Report On Voltage Doubler 5s345v
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Report On Voltage Doubler as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 2,461
- Pages: 19
A Mini Project Report on
VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER Submitted in partial Fulfilment of the Requirement For the award of the degree of
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY In ELECTRICAL & ELCTRONICS ENGINEERING Submitted By G. PAVAN, B15EE132L. Under the guidance of Mr. B. MOHAN SIR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of EEE
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
KAKATIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, Warangal
(An Autonomous Institute under Kakatiya University, Warangal) Warangal – 506015, Telangana, INDIA 2016-2017
KAKATIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE WARANGAL-15 (An Autonomous Institute under Kakatiya University, Warangal) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
CERTIFICATE This is to certify that this is the bonafide record of the Mini project work entitled “VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER” carried out by G. PAVAN, Roll.No.B15EE132L, student of B.Tech., Electrical & Electronics Engineering , as part of partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of B. Tech. Degree in Electrical & Electronics Engineering for the Academic Year 2016-2017.
B. MOHAN, Asst. Prof., Dept. of EEE Project Guide
Prof.V.RAMAIAH Professor and Head Dept. of EEE
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I take the opportunity to acknowledge with heart full thanks and deep sense of gratitude towards our beloved principal Dr. P. VENKATESHWAR RAO who extended his cooperation by giving this opportunity in completing the project work. I express my thanks to Prof. V.RAMAIAH, Head of Electrical and Electronics Engineering section, KITS, Warangal for his encouraging in caring out this project. I feel thankful to Dr.B.VIJAYKUMAR, project co-ordinator & Assistant professor in Electrical and Electronics Engineering section, for his insistences of good technical assistance which helped us to develop a successful project. I take privilege to feel sense of gratitude and my sincere thanks towards our project Guide Mr B. MOHAN, Assistant Professor Dept. of EEE for his/her immense guidance and continue in nurturing the project and to become successful project. I hereby express my sincere regards to all the teaching staff, parents and friends who extended their helping hand in the accomplished of the project.
Yours sincerely, G. PAVAN, B15EE132L,
DECLRATION
I declare that this dissertation entitled “VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER” is original and bonafide work of my own and is submitted in partial fulfilment for
the award of the degree of B.Tech in Electrical and Electronics Engineering department of Kakatiya Institute Of Technology & Science, Warangal and has not been copied from any earlier or other reports. The conclusion and results in this report are based on my own work.
G. PAVAN, B15EE132L, EEE-1,III YEAR.
CONTENTS Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Circuit diagram 3. Components 4. 555 Timer 5. Capacitors 5.1. Types of capacitors 6. Diodes 6.1. Rectification Diode(1N4007) 7. Working 8. Applications 9. Advantages 10.Disadvantages Conclusion References
ABSTRACT
GENERALLY,
CONVENTIONAL POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM PROVIDES 230V AC SUPPLY WHICH IS BEING USED FOR MULTIPLE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS LOADS. BUT, A FEW LOADS OR ELECTRONICS EQUIPMENT LIKE CATHODE RAY TUBES, X-RAY SYSTEMS, ION PUMPS, LASER SYSTEMS, TRAVELLING WAVE TUBE, AND SO ON REQUIRES A HIGH RATING POWER SUPPLY FOR THEIR OPERATION. THUS, THE AVAILABLE VOLTAGE HAS TO BE MULTIPLIED USING THE VOLTAGE MULTIPLIERS. VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER IS AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT COMPRISING OF DIODES AND CAPACITORS THAT CAN BE USED FOR MULTIPLYING OR INCREASING THE VOLTAGE AND CONVERT AC TO DC BY MULTIPLYING VOLTAGE AND RECTIFYING CURRENT. THERE ARE DIFFERENT TYPES OF VOLTAGE MULTIPLIERS SUCH AS VOLTAGE DOUBLER, VOLTAGE TRIPLER, AND VOLTAGE QUADUPLER. PRIMARILY, WE ARE GOING TO DISCUSS ABOUT VOLTAGE DOUBLER USING 555 TIMER.
THE VOLTAGE DOUBLER USING 555 TIMER IS A SIMPLE DC VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER THAT UTILIZES CAPACITORS , DIODES, AND IC 555 TIMER IN ASTABLE MODE.
1. INTRODUCTION
Generally, conventional power supply system provides 230V AC supply which is being used for multiple electrical and electronics loads. But, a few loads or electronics equipment like cathode ray tubes, X-ray systems, Ion pumps, electrostatic system, laser systems, travelling wave tube, and so on requires a high rating power supply for their operation. Thus, the available voltage has to me multiplied using the voltage multipliers. Voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit comprising of diodes and capacitors that can be used for multiplying or increasing the voltage and convert AC to DC by multiplying voltage and rectifying current. There are different types of voltage multipliers such as voltage doubler, voltage Tripler, and voltage quadrupler. Primarily, we are going to discuss about voltage doubler circuit diagram and voltage doubler working. What is a Voltage Doubler? An electronic voltage multiplier circuit that doubles the voltage by using the charging and the discharging principle of capacitors is called as a voltage doubler. It consists of major electronics components such as capacitors and diodes. The simple voltage doubler circuit consists of two capacitors and two diodes connected as shown in the figure. The voltage doubler circuit can be a simple rectifier which takes an input AC voltage and generates an output DC voltage that is approximately twice the input AC voltage. Even though there are DC to DC voltage doublers, but in these types of voltage doubler circuits driving circuit is required for switching control. There are different types of voltage doubler circuits such as a simple voltage doubler as shown above, voltage doubler using 555 timer, voltage doubler rectifiers like Villard circuit, Greinacher circuit, etc.
2. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
3. COMPONENETS
555 timer IC
Diodes -2 (1N4007)
Resistors- 10k, 33k
Capaciotors- 22uf (2), 0.01uF (2)
Resisters
3-12v Power supply source
4. 555 TIMER
The IC 555 has three operating modes: Bistable mode or Schmitt trigger – the 555 can operate as a flip-flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor is used. Uses include bounce-free latched switches. Monostable mode – in this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot" pulse generator. Applications include timers, missing pulse detection, bounce-free switches, touch switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement, pulsewidth modulation (PWM) and so on. Astable (free-running) mode – the 555 can operate as an electronic oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms, pulse position modulation and so on. The 555 can be used as a simple ADC, converting an analog value to a pulse length (e.g., selecting a thermistor as timing resistor allows the use of the 555 in a temperature sensor and The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. The 555 can be used to provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip-flop element. Derivatives provide up to four timing circuits in one package. Introduced in 1971 by American company Signetics, the 555 is still in widespread use due to
its low price, ease of use, and stability. It is now made by many companies in the original bipolar and also in low- power CMOS types.
5. DIODES A device having two terminals and has a low resistance to electrical current in one direction and a high resistance in the other direction. Diode is a two-element device which es a signal in one direction only. They are used most commonly to convert AC to DC, because they the positive part of the wave, and block the negative part of the AC signal, or, if they are reversed, they only the negative part and not the positive part.
5.1 Rectification DIODE (1n4007) The stripe stamped on one end of the diode shows indicates the polarity of the diode. The stripe shows the cathode side. The top two devices shown in the picture are diodes used for rectification. They are made to handle relatively high currents. The device on top can handle as high as 6A, and the one below it can safely handle up to 1A.However, it is best used at about 70% of its rating because this current value is a maximum rating. The third device from the top (red color) has a part number of 1S1588. This diode is used for switching, because it can switch on and off at very high speed. However, the maximum current it can handle is 120 mA. This makes it well suited to use within digital circuits. The maximum reverse voltage (reverse bias) this diode can handle is 30V. The device at the bottom of the picture is a voltage regulation diode with a rating of 6V. When this type of diode is reverse biased, it will resist changes in voltage. If the input voltage is increased, the output voltage will not change. (Or any change will be
an insignificant amount.) While the output voltage does not increase with an increase in input voltage, the output current will. This requires some thought for a protection circuit so that too much current does not flow. The rated current limit for the device is 30 mA. Generally, a 3-terminal voltage regulator is used for the stabilization of a power supply. Therefore, this diode is typically used to protect the circuit from momentary voltage spikes. 3 terminal regulators use voltage regulation diodes inside.
5.2 Features Low forward voltage drop. Diffused Junction High Current Capability ROHS Compliant
RESISTANCE
There is always some resistance in every circuit. • A circuit is always made up of some wire, so there will be some resistance there. • Even the battery has parts that offer resistance to the flow of electrons. • The only circuits that come near to zero resistance are superconductors.
• This resistance that is from the parts of the circuit itself (especially the battery) is called internal resistance. • This internal resistance is usually drawn into a circuit diagram (schematic) as shown in Figure 1. • Notice the squiggly line just before the positive terminal of the battery? That’s to show the internal resistance of the circuit. • That symbol, drawn any other place in the circuit, represents an actual resistor placed in the circuit. • A resistor is a device found in circuits that has a certain amount of resistance. Why would you ever want to add resistance to a circuit by using a resistor? • The most common reason is that we need to be able to adjust the current flowing through a particular part of the circuit. • If voltage is constant, then we can change the resistor to change the current. I=V R If “V” is constant and we change “R”, “I” will be different. 25000 Ω (notice there are three zeros), or even 2.5 x 102 Ω.
CAPACITORS The function of capacitors is to store electricity, or electrical energy. The capacitor also functions as filter, ing AC, and blocking DC. The capacitor is constructed with two electrode plates separated by insulator. They are also used in timing circuits because it takes time for a capacitor to fill with charge. They can be used to smooth varying DC supplies by acting as reservoir of charge.
The capacitor's function is to store electricity, or electrical energy. The capacitor also functions as a filter, ing alternating current (AC), and blocking direct current (DC). This symbol (
)is used to indicate a capacitor in a circuit
diagram. The capacitor is constructed with two electrode plates facing each other but separated by an insulator. When DC voltage is applied to the capacitor, an electric charge is stored on each electrode. While the capacitor is charging up, current flows. The current will stop flowing when the capacitor has fully charged. Commercial capacitors are generally classified according to the dielectric. The most used are mica, paper, electrolytic and ceramic capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors use a molecular thin oxide film as the dielectric resulting in large capacitance values. There is no required polarity, since either side can be the most positive plate, except for electrolytic capacitors. These are marked to indicate which side must be positive to maintain the internal electrolytic action that produces the dielectric required to form the capacitance. It should be noted that the polarity of the charging source determines the polarity of the changing source determines the polarity of the capacitor voltage
4.1 Types of Capacitors There are various types of capacitors available in the market. Some of them are as follows: Mica Capacitor Paper Capacitor Ceramic Capacitor Variable Capacitor Electrolytic Capacitor Tantalum Capacitor Film Capacitor Here we used only two types of capacitor i.e. ceramic capacitor & electrolytic capacitor.
6. WORKING
We can divide the circuit into two parts, first part consist the 555 time IC in Astable mode, to generate the square wave and second part consist 2 diodes and 2 capacitors to double the output voltage. We have configured 555 Timer IC in Astable multivibrator mode to generate the square wave of approx. 2KHz, this frequency is decided by the resistor R1, R2 and capacitor C1. Below is he formulae for the same: F = 1.44 / (R1+2*R2) * C1 When the output at PIN 3 of 555 IC is low, Diode D1 get forward biased and capacitor C3 get charged through the D1. Capacitor C3 get charged up to the same voltage at the source, in our case 5v. Now when output at PIN 3 goes high, D1 get reverse biased and blocks the discharging of the capacitor C3, and at the same time D2 is forward biased and allow the capacitor C4 to charge. Now the capacitor C4 charges with the combined voltage of Capacitor C3 and the input source voltage, means 5v of capacitor C3 and 5v of input supply, so it charges up to 10v (twice the voltage of input source). But in practical we get output voltage less than the twice of input voltage, like in our case we get approx. 8.76v instead of 10v.
7. APPLICATIONS:
Cathode ray tubes. X- Ray systems. Lasser systems. Computer applications.
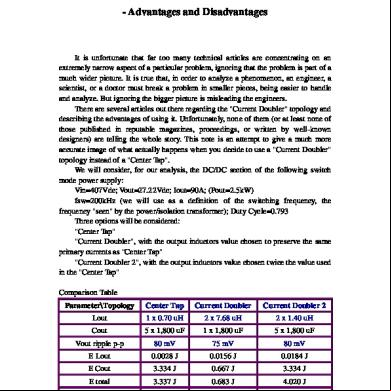
8. ADVANTAGES Construction is simple. Less cost & size. It doubles input voltage.
9. DISADVANTAGES However this circuit is very useful to generate higher voltage from a low power source, but this can only deliver up to 50mA current. So it should only be used for low current driven applications. Also the output voltage may be unstable, so a voltage regulator (IC78XX) of proper rating can be used regulation and smooth output. But voltage regulator IC itself consume some current, and reduce the deliverable current (must not exceed 70mA).
CONCLUSION
The 555 timer output voltage is made to through the voltage doubler for producing double output voltage. But, for maintaining good regulation and to
avoid output voltage from falling below the estimated level, we must restrict the load to less than 5mA. Thus, by eliminating the high current drawing loads we can avoid the poor voltage regulation. By adding more number of multiplier stages, we can obtain an output voltage that is equal to three to ten times the input voltage.
REFFERENCES 1. https://circuitdigest.com/electronic-circuits/voltage-doubler-circuit-diagram 2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage_doubler#CITEREFKindFeser2001 3. http://www.electroschematics.com/648/555-voltage-doubler/
VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER Submitted in partial Fulfilment of the Requirement For the award of the degree of
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY In ELECTRICAL & ELCTRONICS ENGINEERING Submitted By G. PAVAN, B15EE132L. Under the guidance of Mr. B. MOHAN SIR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of EEE
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
KAKATIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, Warangal
(An Autonomous Institute under Kakatiya University, Warangal) Warangal – 506015, Telangana, INDIA 2016-2017
KAKATIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE WARANGAL-15 (An Autonomous Institute under Kakatiya University, Warangal) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
CERTIFICATE This is to certify that this is the bonafide record of the Mini project work entitled “VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER” carried out by G. PAVAN, Roll.No.B15EE132L, student of B.Tech., Electrical & Electronics Engineering , as part of partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of B. Tech. Degree in Electrical & Electronics Engineering for the Academic Year 2016-2017.
B. MOHAN, Asst. Prof., Dept. of EEE Project Guide
Prof.V.RAMAIAH Professor and Head Dept. of EEE
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I take the opportunity to acknowledge with heart full thanks and deep sense of gratitude towards our beloved principal Dr. P. VENKATESHWAR RAO who extended his cooperation by giving this opportunity in completing the project work. I express my thanks to Prof. V.RAMAIAH, Head of Electrical and Electronics Engineering section, KITS, Warangal for his encouraging in caring out this project. I feel thankful to Dr.B.VIJAYKUMAR, project co-ordinator & Assistant professor in Electrical and Electronics Engineering section, for his insistences of good technical assistance which helped us to develop a successful project. I take privilege to feel sense of gratitude and my sincere thanks towards our project Guide Mr B. MOHAN, Assistant Professor Dept. of EEE for his/her immense guidance and continue in nurturing the project and to become successful project. I hereby express my sincere regards to all the teaching staff, parents and friends who extended their helping hand in the accomplished of the project.
Yours sincerely, G. PAVAN, B15EE132L,
DECLRATION
I declare that this dissertation entitled “VOLTAGE DOUBLER CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER” is original and bonafide work of my own and is submitted in partial fulfilment for
the award of the degree of B.Tech in Electrical and Electronics Engineering department of Kakatiya Institute Of Technology & Science, Warangal and has not been copied from any earlier or other reports. The conclusion and results in this report are based on my own work.
