Soil-ch.2 3s86
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Soil-ch.2 as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 917
- Pages: 8
The Islamic University of Gaza
Instructor: Dr. Jehad Hamad T.A: Eng. Waseem Younis
Civil Engineering Department Soil Mechanics Second Semester
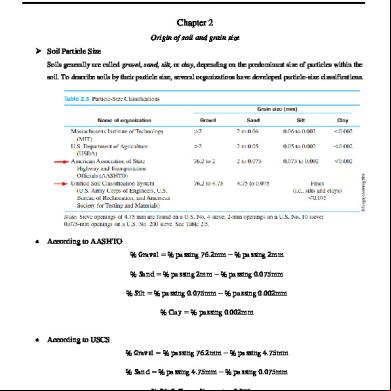
Chapter 2 Origin of soil and grain size Soil Particle Size Soils generally are called gravel, sand, silt, or clay, depending on the predominant size of particles within the soil. To describe soils by their particle size, several organizations have developed particle-size classifications.
According to AASHTO % Gravel = % ing 76.2mm − % ing 2mm % Sand = % ing 2mm − % ing 0.075mm % Silt = % ing 0.075mm − % ing 0.002mm % Clay = % ing 0.002mm
According to USCS % Gravel = % ing 76.2mm − % ing 4.75mm % Sand = % ing 4.75mm − % ing 0.075mm % Silt & Clay = % ing 0.075mm
1
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Specific Gravity Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the unit weight of a given material to the unit weight of water.
G𝑠 =
γ𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 ρ𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 = 𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝜌𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
Mechanical Analysis of Soil Mechanical analysis is the determination of the size range of particles present in a soil, expressed as a percentage of the total dry weight.
Two methods generally are used to find the particle-size distribution of soil: 1.
Sieve analysis — for particle sizes larger than 0.075 mm in diameter.
2.
Hydrometer analysis — for particle sizes smaller than 0.075 mm in diameter.
a) Sieve Analysis Sieve analysis consists of shaking the soil sample through a set of sieves that have progressively smaller openings. U.S. standard sieve numbers and the sizes of openings are given in Table 2.5.
Analysis Steps: 1.
Determine the mass of soil retained on each sieve.
2.
Determine the total mass of the soil.
3.
Determine the cumulative mass of soil retained above each sieve.
4.
Determine the mass of soil ing on each sieve.
5.
The percent of soil ing.
6.
Plot the particle-size distribution curve on semi logarithmic graph paper.
2
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b) Hydrometer Analysis Will be discussed briefly in soil lab.
Particle Size Distribution Curve A particle-size distribution curve can be used to determine the following four parameters for a given soil 1. Effective size (D10): This parameter is the diameter in the particle-size distribution curve corresponding to 10% finer. The effective size of a granular soil is a good measure to estimate the hydraulic conductivity and drainage through soil. 2. Uniformity coefficient (Cu): This parameter is defined as
Cu =
D60 D10
Where D60 = diameter corresponding to 60% finer. 3. Coefficient of gradation (Cc): This parameter is defined as
D30 2 Cc = D10 x D60 D10 , D30 and D60 can be determined as in the figure below
3
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Problem 2.3 The following are the results of a sieve analysis Sieve No.
Mass of soil Retained (g)
4
28
10
42
20
48
40
128
60
221
100
86
200
40
pan
24
a. Determine the percent finer than each sieve and plot the grain size distribution curve. b. Determine D10 , D30 and D60 from the grain size distribution curve. c. Calculate the uniformity coefficient. d. Calculate the coefficient of gradation.
Solution: a. Sieve No.
Sieve size (mm)
Mass of soil Retained (g)
Cum. Ret. (g)
% Cum. Ret.
% ing
4
4.75
28
28
4.54
95.46
10
2
42
70
11.35
88.65
20
0.85
48
118
19.12
80.88
40
0.425
128
246
39.87
60.13
60
0.25
221
467
75.69
24.31
100
0.15
86
553
89.63
10.37
200
0.075
40
593
96.11
3.89
24
617
100.00
0.00
pan
4
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Grain Size Distribution 100.00 90.00 80.00
% ing
70.00 60.00 50.00 40.00 30.00 20.00 10.00 0.00 0.01
0.1
Sieve Size (mm)
1
10
1
10
Grain Size Distribution 100.00 90.00 80.00
% ing
70.00
D60 = 0.43
60.00 50.00 40.00
D30 = 0.28
30.00 20.00
D10 = 0.16
10.00 0.00 0.01
0.1
Sieve Size (mm)
5
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b. D10 = 0.16mm D30 = 0.28mm D60 = 0.43mm c. Cu =
D60 0.43 = = 2.685 D10 0.16
d. D30 2 0.282 Cc = = = 1.1395 D10 x D60 0.16 x 0.43
6
Mechanics of Materials
Problem 2.8 The following are the results of a sieve analysis Grain size (mm)
Percent finer than
0.425
100
0.18
96
0.09
85
0.075
80
0.04
59
0.02
39
0.01
26
0.005
15
0.0015
8
a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve. b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the AASHTO system. c. Repeat part b according to the USCS.
Solution: a.
Grain Size Distribution 100 90 80 70
% ing
Eng. Waseem Younis
60 50 40 30
20 10 0 0.001
0.01
0.1
Grain size (mm)
7
1
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b. % ing 76.2 mm
100
% ing 2 mm
100
% ing 0.075 mm
80
% ing 0.002 mm
24
% Gravel = 100 − 100 = 0 % Sand = 100 − 80 = 20 % Silt = 80 − 24 = 56 % Clay = 24
c. % ing 76.2 mm
100
% ing 4.75 mm
100
% ing 0.075 mm
80
% Gravel = 100 − 100 = 0 % Sand = 100 − 80 = 20 % Silt & Clay = 80
Homework Problems 2.1 2.4 2.6 2.8 2.9 Deadline 20/02/2016
8
Instructor: Dr. Jehad Hamad T.A: Eng. Waseem Younis
Civil Engineering Department Soil Mechanics Second Semester
Chapter 2 Origin of soil and grain size Soil Particle Size Soils generally are called gravel, sand, silt, or clay, depending on the predominant size of particles within the soil. To describe soils by their particle size, several organizations have developed particle-size classifications.
According to AASHTO % Gravel = % ing 76.2mm − % ing 2mm % Sand = % ing 2mm − % ing 0.075mm % Silt = % ing 0.075mm − % ing 0.002mm % Clay = % ing 0.002mm
According to USCS % Gravel = % ing 76.2mm − % ing 4.75mm % Sand = % ing 4.75mm − % ing 0.075mm % Silt & Clay = % ing 0.075mm
1
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Specific Gravity Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the unit weight of a given material to the unit weight of water.
G𝑠 =
γ𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 ρ𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 = 𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝜌𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
Mechanical Analysis of Soil Mechanical analysis is the determination of the size range of particles present in a soil, expressed as a percentage of the total dry weight.
Two methods generally are used to find the particle-size distribution of soil: 1.
Sieve analysis — for particle sizes larger than 0.075 mm in diameter.
2.
Hydrometer analysis — for particle sizes smaller than 0.075 mm in diameter.
a) Sieve Analysis Sieve analysis consists of shaking the soil sample through a set of sieves that have progressively smaller openings. U.S. standard sieve numbers and the sizes of openings are given in Table 2.5.
Analysis Steps: 1.
Determine the mass of soil retained on each sieve.
2.
Determine the total mass of the soil.
3.
Determine the cumulative mass of soil retained above each sieve.
4.
Determine the mass of soil ing on each sieve.
5.
The percent of soil ing.
6.
Plot the particle-size distribution curve on semi logarithmic graph paper.
2
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b) Hydrometer Analysis Will be discussed briefly in soil lab.
Particle Size Distribution Curve A particle-size distribution curve can be used to determine the following four parameters for a given soil 1. Effective size (D10): This parameter is the diameter in the particle-size distribution curve corresponding to 10% finer. The effective size of a granular soil is a good measure to estimate the hydraulic conductivity and drainage through soil. 2. Uniformity coefficient (Cu): This parameter is defined as
Cu =
D60 D10
Where D60 = diameter corresponding to 60% finer. 3. Coefficient of gradation (Cc): This parameter is defined as
D30 2 Cc = D10 x D60 D10 , D30 and D60 can be determined as in the figure below
3
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Problem 2.3 The following are the results of a sieve analysis Sieve No.
Mass of soil Retained (g)
4
28
10
42
20
48
40
128
60
221
100
86
200
40
pan
24
a. Determine the percent finer than each sieve and plot the grain size distribution curve. b. Determine D10 , D30 and D60 from the grain size distribution curve. c. Calculate the uniformity coefficient. d. Calculate the coefficient of gradation.
Solution: a. Sieve No.
Sieve size (mm)
Mass of soil Retained (g)
Cum. Ret. (g)
% Cum. Ret.
% ing
4
4.75
28
28
4.54
95.46
10
2
42
70
11.35
88.65
20
0.85
48
118
19.12
80.88
40
0.425
128
246
39.87
60.13
60
0.25
221
467
75.69
24.31
100
0.15
86
553
89.63
10.37
200
0.075
40
593
96.11
3.89
24
617
100.00
0.00
pan
4
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
Grain Size Distribution 100.00 90.00 80.00
% ing
70.00 60.00 50.00 40.00 30.00 20.00 10.00 0.00 0.01
0.1
Sieve Size (mm)
1
10
1
10
Grain Size Distribution 100.00 90.00 80.00
% ing
70.00
D60 = 0.43
60.00 50.00 40.00
D30 = 0.28
30.00 20.00
D10 = 0.16
10.00 0.00 0.01
0.1
Sieve Size (mm)
5
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b. D10 = 0.16mm D30 = 0.28mm D60 = 0.43mm c. Cu =
D60 0.43 = = 2.685 D10 0.16
d. D30 2 0.282 Cc = = = 1.1395 D10 x D60 0.16 x 0.43
6
Mechanics of Materials
Problem 2.8 The following are the results of a sieve analysis Grain size (mm)
Percent finer than
0.425
100
0.18
96
0.09
85
0.075
80
0.04
59
0.02
39
0.01
26
0.005
15
0.0015
8
a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve. b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the AASHTO system. c. Repeat part b according to the USCS.
Solution: a.
Grain Size Distribution 100 90 80 70
% ing
Eng. Waseem Younis
60 50 40 30
20 10 0 0.001
0.01
0.1
Grain size (mm)
7
1
Mechanics of Materials
Eng. Waseem Younis
b. % ing 76.2 mm
100
% ing 2 mm
100
% ing 0.075 mm
80
% ing 0.002 mm
24
% Gravel = 100 − 100 = 0 % Sand = 100 − 80 = 20 % Silt = 80 − 24 = 56 % Clay = 24
c. % ing 76.2 mm
100
% ing 4.75 mm
100
% ing 0.075 mm
80
% Gravel = 100 − 100 = 0 % Sand = 100 − 80 = 20 % Silt & Clay = 80
Homework Problems 2.1 2.4 2.6 2.8 2.9 Deadline 20/02/2016
8