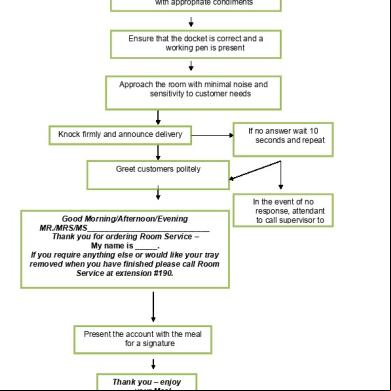
Service Delivery Management 51j4p
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Service Delivery Management as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 934
- Pages: 11
Service Delivery Management – People This course will give you an overview of the people management skills required in Service Delivery Management (SDM). Elements of SDM People, Operations, Financials and Stakeholders are the four pillars of SDM.
For smooth operations, all of these have to be in a balance. All the pillars are interconnected and are required for others to sustain. Soft skills required for SDM. 1) Communication skills(Written, Verbal, Tracking 2) Customer centric values and Business skills Team management and team playing skills. 3) Decision-Making and Analytical skills. Co-relation skills. 4) Skill and Knowledge Management. Time Management and Prioritizing Skills 5) Leadership and Ownership Skills. Maturity in knowing when to ask for help.
and Closing Loops)
People Resources The guidelines for managing team better, are as follows: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Understanding the business priorities and enabling IT to add business value. Building strong, synergistic, motivated and committed virtual teams. Utilizing IT automation and knowledge management tools. Attracting, developing and retaining skilled and talented IT operations staff. Creating a team which has innovation rooted as its core.
Growing People Resources Strategies for managing people resources at the different stages of their tenure. Induction: 1) First level training. 2) Gap Analysis and Action Plan. 3) Plugging Gaps. 4) from New-ee. On-boarding to a project
1) 2) 3) 4)
Multi skilling. Job Rotation Plan to minimize attrition Team Bonding Activities. Training and Development.
Exit of a Team Member 1) from a person leaving the system.
Introduction to Leadership Leadership Methods Let us look at the various aspects of Leadership and Management Leadership Produces change and movement 1. Establishes direction a) Creates a vision b) Clarifies the big picture. c) Sets strategies. 2. Aligns People a) Communicates goals b) Seeks commitment c) Builds teams, coalitions and alliances.
3. Motivates and Inspires a) Energizes b) Empowers subordinates and colleagues c) Satisfies unmet needs
Management Produces order and consistency 1) Planning and budgeting a) Establishes agendas b) Sets timetable c) Allocates resources 2) Organizing and staffing a) Provides structure b) Make job placements c) Establish rules and procedures. 3) Controlling and problem solving a) Develop incentives b) Generate creative solutions c) Take corrective actions
The table below lists the responsibilities of Managers as compared to Leaders. Managers Focus on things Do things right Plan Organize Direct Control Follow the rules
Common Activities Planning Organizing Directing Controlling
Types of Leadership 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7)
Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader
by the position achieved. by personality charisma by moral example by power held by virtue of intellect because of ability to accomplish things based on situation.
Leaders Focus on people Do the right things Inspire Influence Motivate Build Shape Entities Think and act long term Have and propagate vision and act pro-actively Instill and encourage thought leadership
Leadership Methods Delegating Low relationship/low task Responsibility Willing employees
Participating High relationship/low task Decisions facilitated Able but unwilling employees
Team motivation Strategies for team motivation
Selling High task/high relationship
Telling High task/Low relationship
Decisions explained Willing but unable employees
Instruction provided Close supervision
Motivation: The Four Key Drivers 1) Set Realistic Goals In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • It is important to get input and agreement from team about the work load, at the beginning of a new project, while formulating the plan. • It is advisable to ensure that none of the team are stuck with work that suddenly appeared on the timeline without their input. 2) Measure Performance In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • A tool that measures and tracks performance should be introduced • The tool should be able to help the team understand how they are doing against the baseline of what was planned, whether they are on track and if they are not, how they can get back • The tool should also help to determine what kind of or resources the team might need in order to get back on track, like additional training, expertise on handling issues. 3) Celebrate Success In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind:
• Success should be celebrated all along the way, after small milestones not just at the end of the project • Meeting milestones should be approached with enthusiasm • The team should be rewarded for achieving success and more importantly, for working together as a team. 4) Know your Team In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • It is important to be aware of the nature of individual team . A job that needs a detailed task to be handled, needs to be delegated to the right person, who is detail oriented • It is also advisable to know whether or not a team member is an introvert or extrovert, as rewards for introverts and extroverts need to be different. • It is important to know the team member’s skills, expertise and idiosyncrasies, what they like and what they don’t like.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Service Delivery Management – Overview After completing the course, you will be able to:
Describe Service Delivery Management (SDM). Identify the various competency levels of SDM. Explain the different challenges of SDM.