G. PAVAN, B15EE132L, EEE-1,III YEAR.
CONTENTS Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Circuit diagram 3. Components 4. 555 Timer 5. Capacitors 5.1. Types of capacitors 6. Diodes 6.1. Rectification Diode(1N4007) 7. Working 8. Applications 9. Advantages 10.Disadvantages Conclusion References
ABSTRACT
GENERALLY,
CONVENTIONAL POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM PROVIDES 230V AC SUPPLY WHICH IS BEING USED FOR MULTIPLE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS LOADS. BUT, A FEW LOADS OR ELECTRONICS EQUIPMENT LIKE CATHODE RAY TUBES, X-RAY SYSTEMS, ION PUMPS, LASER SYSTEMS, TRAVELLING WAVE TUBE, AND SO ON REQUIRES A HIGH RATING POWER SUPPLY FOR THEIR OPERATION. THUS, THE AVAILABLE VOLTAGE HAS TO BE MULTIPLIED USING THE VOLTAGE MULTIPLIERS. VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER IS AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT COMPRISING OF DIODES AND CAPACITORS THAT CAN BE USED FOR MULTIPLYING OR INCREASING THE VOLTAGE AND CONVERT AC TO DC BY MULTIPLYING VOLTAGE AND RECTIFYING CURRENT. THERE ARE DIFFERENT TYPES OF VOLTAGE MULTIPLIERS SUCH AS VOLTAGE DOUBLER, VOLTAGE TRIPLER, AND VOLTAGE QUADUPLER. PRIMARILY, WE ARE GOING TO DISCUSS ABOUT VOLTAGE DOUBLER USING 555 TIMER.
THE VOLTAGE DOUBLER USING 555 TIMER IS A SIMPLE DC VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER THAT UTILIZES CAPACITORS , DIODES, AND IC 555 TIMER IN ASTABLE MODE.
1. INTRODUCTION
Generally, conventional power supply system provides 230V AC supply which is being used for multiple electrical and electronics loads. But, a few loads or electronics equipment like cathode ray tubes, X-ray systems, Ion pumps, electrostatic system, laser systems, travelling wave tube, and so on requires a high rating power supply for their operation. Thus, the available voltage has to me multiplied using the voltage multipliers. Voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit comprising of diodes and capacitors that can be used for multiplying or increasing the voltage and convert AC to DC by multiplying voltage and rectifying current. There are different types of voltage multipliers such as voltage doubler, voltage Tripler, and voltage quadrupler. Primarily, we are going to discuss about voltage doubler circuit diagram and voltage doubler working. What is a Voltage Doubler? An electronic voltage multiplier circuit that doubles the voltage by using the charging and the discharging principle of capacitors is called as a voltage doubler. It consists of major electronics components such as capacitors and diodes. The simple voltage doubler circuit consists of two capacitors and two diodes connected as shown in the figure. The voltage doubler circuit can be a simple rectifier which takes an input AC voltage and generates an output DC voltage that is approximately twice the input AC voltage. Even though there are DC to DC voltage doublers, but in these types of voltage doubler circuits driving circuit is required for switching control. There are different types of voltage doubler circuits such as a simple voltage doubler as shown above, voltage doubler using 555 timer, voltage doubler rectifiers like Villard circuit, Greinacher circuit, etc.
2. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
3. COMPONENETS
555 timer IC
Diodes -2 (1N4007)
Resistors- 10k, 33k
Capaciotors- 22uf (2), 0.01uF (2)
Resisters
3-12v Power supply source
4. 555 TIMER
The IC 555 has three operating modes: Bistable mode or Schmitt trigger – the 555 can operate as a flip-flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor is used. Uses include bounce-free latched switches. Monostable mode – in this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot" pulse generator. Applications include timers, missing pulse detection, bounce-free switches, touch switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement, pulsewidth modulation (PWM) and so on. Astable (free-running) mode – the 555 can operate as an electronic oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms, pulse position modulation and so on. The 555 can be used as a simple ADC, converting an analog value to a pulse length (e.g., selecting a thermistor as timing resistor allows the use of the 555 in a temperature sensor and The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. The 555 can be used to provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip-flop element. Derivatives provide up to four timing circuits in one package. Introduced in 1971 by American company Signetics, the 555 is still in widespread use due to
its low price, ease of use, and stability. It is now made by many companies in the original bipolar and also in low- power CMOS types.
5. DIODES A device having two terminals and has a low resistance to electrical current in one direction and a high resistance in the other direction. Diode is a two-element device which es a signal in one direction only. They are used most commonly to convert AC to DC, because they the positive part of the wave, and block the negative part of the AC signal, or, if they are reversed, they only the negative part and not the positive part.
