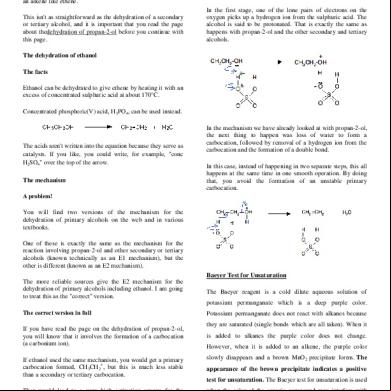
Dehydration Of Milk 1m2f5z
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Dehydration Of Milk as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 1,536
- Pages: 23
Dehydration / Desiccation Dr . Mohammad Ashraf Paul Division of Livestock Products Technology Faculty of Veterinary Sciences & Animal Husbandry SKUAST - K Alusteng , Ganderbal Kashmir
Dehydration : §Near complete removal of water from milk to § a < 5 % level . §Water in a liquid product – in this case milk concentrate is removed , so that the product takes on a solid form §Microorganisms are unable to reproduce at such a low water content thus shelf life of the milk is extended §Reduces weight and volume §Reduces the cost of transporting and storing the product . §Skim milk powder has a maximum shelf life of about three years while whole milk powder has a maximum shelf life of six months. §Because the fat in the powder oxidises during storage , with consequent deterioration in flavour . However , the
Dehydration /Desiccation Methods
‘According to Marco Polo’s s of his travels in Asia, Mongolians produced milk powder by drying milk in the sun’
Cold Methods: v Freezing out water & centrifuging v Freezing milk & Sublimation • Produces very high quality powder • Product is deep-frozen and the water frozen in the product is evaporated under vacuum • Ensures high product quality as, among other things, no protein denaturing takes place compared to drying milk at higher temperatures where the proteins are denatured to a greater or
Hot Methods : Film , roller or drum drying Less common , used for a few special products Spray drying §In spray drying , the milk is first concentrated by evaporation and then dried in a spray tower §Although there are many types of driers , spray driers are the most widely used type of air convection drier . §It turns out more tonnage of dehydrated products than all other types of driers combined . §It is limited to food that can be atomized , i . e . liquids , low viscosity pastes , and purees §Drying takes place within a matter of seconds at temperatures approximately 200 ° C . §Evaporative cooling maintains low product temperatures , however , prompt removal of the
Principal components include :
High pressure pump for introducing liquid into the tower Device for atomizing the feed stream Heated air source with blower Secondary collection vessel for removing the dried food from the airstream Means for exhausting the moist air
Atomizers :
Provide a large surface area for exposure to drying forces : 1 litre = 12 billion particles = > 300 ft 2 (30m 2 )
i. Compressed air Rotary disc ii. Pressure spray iii. Centrifugal disc
Pressure nozzles Two - fluid nozzl
Powder Recovery systems : Bag filters - very efficient ( 99 . 9 %) Cyclone collector- efficient ( 99 . 5 %) Wet scrubber - the most economical outlet air cleaner . The principle of a wet scrubber is to dissolve any dust powder left in the airstream into either water or the feed stream by spraying the wash stream through the air . This also recovers heat from the exiting air and evaporates some of the water in the feed stream
Two and Three Stage Drying Processes
In single stage spray drying , the rate of evaporation is high in the first part of the process , and it gradually decreases because of the falling moisture content of the particle surfaces In order to complete the drying in one stage , a relatively high outlet temperature is required during the final drying phase resulting in high particle temperature and thus heat damage . Two stage drying process - is superior to the traditional single stage drying in of product quality and cost of production . consists of a spray drier with an external vibrating fluid bed placed below the drying chamber . The product can be removed from the drying chamber with a higher moisture content , and the final drying takes place in the external
Three stage drier : Here second stage is a
fluid bed built into the cone of the spray drying chamber ( integrated fluid bed ). Thus it is possible to achieve an even higher moisture content in the first drying stage and a lower outlet air temperature from the spray drier . The inlet air temperature can be raised resulting in a larger temperature difference and improved efficiency in the drying process . The exhaust heat from the chamber is used to preheat the feed stream . The third stage is again the external fluid bed , for final drying and / or cooling the powder . The results are as follows : oHigher quality powders with much better rehydrating properties directly from the drier oLower energy consumption oIncreased range of products can be spray dried oSmaller space requirements
Roller drying Process summary:
Atmospheric / Vacuum
Milk concentr ate Adjustable pump Feeding Drying drum
Drying drum cont . Scraper ( Doctors blade )
Grinder Sifter Dried product
Spray drying - Process summary : The liquid food is generally preconcentrated by evaporation to economically reduce the water content The concentrate is then introduced as a fine spray or mist into a tower or chamber with heated air . As the small droplets make intimate with the heated air, they flash off their moisture , become small particles , and drop to the bottom of the tower and are removed . The advantages of spray drying include a low heat and short time combination which leads to a better quality product .
Skim Milk Powder manufacture Receiving milk
Cooling@ 50C
Preheating (350C) â Separation â Pasteurization (710C /15s) â
Low heat SMP High heat S M P
â Condensing
L o w h e a t S M P. . â High heat SMP â
Reheating (630C)
P re h e a tin g 8 5 0 C / 2 0 m in .
â
Filtration
â C o n d e n sin g â R e h e a tin g ( 7 4 0 C ) â R e m a in in g ste p s sa m e
Whole Milk Powder S ta n d a rd iz a tio n
Fat / SNF = 1 : 2 . 77
Preheating (71 0 C )
Filtration / Cl arification Homogenizati on
2500 psi / 63 - 74 0 C – I ; 500psi - II
Heating (93 0 C / 3min .) Condensing
Preheating71 0 C Pumping ( 2500psi ) Spray Drying
(82 0 C outlet temp .)
Cooling (32 0 C ) Sifting Vacuum + N 2 Packaging & Storage @RT
Instantiation :
Process of making dried milk products instant –soluble. Process: 1. Wetting of particle surface (steam, atomized water or both in a tube or chamber or cyclone 2. Agglomeration (particles collide with each other due to turbulence and adhere to form clusters) 3. Re drying – with hot filtered air 4. Cooling 5. Sizing to exclude very large agglomerates & very small particles 6. Sifting & packaging.
PFA Standards:
• WMP : • A product obtained from cow or buffalo milk, or a combination thereof , or from standardized milk, by the removal of water. It may contain Cacl2,Citric acid and sodium citrate , sodium salts of orthophosphoricacid and poly phosphoric acids , not exceeding 0.3% by weight of the finished product , and 0.01% of BHA(by Wt.) of the product. Such addition need not to be declared on the label. Milk powder should contain not more than 5% moisture and not less than 26% fat. The total acidity expressed as lactic should not be more than 1.2%.The SPC may not exceed 50000/g and coliform count may not exceed 90/g. Max. solubility index should be 15.0 for a roller dried and 2.0 for spray dried product.
Various uses of milk powder :
Recombination of milk and milk products Reconstituted Milk and milk products In the bakery industry to increase the volume of bread and improve its water binding capacity . The bread will then remain fresh for a longer period of time Substitute for eggs in bread and pastries Producing milk chocolate Producing various types of ready - cooked foods in food and catering trade In baby foods Production of ice cream Animal feed , calf growth accelerator , pharmaceuticals , microbiological media preparations
Typical properties of spray - dried milk powder : Characteristics Solubility (ml)
WMP
SMP
0.1 – 0.5
0.1 – 0.5
Scorched particles ( standard disc grading )
A
A
Residual moisture ( max .%)
Bulk density ( g / ml )
4.0 0 . 45 – 0 . 57
3.0
Composition of milk powder Characteristics milk
Fat , % solids content
Whole Skim milk 26 – 29 1 . 25
Protein , % solids content 25 – 27 34 – 38 Lactose , % solids content 35 – 38 48 – 56 pH 6.7
6.6 – 6.7
6.6 –
Dehydration : §Near complete removal of water from milk to § a < 5 % level . §Water in a liquid product – in this case milk concentrate is removed , so that the product takes on a solid form §Microorganisms are unable to reproduce at such a low water content thus shelf life of the milk is extended §Reduces weight and volume §Reduces the cost of transporting and storing the product . §Skim milk powder has a maximum shelf life of about three years while whole milk powder has a maximum shelf life of six months. §Because the fat in the powder oxidises during storage , with consequent deterioration in flavour . However , the
Dehydration /Desiccation Methods
‘According to Marco Polo’s s of his travels in Asia, Mongolians produced milk powder by drying milk in the sun’
Cold Methods: v Freezing out water & centrifuging v Freezing milk & Sublimation • Produces very high quality powder • Product is deep-frozen and the water frozen in the product is evaporated under vacuum • Ensures high product quality as, among other things, no protein denaturing takes place compared to drying milk at higher temperatures where the proteins are denatured to a greater or
Hot Methods : Film , roller or drum drying Less common , used for a few special products Spray drying §In spray drying , the milk is first concentrated by evaporation and then dried in a spray tower §Although there are many types of driers , spray driers are the most widely used type of air convection drier . §It turns out more tonnage of dehydrated products than all other types of driers combined . §It is limited to food that can be atomized , i . e . liquids , low viscosity pastes , and purees §Drying takes place within a matter of seconds at temperatures approximately 200 ° C . §Evaporative cooling maintains low product temperatures , however , prompt removal of the
Principal components include :
High pressure pump for introducing liquid into the tower Device for atomizing the feed stream Heated air source with blower Secondary collection vessel for removing the dried food from the airstream Means for exhausting the moist air
Atomizers :
Provide a large surface area for exposure to drying forces : 1 litre = 12 billion particles = > 300 ft 2 (30m 2 )
i. Compressed air Rotary disc ii. Pressure spray iii. Centrifugal disc
Pressure nozzles Two - fluid nozzl
Powder Recovery systems : Bag filters - very efficient ( 99 . 9 %) Cyclone collector- efficient ( 99 . 5 %) Wet scrubber - the most economical outlet air cleaner . The principle of a wet scrubber is to dissolve any dust powder left in the airstream into either water or the feed stream by spraying the wash stream through the air . This also recovers heat from the exiting air and evaporates some of the water in the feed stream
Two and Three Stage Drying Processes
In single stage spray drying , the rate of evaporation is high in the first part of the process , and it gradually decreases because of the falling moisture content of the particle surfaces In order to complete the drying in one stage , a relatively high outlet temperature is required during the final drying phase resulting in high particle temperature and thus heat damage . Two stage drying process - is superior to the traditional single stage drying in of product quality and cost of production . consists of a spray drier with an external vibrating fluid bed placed below the drying chamber . The product can be removed from the drying chamber with a higher moisture content , and the final drying takes place in the external
Three stage drier : Here second stage is a
fluid bed built into the cone of the spray drying chamber ( integrated fluid bed ). Thus it is possible to achieve an even higher moisture content in the first drying stage and a lower outlet air temperature from the spray drier . The inlet air temperature can be raised resulting in a larger temperature difference and improved efficiency in the drying process . The exhaust heat from the chamber is used to preheat the feed stream . The third stage is again the external fluid bed , for final drying and / or cooling the powder . The results are as follows : oHigher quality powders with much better rehydrating properties directly from the drier oLower energy consumption oIncreased range of products can be spray dried oSmaller space requirements
Roller drying Process summary:
Atmospheric / Vacuum
Milk concentr ate Adjustable pump Feeding Drying drum
Drying drum cont . Scraper ( Doctors blade )
Grinder Sifter Dried product
Spray drying - Process summary : The liquid food is generally preconcentrated by evaporation to economically reduce the water content The concentrate is then introduced as a fine spray or mist into a tower or chamber with heated air . As the small droplets make intimate with the heated air, they flash off their moisture , become small particles , and drop to the bottom of the tower and are removed . The advantages of spray drying include a low heat and short time combination which leads to a better quality product .
Skim Milk Powder manufacture Receiving milk
Cooling@ 50C
Preheating (350C) â Separation â Pasteurization (710C /15s) â
Low heat SMP High heat S M P
â Condensing
L o w h e a t S M P. . â High heat SMP â
Reheating (630C)
P re h e a tin g 8 5 0 C / 2 0 m in .
â
Filtration
â C o n d e n sin g â R e h e a tin g ( 7 4 0 C ) â R e m a in in g ste p s sa m e
Whole Milk Powder S ta n d a rd iz a tio n
Fat / SNF = 1 : 2 . 77
Preheating (71 0 C )
Filtration / Cl arification Homogenizati on
2500 psi / 63 - 74 0 C – I ; 500psi - II
Heating (93 0 C / 3min .) Condensing
Preheating71 0 C Pumping ( 2500psi ) Spray Drying
(82 0 C outlet temp .)
Cooling (32 0 C ) Sifting Vacuum + N 2 Packaging & Storage @RT
Instantiation :
Process of making dried milk products instant –soluble. Process: 1. Wetting of particle surface (steam, atomized water or both in a tube or chamber or cyclone 2. Agglomeration (particles collide with each other due to turbulence and adhere to form clusters) 3. Re drying – with hot filtered air 4. Cooling 5. Sizing to exclude very large agglomerates & very small particles 6. Sifting & packaging.
PFA Standards:
• WMP : • A product obtained from cow or buffalo milk, or a combination thereof , or from standardized milk, by the removal of water. It may contain Cacl2,Citric acid and sodium citrate , sodium salts of orthophosphoricacid and poly phosphoric acids , not exceeding 0.3% by weight of the finished product , and 0.01% of BHA(by Wt.) of the product. Such addition need not to be declared on the label. Milk powder should contain not more than 5% moisture and not less than 26% fat. The total acidity expressed as lactic should not be more than 1.2%.The SPC may not exceed 50000/g and coliform count may not exceed 90/g. Max. solubility index should be 15.0 for a roller dried and 2.0 for spray dried product.
Various uses of milk powder :
Recombination of milk and milk products Reconstituted Milk and milk products In the bakery industry to increase the volume of bread and improve its water binding capacity . The bread will then remain fresh for a longer period of time Substitute for eggs in bread and pastries Producing milk chocolate Producing various types of ready - cooked foods in food and catering trade In baby foods Production of ice cream Animal feed , calf growth accelerator , pharmaceuticals , microbiological media preparations
Typical properties of spray - dried milk powder : Characteristics Solubility (ml)
WMP
SMP
0.1 – 0.5
0.1 – 0.5
Scorched particles ( standard disc grading )
A
A
Residual moisture ( max .%)
Bulk density ( g / ml )
4.0 0 . 45 – 0 . 57
3.0
Composition of milk powder Characteristics milk
Fat , % solids content
Whole Skim milk 26 – 29 1 . 25
Protein , % solids content 25 – 27 34 – 38 Lactose , % solids content 35 – 38 48 – 56 pH 6.7
6.6 – 6.7
6.6 –