Timeline 4h6c51
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Timeline as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 1,025
- Pages: 6
FINAL PROJECT
THEORIES OF LEARNING This paper is submitted to fulfill Foundation of English Education and Instruction
Supervised by Dr. H. Fathor Rasyid, M.Pd. and Dr. Thoyyibah, SS., M.Pd
Written By:
Rizki Amalia Intias
926.001.18.019
ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING PROGRAM GRADUATE PROGRAM ISLAMIC STATE INSTITUTE OF KEDIRI 2018
THEORIES OF LEARNING
1.
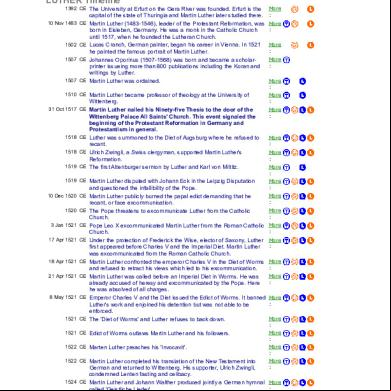
1849-1936 Ivan Petrovich Pavlov Key :
Theory of stimulus-response associative conditioning
Learning is a process of change that occurs the conditions then reaction (response)
Impression: This theory is suitable for learning that requires mastery of skills with training, or requires certain behaviors in learning. And it also makes easy for educators to control learning because individuals do not realize that they are controlled by stimuli that come from outside themselves.
2.
1874-1949 Edward Lee Thorndike Key :
Connectionism
The association between sense impressions and impulses to action a bond or a connection
Functional aspects of behavior is due mainly to the influence of Darwin
Selecting and connecting
Learning was incremental rather than insightful
The spread of effect
The law of readiness, exercise, effect.
Impression: This theory teaches children to think linearly and convergent. Learning is a process of forming or shaping which is to bring the child to reach or reach a certain target. 3.
1880-1967 Gestalt Theory Key :
Cognitive
Apply field theory from physics to the problems of psychology
Perceptual phenomena
The actual stimulation has changed radically
To inhibit understanding is based on the doctrine of associationism
Reaching an understanding involves many aspects of learner
Impression: This theory looks the human as unique individu, they connect with the environment around them, and this theory is more emphazise for the important of the insight or understanding in learn anything, so they will more success to reach comprehension in learning process. 4.
1884-1952 Clark Leonard Hull Key :
Quantitative experimental methods for learning
Phenomenon of hypnosis
Mathematical expressions for psychological theory
Impression: This only happens when skills are well-learned. In contrast, if the athletic skill is not well-learned, performance will deteriorate. This theory helps explain why beginners find it difficult to perform well under pressure. Often beginners’ skill level decreases if they are competing in a relay race using new skills. 5.
1886-1959 Edward Chace Tolman Key :
Mixture of Gestalt and Behaviorism theory
Learn behavior to determine cognitive processes
Stimulus response controlled by rewards
Physical phenomena and ignores mental aspect
Impression: This theory shows that students should be faced with different topics and different points of view. This process will allow students to develop cognitive maps that will be used to answer questions about a particular topic and other topics.
6.
1886-1959 Edwin Ray Guthrie Key :
The law of contingency
Stimulus and response relationship variables to explain the occurrence of the learning process
The punishment given at the right time will be able to change a person's behavior
human behavior as a whole can be viewed as a series of behaviors consisting of units
Impression: The education process begins with stating the purpose, that is state what response must be made to stimuli. 7.
1896-1934 Lev Vygotsky Key :
Sociocultural theory
Social interaction plays a fundamental role in the development of cognition
The more complex cognitive activities of children that are governed and influenced by several principles
Zone of Proximal Development pertaining to the learning of children
Impression: Vygotsky’s theory focused more upon the processes through which children develop rather than the characteristics of that children of particular ages are likely to demonstrate. 8.
1896-1980 Jean Piaget Key :
Sensorimotor schemata
Interaction with the environment
Impression: Piaget's theory argues that we have to conquer four stages of cognitive development. First, the sensori-motor stage. Second, the pre-operational stage. Third the concrete operational stage and fourth the formal operational stage. 9.
1904-1985 Donald Olding Hebb Key :
Cell assembly and phase sequence
Sensory deprivation disrupts normal cognitive functioning
An environmental cue has two function: conveys information about environment, stimulates the reticular activating system
Impression: This had incredible implications for physiology and psychology both, and has recently been used in application as far-removed from psychology as engineering and computer science 10. 1904-1990 Burrhus Frederic Skinner Key :
Theory of behaviorism
There is interaction between stimulus (S) and response (R)
Impression: This theory discusses problem
solving and shows that it is that behavior
which is primarily effective, and hence reinforced, by producing the controlling
circumstances, principally SDS,for other, rule-governed
behavior. 11. 1916-2002 Robert Mills Gagne Key :
Learning is influenced by the growth and the environment, but the greatest effect is the individual person's environment
Learning is complex
Three elements of learning: the individual study, the stimulus situation, and respondents
Eight types of learning, namely: signal learning, stimulus response learning, chaining, verbal Association, discrimination learning, learning concept, learn the rules, and problem solving learning
Impression: This theory is only teacher centered learning, where the teacher is authoritarian. The student only listens in an orderly manner the teacher explains and memorizes what is heard and is seen as an effective way of learning. 12. 1919-2011 (1997) William Kaye Estes Key :
Stimulus sampling theory
Right and incorrect response (A1 and A2)
Impression: The scope of the theory is very limited. Mathematical abstraction in this theory in very limited experimental conditions. 13. 1925-1977 Albert Bandura Key :
Social Learning Theory (SLT) and Social Cognitive Learning Theory (SCLT)
Imitation involves the actual reproduction of observed motor activities
Human behavior is largely self-regulated
Intrinsic reinforcement comes from self-evaluation
Working at goals that are too distant or too difficult can be disappointing
Observation, imitation, modeling
Impression: This theory focus on how setting influences behavior places more weight on the people and community that the child is part of, and not enough weight on how the child handles and process new information. It neglects the child’s ability and may go too far in stating that society direct how the individual behaves and acts.
THEORIES OF LEARNING This paper is submitted to fulfill Foundation of English Education and Instruction
Supervised by Dr. H. Fathor Rasyid, M.Pd. and Dr. Thoyyibah, SS., M.Pd
Written By:
Rizki Amalia Intias
926.001.18.019
ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING PROGRAM GRADUATE PROGRAM ISLAMIC STATE INSTITUTE OF KEDIRI 2018
THEORIES OF LEARNING
1.
1849-1936 Ivan Petrovich Pavlov Key :
Theory of stimulus-response associative conditioning
Learning is a process of change that occurs the conditions then reaction (response)
Impression: This theory is suitable for learning that requires mastery of skills with training, or requires certain behaviors in learning. And it also makes easy for educators to control learning because individuals do not realize that they are controlled by stimuli that come from outside themselves.
2.
1874-1949 Edward Lee Thorndike Key :
Connectionism
The association between sense impressions and impulses to action a bond or a connection
Functional aspects of behavior is due mainly to the influence of Darwin
Selecting and connecting
Learning was incremental rather than insightful
The spread of effect
The law of readiness, exercise, effect.
Impression: This theory teaches children to think linearly and convergent. Learning is a process of forming or shaping which is to bring the child to reach or reach a certain target. 3.
1880-1967 Gestalt Theory Key :
Cognitive
Apply field theory from physics to the problems of psychology
Perceptual phenomena
The actual stimulation has changed radically
To inhibit understanding is based on the doctrine of associationism
Reaching an understanding involves many aspects of learner
Impression: This theory looks the human as unique individu, they connect with the environment around them, and this theory is more emphazise for the important of the insight or understanding in learn anything, so they will more success to reach comprehension in learning process. 4.
1884-1952 Clark Leonard Hull Key :
Quantitative experimental methods for learning
Phenomenon of hypnosis
Mathematical expressions for psychological theory
Impression: This only happens when skills are well-learned. In contrast, if the athletic skill is not well-learned, performance will deteriorate. This theory helps explain why beginners find it difficult to perform well under pressure. Often beginners’ skill level decreases if they are competing in a relay race using new skills. 5.
1886-1959 Edward Chace Tolman Key :
Mixture of Gestalt and Behaviorism theory
Learn behavior to determine cognitive processes
Stimulus response controlled by rewards
Physical phenomena and ignores mental aspect
Impression: This theory shows that students should be faced with different topics and different points of view. This process will allow students to develop cognitive maps that will be used to answer questions about a particular topic and other topics.
6.
1886-1959 Edwin Ray Guthrie Key :
The law of contingency
Stimulus and response relationship variables to explain the occurrence of the learning process
The punishment given at the right time will be able to change a person's behavior
human behavior as a whole can be viewed as a series of behaviors consisting of units
Impression: The education process begins with stating the purpose, that is state what response must be made to stimuli. 7.
1896-1934 Lev Vygotsky Key :
Sociocultural theory
Social interaction plays a fundamental role in the development of cognition
The more complex cognitive activities of children that are governed and influenced by several principles
Zone of Proximal Development pertaining to the learning of children
Impression: Vygotsky’s theory focused more upon the processes through which children develop rather than the characteristics of that children of particular ages are likely to demonstrate. 8.
1896-1980 Jean Piaget Key :
Sensorimotor schemata
Interaction with the environment
Impression: Piaget's theory argues that we have to conquer four stages of cognitive development. First, the sensori-motor stage. Second, the pre-operational stage. Third the concrete operational stage and fourth the formal operational stage. 9.
1904-1985 Donald Olding Hebb Key :
Cell assembly and phase sequence
Sensory deprivation disrupts normal cognitive functioning
An environmental cue has two function: conveys information about environment, stimulates the reticular activating system
Impression: This had incredible implications for physiology and psychology both, and has recently been used in application as far-removed from psychology as engineering and computer science 10. 1904-1990 Burrhus Frederic Skinner Key :
Theory of behaviorism
There is interaction between stimulus (S) and response (R)
Impression: This theory discusses problem
solving and shows that it is that behavior
which is primarily effective, and hence reinforced, by producing the controlling
circumstances, principally SDS,for other, rule-governed
behavior. 11. 1916-2002 Robert Mills Gagne Key :
Learning is influenced by the growth and the environment, but the greatest effect is the individual person's environment
Learning is complex
Three elements of learning: the individual study, the stimulus situation, and respondents
Eight types of learning, namely: signal learning, stimulus response learning, chaining, verbal Association, discrimination learning, learning concept, learn the rules, and problem solving learning
Impression: This theory is only teacher centered learning, where the teacher is authoritarian. The student only listens in an orderly manner the teacher explains and memorizes what is heard and is seen as an effective way of learning. 12. 1919-2011 (1997) William Kaye Estes Key :
Stimulus sampling theory
Right and incorrect response (A1 and A2)
Impression: The scope of the theory is very limited. Mathematical abstraction in this theory in very limited experimental conditions. 13. 1925-1977 Albert Bandura Key :
Social Learning Theory (SLT) and Social Cognitive Learning Theory (SCLT)
Imitation involves the actual reproduction of observed motor activities
Human behavior is largely self-regulated
Intrinsic reinforcement comes from self-evaluation
Working at goals that are too distant or too difficult can be disappointing
Observation, imitation, modeling
Impression: This theory focus on how setting influences behavior places more weight on the people and community that the child is part of, and not enough weight on how the child handles and process new information. It neglects the child’s ability and may go too far in stating that society direct how the individual behaves and acts.