What is Service Delivery Management? Service Delivery Management is a discipline or role that is responsible for managing service delivery to one or more clients. As a part of service delivery management, you are able for the following activities:
For smooth operations, all of these have to be in a balance. All the pillars are interconnected and are required for others to sustain. Soft skills required for SDM. 1) Communication skills(Written, Verbal, Tracking 2) Customer centric values and Business skills Team management and team playing skills. 3) Decision-Making and Analytical skills. Co-relation skills. 4) Skill and Knowledge Management. Time Management and Prioritizing Skills 5) Leadership and Ownership Skills. Maturity in knowing when to ask for help.
and Closing Loops)
People Resources The guidelines for managing team better, are as follows: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Understanding the business priorities and enabling IT to add business value. Building strong, synergistic, motivated and committed virtual teams. Utilizing IT automation and knowledge management tools. Attracting, developing and retaining skilled and talented IT operations staff. Creating a team which has innovation rooted as its core.
Growing People Resources Strategies for managing people resources at the different stages of their tenure. Induction: 1) First level training. 2) Gap Analysis and Action Plan. 3) Plugging Gaps. 4) from New-ee. On-boarding to a project
1) 2) 3) 4)
Multi skilling. Job Rotation Plan to minimize attrition Team Bonding Activities. Training and Development.
Exit of a Team Member 1) from a person leaving the system.
Introduction to Leadership Leadership Methods Let us look at the various aspects of Leadership and Management Leadership Produces change and movement 1. Establishes direction a) Creates a vision b) Clarifies the big picture. c) Sets strategies. 2. Aligns People a) Communicates goals b) Seeks commitment c) Builds teams, coalitions and alliances.
3. Motivates and Inspires a) Energizes b) Empowers subordinates and colleagues c) Satisfies unmet needs
Management Produces order and consistency 1) Planning and budgeting a) Establishes agendas b) Sets timetable c) Allocates resources 2) Organizing and staffing a) Provides structure b) Make job placements c) Establish rules and procedures. 3) Controlling and problem solving a) Develop incentives b) Generate creative solutions c) Take corrective actions
The table below lists the responsibilities of Managers as compared to Leaders. Managers Focus on things Do things right Plan Organize Direct Control Follow the rules
Common Activities Planning Organizing Directing Controlling
Types of Leadership 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7)
Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader
by the position achieved. by personality charisma by moral example by power held by virtue of intellect because of ability to accomplish things based on situation.
Leaders Focus on people Do the right things Inspire Influence Motivate Build Shape Entities Think and act long term Have and propagate vision and act pro-actively Instill and encourage thought leadership
Leadership Methods Delegating Low relationship/low task Responsibility Willing employees
Participating High relationship/low task Decisions facilitated Able but unwilling employees
Team motivation Strategies for team motivation
Selling High task/high relationship
Telling High task/Low relationship
Decisions explained Willing but unable employees
Instruction provided Close supervision
Motivation: The Four Key Drivers 1) Set Realistic Goals In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • It is important to get input and agreement from team about the work load, at the beginning of a new project, while formulating the plan. • It is advisable to ensure that none of the team are stuck with work that suddenly appeared on the timeline without their input. 2) Measure Performance In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • A tool that measures and tracks performance should be introduced • The tool should be able to help the team understand how they are doing against the baseline of what was planned, whether they are on track and if they are not, how they can get back • The tool should also help to determine what kind of or resources the team might need in order to get back on track, like additional training, expertise on handling issues. 3) Celebrate Success In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind:
• Success should be celebrated all along the way, after small milestones not just at the end of the project • Meeting milestones should be approached with enthusiasm • The team should be rewarded for achieving success and more importantly, for working together as a team. 4) Know your Team In order to keep the team motivated, the management needs to keep the following in mind: • It is important to be aware of the nature of individual team . A job that needs a detailed task to be handled, needs to be delegated to the right person, who is detail oriented • It is also advisable to know whether or not a team member is an introvert or extrovert, as rewards for introverts and extroverts need to be different. • It is important to know the team member’s skills, expertise and idiosyncrasies, what they like and what they don’t like.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Service Delivery Management – Overview After completing the course, you will be able to:
Describe Service Delivery Management (SDM). Identify the various competency levels of SDM. Explain the different challenges of SDM.
What is Service Delivery Management? Service Delivery Management is a discipline or role that is responsible for managing service delivery to one or more clients. As a part of service delivery management, you are able for the following activities: