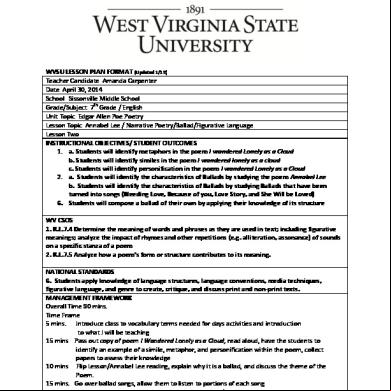
Lesson Plan And Obe 5y5n4d
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Lesson Plan And Obe as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 735
- Pages: 14
ECW 557: ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
BRIEFING ON OBE AND COURSE By:
MADAM IRMA NOORAZURAH MOHAMAD T1-A13-2C 03-5543 6409/ 012-219 0315
?
?
PEOs
POs
COs
LOs
?
?
PROGRAMME EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES: At the end of the EC220 Programme, students should be able to: PEO 1: Have a sound understanding of, as well as the ability to apply fundamental principles of engineering knowledge and are capable of expanding this knowledge through engineering and scientific research. PEO 2: Practice with strong professional ethics and understand the impacts of engineering projects on the environment, society, politics and the wellbeing of local and regional economy. PEO 3: Are able to communicate effectively with of the profession and the society in general on engineering and non-engineering subjects. PEO 4: Have the competency to contribute as ateam member of a multidisciplinary team or assume the role of a team leader in projects undertaken within or beyond the national boundaries. PEO 5: Have the ability to adapt to changes in economic climate through awareness on contemporary issues, entrepreneurship and lifelong learning skills.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES: Graduates from an accredited programme should have the following attributes:
1. Ability to acquire and apply basic knowledge of science, mathematics and engineering. 2. Ability to communicate effectively, not only with engineers but also with the public. 3. Ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems. 4. Ability to use a system approach to design and evaluate operational performance. 5. Ability to act effectively as an individual and in a group with leadership and managerial capabilities. 6. Understanding of the social, cultural, global and environmental responsibilities and ethics of a professional engineer, and the need for sustainable development. 7. Acquiring the need to undertake lifelong learning and the capacity to do so. 8. Ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data 9. Ability to function in multidisciplinary teams. 10. Having technical competency and ability to apply to specific civil engineering discipline. 11. Having the knowledge of contemporary issues. 12. Ability to demonstrate and apply knowledge and understanding of project management principles, finance and entrepreneurship.
COURSE OUTCOMES: At the end of the course, students should be able to: 1. Apply knowledge of fundamentals in hydrology namely water budget equation, precipitation, evaporation, infiltration and streamflow measurement; 2. Undertake problem identification, formulation and solution pertaining to hydrograph analysis, frequency analysis, and flood routing and groundwater analysis; and 2. Design project related to urban hydrology using the current Malaysian standard.
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS: The course introduces hydrological cycle and concept of water budget. Precipitation, evaporation and infiltration processes are discussed that include measurements and analysis. Stream flow measurements, stage-discharge, rainfall-runoff relationships and hydrograph analysis are explained. Rational method, flood routing and the use of probability and statistical method in hydrologic analysis are presented. Applications of hydrology principles in urban stormwater design using procedures outlined in Manual Saliran Mesra Alam Malaysia (MSMA) are discussed. The course concludes with an introduction to hydrologic modeling and simulation.
CO-PO MATRIX
PRIMARY TOPICS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Introduction (Water Budget Eqtn) (2 hours) Precipitation (3 hours) Evaporation & Infiltration (2 hours) Streamflow Measurement (2 hours) Surface Runoff and Hydrograph Analysis (7 hours) Hydrologic and Hydraulic Routing (6 hours) Probability in Hydrology (6 hours) Applications of Hydrology (6 hours) Groundwater Hydrology (6 hours) Demonstration (2 hours)
ASSESSMENT: Final Examination:
60%
1 Mid Term Test:
30% (week 8)
Assignment&Project : 10% TOTAL
100%
TEXTBOOK: 1) Subramanya, K. (1984). Engineering Hydrology 3rd Ed. Tata McGraw-Hill.
REFERENCES: 1. Viessman, W. & Lewis, G.L. (2002). Introduction to Hydrology 5th Ed. Prentice Hall. 2. Wilson, E.M. (1987). Engineering Hydrology 3rd Ed. ELBS/ Macmillan. 3. Chow, V.T. (1964). Handbook of Applied Hydrology. McGraw-Hill. 4. Dept of Irrigation & Drainage, Malaysia (2000). Urban Stormwater Management Manual for Malaysia DID, Malaysia.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this PowerPoint slide may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this PowerPoint slide, you are using it without permission.
LESSON PLAN MARCH 2013 – JULY 2013
ISSUES: • • • •
ATTENDANCE ATTIRE ASSIGNMENTS/GROUP PROJECT i-learn ; NOTES, ANNOUNCEMENT, ENTRANCE-EXIT SURVEY, SU-FO • COURSE FILE - CHECKLIST
ACTIVITY 1 - ICE BREAKING
BRIEFING ON OBE AND COURSE By:
MADAM IRMA NOORAZURAH MOHAMAD T1-A13-2C 03-5543 6409/ 012-219 0315
?
?
PEOs
POs
COs
LOs
?
?
PROGRAMME EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES: At the end of the EC220 Programme, students should be able to: PEO 1: Have a sound understanding of, as well as the ability to apply fundamental principles of engineering knowledge and are capable of expanding this knowledge through engineering and scientific research. PEO 2: Practice with strong professional ethics and understand the impacts of engineering projects on the environment, society, politics and the wellbeing of local and regional economy. PEO 3: Are able to communicate effectively with of the profession and the society in general on engineering and non-engineering subjects. PEO 4: Have the competency to contribute as ateam member of a multidisciplinary team or assume the role of a team leader in projects undertaken within or beyond the national boundaries. PEO 5: Have the ability to adapt to changes in economic climate through awareness on contemporary issues, entrepreneurship and lifelong learning skills.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES: Graduates from an accredited programme should have the following attributes:
1. Ability to acquire and apply basic knowledge of science, mathematics and engineering. 2. Ability to communicate effectively, not only with engineers but also with the public. 3. Ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems. 4. Ability to use a system approach to design and evaluate operational performance. 5. Ability to act effectively as an individual and in a group with leadership and managerial capabilities. 6. Understanding of the social, cultural, global and environmental responsibilities and ethics of a professional engineer, and the need for sustainable development. 7. Acquiring the need to undertake lifelong learning and the capacity to do so. 8. Ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data 9. Ability to function in multidisciplinary teams. 10. Having technical competency and ability to apply to specific civil engineering discipline. 11. Having the knowledge of contemporary issues. 12. Ability to demonstrate and apply knowledge and understanding of project management principles, finance and entrepreneurship.
COURSE OUTCOMES: At the end of the course, students should be able to: 1. Apply knowledge of fundamentals in hydrology namely water budget equation, precipitation, evaporation, infiltration and streamflow measurement; 2. Undertake problem identification, formulation and solution pertaining to hydrograph analysis, frequency analysis, and flood routing and groundwater analysis; and 2. Design project related to urban hydrology using the current Malaysian standard.
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS: The course introduces hydrological cycle and concept of water budget. Precipitation, evaporation and infiltration processes are discussed that include measurements and analysis. Stream flow measurements, stage-discharge, rainfall-runoff relationships and hydrograph analysis are explained. Rational method, flood routing and the use of probability and statistical method in hydrologic analysis are presented. Applications of hydrology principles in urban stormwater design using procedures outlined in Manual Saliran Mesra Alam Malaysia (MSMA) are discussed. The course concludes with an introduction to hydrologic modeling and simulation.
CO-PO MATRIX
PRIMARY TOPICS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Introduction (Water Budget Eqtn) (2 hours) Precipitation (3 hours) Evaporation & Infiltration (2 hours) Streamflow Measurement (2 hours) Surface Runoff and Hydrograph Analysis (7 hours) Hydrologic and Hydraulic Routing (6 hours) Probability in Hydrology (6 hours) Applications of Hydrology (6 hours) Groundwater Hydrology (6 hours) Demonstration (2 hours)
ASSESSMENT: Final Examination:
60%
1 Mid Term Test:
30% (week 8)
Assignment&Project : 10% TOTAL
100%
TEXTBOOK: 1) Subramanya, K. (1984). Engineering Hydrology 3rd Ed. Tata McGraw-Hill.
REFERENCES: 1. Viessman, W. & Lewis, G.L. (2002). Introduction to Hydrology 5th Ed. Prentice Hall. 2. Wilson, E.M. (1987). Engineering Hydrology 3rd Ed. ELBS/ Macmillan. 3. Chow, V.T. (1964). Handbook of Applied Hydrology. McGraw-Hill. 4. Dept of Irrigation & Drainage, Malaysia (2000). Urban Stormwater Management Manual for Malaysia DID, Malaysia.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this PowerPoint slide may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this PowerPoint slide, you are using it without permission.
LESSON PLAN MARCH 2013 – JULY 2013
ISSUES: • • • •
ATTENDANCE ATTIRE ASSIGNMENTS/GROUP PROJECT i-learn ; NOTES, ANNOUNCEMENT, ENTRANCE-EXIT SURVEY, SU-FO • COURSE FILE - CHECKLIST
ACTIVITY 1 - ICE BREAKING