This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Shortnote_gallbladder & Biliary as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 1,382
- Pages: 24
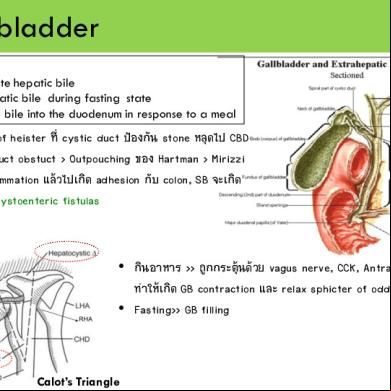
Gallbladder Function - concentrate hepatic bile - store hepatic bile during fasting state - to deliver bile into the duodenum in response to a meal
• มี valve of heister ที่ cystic duct ป้องกัน stone หลุดไป CBD • Cystic duct obstuct > Outpouching ของ Hartman > Mirizzi • เกิด inflammation แล้วไปเกิด adhesion กับ colon, SB จะเกิด cholecystoenteric fistulas
• กินอาหาร >> ถูกกระตุ้นด้วย vagus nerve, CCK, Antral distention ทาให้เกิด GB contraction และ relax sphicter of oddi • Fasting>> GB filling
Calot’s Triangle
CBD เปิดเข้า Ampulla of Vater (ใต้ pylorus 10 cm) Duct of luschka Drain bile liver ไป body ของ GB โดยตรง Leak ออกมา เกิด Biloma
Bile ประกอบด้วย • bile acids and pigments • phospholipids and cholesterol • proteins, and electrolytes
secreted 500 to 1000 mL/24 h composition of bile is similar to plasma [iso-osmotic with plasma] replacement with lactated Ringer's solution
Gallstone Disease หญิง > ชาย 3:1 4 F: Fat, Forty, Female, Fertile ปัจจัยเสี่ยง: อ้วน, ท้อง, ตัดกระเพาะ+terminal ileum, hemolytc anemia ส่วนมากจะเป็น Asymptomatic GS จะกลายเป็น complicate GS เพียง 5-7% ชนิดของ GS Cholesterol stone: radiolucent พบได้แค่ 10% Pigmented stone: radiopaque พบได้ 15% Black stone [Ca Billirubinate] พบใน hemolytic anemia, ileal resection Brown stone พบในคนที่มี bile stasis หรือมี infection Mixed stones(75%)= Cholesterol stones+ pigment stones +calcium+proteins Prophylactic Cholecystectomy GS ในเด็ก Splenectomy in hemolytic anemia พวกบ้านอยู่ไกล รพ. Bariatric surgery populations with increased risk of gallbladder cancer e.g. Porcelain gallbladder GB polyp > 1 cm GS > 3 cm. choledochal cyst
Long term TPN Liver Transplant
Symptomatic GS • 2/3 มาด้วย chronic cholecystitis • มีอาการ recurrent pain แบบ biliary colic 1.Severe epigastrium or RUQ pain is constant and ↑ in severity over the 1st hr. Typically lasts 1 to 5 hrs. radiates to the right upper back or between the scapulae 2.comes on abruptly 3.Typically during the night or after a fatty meal
4.associated with nausea and sometimes vomiting
Acute Cholecystitis
Acute Cholecystitis S/S Sudden attack of biliary colic the pain does not subside it is unremitting typically in RUQ or epigastrium radiate to the right upper part of the back or the interscapular area febrile anorexia, nausea, &vomiting reluctant to move(Peritoneal involvement) P.E.=focal tenderness & guarding in RUQ Murphy sign’s +ve May?palpable tender mass (GBand adherent omentum)
mild to moderate leukocytosis (12,000 to 15,000 cells/mm A high WBC (above 20,000) is suggestive of a complicated form of cholecystitis LFT are usually normal mild ↑ of serum bilirubin mild ↑ AP, transaminases & amylase Severe jaundice is suggestive of CBD stones obstruction of the bile ducts by severe pericholecystic inflammation secondary to impaction of a stone in the infundibulum of the gallbladder
(Mirizzi's syndrome)
Acute Cholecystitis Investigation U/S: most useful >> Sensitivity & Specificity 95% เห็น GS GB wall หนา > 4 mm Pericholecystic fluid Sonographic Murphy's sign Treatment Intravenous fluids, antibiotics, & analgesia Cholecystectomy = Definitive Tx. Early cholecystectomy performed within 2 to 3 days of the illness is preferred over interval or delayed cholecystectomy (6 to 10 wk.) ปัจจุบัน ทา LC เป็น Standard percutaneous cholecystostomy or an open cholecystostomy ในคนที่ไม่เหมาะกับ Sx
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis Acute inflammation of GB without GS มักเกิดในผู้ป่วยสภาพแย่ๆ อยู่ในICU เช่น sepsis, major surgery, Parenteral nutrition, Multiple trauma เป็นต้น The cause is unknown พบ GB distention with bile stasis & ischemia GB wall reveals edema of the serosa &muscular layers, with patchy thrombosis of arterioles &venules. Investigation U/S มักเป็น test of choice => พบ distended GB Wall, Bile sludge, Pericholecystic fluid, +/- abscess Treatment of choice คือ Cholecystectomy
Common bile duct stones (Choledocholithiasis) พบได้ 6-12% ของ GS Patient Primary Stone สร้างใน bile duct เอง ≫ brown pigment stones ซึ่งก็เกิดจาก bile stasis หรือมี infection พบเยอะในพวก Asia Secondary stone สร้างใน GB แล้วมาหล่นลงมาใน CBD ส่วนมากก็เป็น Cholesterol stone พบเยอะ ในพวกตะวันตก Sign & Symptom • • • • •
may be silent ถ้ามี Pain ≈ biliary colic of the CD stone Nausea and vomiting mild epigastric or RUQ tenderness mild icterus Intermittent symptoms , pain and transient jaundice, temporarily stone impacts & subsequently moves away a
ball valve
• completely impacted stones caused obstructive Jx • ↑ serum bilirubin, AP, & transaminases
Common bile duct stones (Choledocholithiasis) Investigation U/S เจอ • Stone ใน GB, CBD • Dilate CBD >8 mm MR o Excellent anatomic detail o sensitivity 81%-100% o Specificity 92%-100% ER เป็น Gold standard ในการ dx CBD Stone รวมถึงยังสามารถเป็น therapeutic ได้ด้วย เช่นการทา sphincterectomy PTC: frequently performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic reasons in patients with 1ry bile duct stones
Acute Cholangitis is an ascending bacterial infection in association with partial or complete obstruction of the bile ducts
Cause CBD stones benign & malignant strictures Parasites instrumentation of the ducts and indwelling stents partially obstructed biliary-enteric anastomosis
Acute Cholangitis Diagnosis - Leukocytosis, Direct hyperbillirubinemia. ALP และ Transaminase↑ - U/s, CT, MRI ใช้บอกตาแหน่งและสาเหตุการ obstruction - ER ใช้ในการ Dx. แล Treatment ได้ - ทา PTC เพื่อหาตาแหน่งที่อุดตันและยังทา PTBD เพื่อระบายนาดีออกมาได้ Treatment 1.
กรณีเป็นแค่ acute cholangitis การรักษาหลักประกอบด้วย 1.1 resuscitation and close monitoring 1.2 IV antibiotics and correct coagulopathy > 85% improve in 72 hr then continue ATB 1-2 wk 1.3 Difinitive surgery : ER then elective LC with IOC in 6-12 wk ( 14% มี recurrent cholangitis in 6-12 wk) 2. 15% ของผู้ปว่ ย แย่ลง อาการไม่ดีขึนใน 12-24 hr > Acute toxic cholangitis 2.1 first line > urgent ER + drainage 2.2 if fail 2.1 > PTC and PTBD 2.3 if fail 2.2 > surgical drainage with T- tube
Acute Cholangitis (Management)
Sclerosing Cholangitis • inflammatory strictures involving the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tree progressive disease that eventually results in secondary biliary cirrhosis, liver failure • risk for developing cholangiocarcinoma Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Symptoms:: ไม่ทราบสาเหตุที่แน่นอน intermittent Jx, มักสัมพันธ์กบั Ilcerative Colitis, Reidel thyroiditis fatigue, Pathogenesis: Autoimmune reaction, chronic low-grade weight loss, bacterial or viral infection, toxic reaction, genetic pruritus, factors abdominal pain ไม่มีการรักษาที่ effective, ที่ดู OK สุดในชีทก็ dilated and stent Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis : stricture ของ bile duct จากสาเหตุอื่นๆ เช่น bile duct stones, acute cholangitis, previous biliary surgery, toxic agents
Choledochal cyst • congenital cystic dilatations of the extrahepatic and/or intrahepatic biliary tree
• ♀>♂ = 8 times • The cause is unknown
• Triad :: 10% abdominal pain, jaundice, a mass.
Risk of cholangiocarcinoma
CA Gallbladder Rare CA, 2-4% ของ CA of GI Tract พบในคนแก่, prognosis แย่มากๆ>> 5 year SVR = 5% 90% of CA GB pt. ☞ have GS. papillary,<10%,but better outcome Stone > 3cm เพิ่ม risk CA 10X 80 -90% are adenocarcinomas nodular, tubular
RISK of CA Gallbladder Risk ที่ต้องจาเกี่ยวกับ CA GB [น่าจะออกสอบได้] •higher in symptom. > asymptom. GS •GB polyps > 10 mm , GS > 2 cm. •"porcelain" GB, > 20% incidence of CA GB •choledochal cysts , anywhere in the biliary tree &GB •Sclerosing cholangitis, •anomalous pancreaticobiliary duct junction, • exposure to carcinogens (azotoluene, nitrosamines)
T
description
Operation
5-Y SR
T1
limited to the muscular simple layer of the GB cholecystectomy
T2
invades the perimuscular connective tissue without extension beyond the serosa or into the liver
extended 70% cholecystectomy(resec tion segments IVB and V)+ regional lymphadenectomy
T3 & T4
grow beyond the serosa or invade the liver or other organs
extended right hepatectomy (segments IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII)
85 to 100%
20 to 50%
CA Gallbladder Investigation 1. U/S >> 70 to 100%. Sensitivity • เจอ thickened wall of GB, Heterogeneous mass in GB Lumen, Polyp size >1 cm • อาจมี invasion ไป liver 2. CT scan (staging, Plan of surgery) 3. MR 4. PCT 5. ER
Cholangiocarcinoma
Bile duct CA Risk factor หลักๆ คือ Liver fluke เช่น OV > 95% are adenocarcinomas, Nodular type is M/C แบ่งเป็น Intrahepatic และ Extrahepatic Intrahepatic แบ่งเป็น Peripheral กับ Central Extrahepatic แบ่งเป็น Proximal, Hilar, Klatskin, Middle, Distal
⅔
of cholangiocarcinomas are located in the perihilar location Klatskin tumors
S/S & Invest. of Cholangiocarcinoma Painless jaundice is the most common presentation Pruritus, mild RUQ pain, anorexia, fatigue, weight loss Cholangitis ∼ 10%
Invest. & Mx. of Cholangiocarcinoma Intrahepatic duct dilatation
Mx. of Cholangiocarcinoma Hepatectomy Hepatectomy & bile duct resection Pancreaticoduodenectomy
ER with Biliary stent PTBD **รูปเพิ่มเติมดูในสไลด์ อ.กมเลส เลย ไม่อยากเอามาใส่เดียวเยอะเกิน
In resectable tumor
Palliative Care
• มี valve of heister ที่ cystic duct ป้องกัน stone หลุดไป CBD • Cystic duct obstuct > Outpouching ของ Hartman > Mirizzi • เกิด inflammation แล้วไปเกิด adhesion กับ colon, SB จะเกิด cholecystoenteric fistulas
• กินอาหาร >> ถูกกระตุ้นด้วย vagus nerve, CCK, Antral distention ทาให้เกิด GB contraction และ relax sphicter of oddi • Fasting>> GB filling
Calot’s Triangle
CBD เปิดเข้า Ampulla of Vater (ใต้ pylorus 10 cm) Duct of luschka Drain bile liver ไป body ของ GB โดยตรง Leak ออกมา เกิด Biloma
Bile ประกอบด้วย • bile acids and pigments • phospholipids and cholesterol • proteins, and electrolytes
secreted 500 to 1000 mL/24 h composition of bile is similar to plasma [iso-osmotic with plasma] replacement with lactated Ringer's solution
Gallstone Disease หญิง > ชาย 3:1 4 F: Fat, Forty, Female, Fertile ปัจจัยเสี่ยง: อ้วน, ท้อง, ตัดกระเพาะ+terminal ileum, hemolytc anemia ส่วนมากจะเป็น Asymptomatic GS จะกลายเป็น complicate GS เพียง 5-7% ชนิดของ GS Cholesterol stone: radiolucent พบได้แค่ 10% Pigmented stone: radiopaque พบได้ 15% Black stone [Ca Billirubinate] พบใน hemolytic anemia, ileal resection Brown stone พบในคนที่มี bile stasis หรือมี infection Mixed stones(75%)= Cholesterol stones+ pigment stones +calcium+proteins Prophylactic Cholecystectomy GS ในเด็ก Splenectomy in hemolytic anemia พวกบ้านอยู่ไกล รพ. Bariatric surgery populations with increased risk of gallbladder cancer e.g. Porcelain gallbladder GB polyp > 1 cm GS > 3 cm. choledochal cyst
Long term TPN Liver Transplant
Symptomatic GS • 2/3 มาด้วย chronic cholecystitis • มีอาการ recurrent pain แบบ biliary colic 1.Severe epigastrium or RUQ pain is constant and ↑ in severity over the 1st hr. Typically lasts 1 to 5 hrs. radiates to the right upper back or between the scapulae 2.comes on abruptly 3.Typically during the night or after a fatty meal
4.associated with nausea and sometimes vomiting
Acute Cholecystitis
Acute Cholecystitis S/S Sudden attack of biliary colic the pain does not subside it is unremitting typically in RUQ or epigastrium radiate to the right upper part of the back or the interscapular area febrile anorexia, nausea, &vomiting reluctant to move(Peritoneal involvement) P.E.=focal tenderness & guarding in RUQ Murphy sign’s +ve May?palpable tender mass (GBand adherent omentum)
mild to moderate leukocytosis (12,000 to 15,000 cells/mm A high WBC (above 20,000) is suggestive of a complicated form of cholecystitis LFT are usually normal mild ↑ of serum bilirubin mild ↑ AP, transaminases & amylase Severe jaundice is suggestive of CBD stones obstruction of the bile ducts by severe pericholecystic inflammation secondary to impaction of a stone in the infundibulum of the gallbladder
(Mirizzi's syndrome)
Acute Cholecystitis Investigation U/S: most useful >> Sensitivity & Specificity 95% เห็น GS GB wall หนา > 4 mm Pericholecystic fluid Sonographic Murphy's sign Treatment Intravenous fluids, antibiotics, & analgesia Cholecystectomy = Definitive Tx. Early cholecystectomy performed within 2 to 3 days of the illness is preferred over interval or delayed cholecystectomy (6 to 10 wk.) ปัจจุบัน ทา LC เป็น Standard percutaneous cholecystostomy or an open cholecystostomy ในคนที่ไม่เหมาะกับ Sx
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis Acute inflammation of GB without GS มักเกิดในผู้ป่วยสภาพแย่ๆ อยู่ในICU เช่น sepsis, major surgery, Parenteral nutrition, Multiple trauma เป็นต้น The cause is unknown พบ GB distention with bile stasis & ischemia GB wall reveals edema of the serosa &muscular layers, with patchy thrombosis of arterioles &venules. Investigation U/S มักเป็น test of choice => พบ distended GB Wall, Bile sludge, Pericholecystic fluid, +/- abscess Treatment of choice คือ Cholecystectomy
Common bile duct stones (Choledocholithiasis) พบได้ 6-12% ของ GS Patient Primary Stone สร้างใน bile duct เอง ≫ brown pigment stones ซึ่งก็เกิดจาก bile stasis หรือมี infection พบเยอะในพวก Asia Secondary stone สร้างใน GB แล้วมาหล่นลงมาใน CBD ส่วนมากก็เป็น Cholesterol stone พบเยอะ ในพวกตะวันตก Sign & Symptom • • • • •
may be silent ถ้ามี Pain ≈ biliary colic of the CD stone Nausea and vomiting mild epigastric or RUQ tenderness mild icterus Intermittent symptoms , pain and transient jaundice, temporarily stone impacts & subsequently moves away a
ball valve
• completely impacted stones caused obstructive Jx • ↑ serum bilirubin, AP, & transaminases
Common bile duct stones (Choledocholithiasis) Investigation U/S เจอ • Stone ใน GB, CBD • Dilate CBD >8 mm MR o Excellent anatomic detail o sensitivity 81%-100% o Specificity 92%-100% ER เป็น Gold standard ในการ dx CBD Stone รวมถึงยังสามารถเป็น therapeutic ได้ด้วย เช่นการทา sphincterectomy PTC: frequently performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic reasons in patients with 1ry bile duct stones
Acute Cholangitis is an ascending bacterial infection in association with partial or complete obstruction of the bile ducts
Cause CBD stones benign & malignant strictures Parasites instrumentation of the ducts and indwelling stents partially obstructed biliary-enteric anastomosis
Acute Cholangitis Diagnosis - Leukocytosis, Direct hyperbillirubinemia. ALP และ Transaminase↑ - U/s, CT, MRI ใช้บอกตาแหน่งและสาเหตุการ obstruction - ER ใช้ในการ Dx. แล Treatment ได้ - ทา PTC เพื่อหาตาแหน่งที่อุดตันและยังทา PTBD เพื่อระบายนาดีออกมาได้ Treatment 1.
กรณีเป็นแค่ acute cholangitis การรักษาหลักประกอบด้วย 1.1 resuscitation and close monitoring 1.2 IV antibiotics and correct coagulopathy > 85% improve in 72 hr then continue ATB 1-2 wk 1.3 Difinitive surgery : ER then elective LC with IOC in 6-12 wk ( 14% มี recurrent cholangitis in 6-12 wk) 2. 15% ของผู้ปว่ ย แย่ลง อาการไม่ดีขึนใน 12-24 hr > Acute toxic cholangitis 2.1 first line > urgent ER + drainage 2.2 if fail 2.1 > PTC and PTBD 2.3 if fail 2.2 > surgical drainage with T- tube
Acute Cholangitis (Management)
Sclerosing Cholangitis • inflammatory strictures involving the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tree progressive disease that eventually results in secondary biliary cirrhosis, liver failure • risk for developing cholangiocarcinoma Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Symptoms:: ไม่ทราบสาเหตุที่แน่นอน intermittent Jx, มักสัมพันธ์กบั Ilcerative Colitis, Reidel thyroiditis fatigue, Pathogenesis: Autoimmune reaction, chronic low-grade weight loss, bacterial or viral infection, toxic reaction, genetic pruritus, factors abdominal pain ไม่มีการรักษาที่ effective, ที่ดู OK สุดในชีทก็ dilated and stent Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis : stricture ของ bile duct จากสาเหตุอื่นๆ เช่น bile duct stones, acute cholangitis, previous biliary surgery, toxic agents
Choledochal cyst • congenital cystic dilatations of the extrahepatic and/or intrahepatic biliary tree
• ♀>♂ = 8 times • The cause is unknown
• Triad :: 10% abdominal pain, jaundice, a mass.
Risk of cholangiocarcinoma
CA Gallbladder Rare CA, 2-4% ของ CA of GI Tract พบในคนแก่, prognosis แย่มากๆ>> 5 year SVR = 5% 90% of CA GB pt. ☞ have GS. papillary,<10%,but better outcome Stone > 3cm เพิ่ม risk CA 10X 80 -90% are adenocarcinomas nodular, tubular
RISK of CA Gallbladder Risk ที่ต้องจาเกี่ยวกับ CA GB [น่าจะออกสอบได้] •higher in symptom. > asymptom. GS •GB polyps > 10 mm , GS > 2 cm. •"porcelain" GB, > 20% incidence of CA GB •choledochal cysts , anywhere in the biliary tree &GB •Sclerosing cholangitis, •anomalous pancreaticobiliary duct junction, • exposure to carcinogens (azotoluene, nitrosamines)
T
description
Operation
5-Y SR
T1
limited to the muscular simple layer of the GB cholecystectomy
T2
invades the perimuscular connective tissue without extension beyond the serosa or into the liver
extended 70% cholecystectomy(resec tion segments IVB and V)+ regional lymphadenectomy
T3 & T4
grow beyond the serosa or invade the liver or other organs
extended right hepatectomy (segments IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII)
85 to 100%
20 to 50%
CA Gallbladder Investigation 1. U/S >> 70 to 100%. Sensitivity • เจอ thickened wall of GB, Heterogeneous mass in GB Lumen, Polyp size >1 cm • อาจมี invasion ไป liver 2. CT scan (staging, Plan of surgery) 3. MR 4. PCT 5. ER
Cholangiocarcinoma
Bile duct CA Risk factor หลักๆ คือ Liver fluke เช่น OV > 95% are adenocarcinomas, Nodular type is M/C แบ่งเป็น Intrahepatic และ Extrahepatic Intrahepatic แบ่งเป็น Peripheral กับ Central Extrahepatic แบ่งเป็น Proximal, Hilar, Klatskin, Middle, Distal
⅔
of cholangiocarcinomas are located in the perihilar location Klatskin tumors
S/S & Invest. of Cholangiocarcinoma Painless jaundice is the most common presentation Pruritus, mild RUQ pain, anorexia, fatigue, weight loss Cholangitis ∼ 10%
Invest. & Mx. of Cholangiocarcinoma Intrahepatic duct dilatation
Mx. of Cholangiocarcinoma Hepatectomy Hepatectomy & bile duct resection Pancreaticoduodenectomy
ER with Biliary stent PTBD **รูปเพิ่มเติมดูในสไลด์ อ.กมเลส เลย ไม่อยากเอามาใส่เดียวเยอะเกิน
In resectable tumor
Palliative Care