5.1 Rectification DIODE (1n4007) The stripe stamped on one end of the diode shows indicates the polarity of the diode. The stripe shows the cathode side. The top two devices shown in the picture are diodes used for rectification. They are made to handle relatively high currents. The device on top can handle as high as 6A, and the one below it can safely handle up to 1A.However, it is best used at about 70% of its rating because this current value is a maximum rating. The third device from the top (red color) has a part number of 1S1588. This diode is used for switching, because it can switch on and off at very high speed. However, the maximum current it can handle is 120 mA. This makes it well suited to use within digital circuits. The maximum reverse voltage (reverse bias) this diode can handle is 30V. The device at the bottom of the picture is a voltage regulation diode with a rating of 6V. When this type of diode is reverse biased, it will resist changes in voltage. If the input voltage is increased, the output voltage will not change. (Or any change will be
an insignificant amount.) While the output voltage does not increase with an increase in input voltage, the output current will. This requires some thought for a protection circuit so that too much current does not flow. The rated current limit for the device is 30 mA. Generally, a 3-terminal voltage regulator is used for the stabilization of a power supply. Therefore, this diode is typically used to protect the circuit from momentary voltage spikes. 3 terminal regulators use voltage regulation diodes inside.
5.2 Features Low forward voltage drop. Diffused Junction High Current Capability ROHS Compliant
RESISTANCE
There is always some resistance in every circuit. • A circuit is always made up of some wire, so there will be some resistance there. • Even the battery has parts that offer resistance to the flow of electrons. • The only circuits that come near to zero resistance are superconductors.
• This resistance that is from the parts of the circuit itself (especially the battery) is called internal resistance. • This internal resistance is usually drawn into a circuit diagram (schematic) as shown in Figure 1. • Notice the squiggly line just before the positive terminal of the battery? That’s to show the internal resistance of the circuit. • That symbol, drawn any other place in the circuit, represents an actual resistor placed in the circuit. • A resistor is a device found in circuits that has a certain amount of resistance. Why would you ever want to add resistance to a circuit by using a resistor? • The most common reason is that we need to be able to adjust the current flowing through a particular part of the circuit. • If voltage is constant, then we can change the resistor to change the current. I=V R If “V” is constant and we change “R”, “I” will be different. 25000 Ω (notice there are three zeros), or even 2.5 x 102 Ω.
CAPACITORS The function of capacitors is to store electricity, or electrical energy. The capacitor also functions as filter, ing AC, and blocking DC. The capacitor is constructed with two electrode plates separated by insulator. They are also used in timing circuits because it takes time for a capacitor to fill with charge. They can be used to smooth varying DC supplies by acting as reservoir of charge.
The capacitor's function is to store electricity, or electrical energy. The capacitor also functions as a filter, ing alternating current (AC), and blocking direct current (DC). This symbol (
)is used to indicate a capacitor in a circuit
diagram. The capacitor is constructed with two electrode plates facing each other but separated by an insulator. When DC voltage is applied to the capacitor, an electric charge is stored on each electrode. While the capacitor is charging up, current flows. The current will stop flowing when the capacitor has fully charged. Commercial capacitors are generally classified according to the dielectric. The most used are mica, paper, electrolytic and ceramic capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors use a molecular thin oxide film as the dielectric resulting in large capacitance values. There is no required polarity, since either side can be the most positive plate, except for electrolytic capacitors. These are marked to indicate which side must be positive to maintain the internal electrolytic action that produces the dielectric required to form the capacitance. It should be noted that the polarity of the charging source determines the polarity of the changing source determines the polarity of the capacitor voltage
4.1 Types of Capacitors There are various types of capacitors available in the market. Some of them are as follows: Mica Capacitor Paper Capacitor Ceramic Capacitor Variable Capacitor Electrolytic Capacitor Tantalum Capacitor Film Capacitor Here we used only two types of capacitor i.e. ceramic capacitor & electrolytic capacitor.
6. WORKING
We can divide the circuit into two parts, first part consist the 555 time IC in Astable mode, to generate the square wave and second part consist 2 diodes and 2 capacitors to double the output voltage. We have configured 555 Timer IC in Astable multivibrator mode to generate the square wave of approx. 2KHz, this frequency is decided by the resistor R1, R2 and capacitor C1. Below is he formulae for the same: F = 1.44 / (R1+2*R2) * C1 When the output at PIN 3 of 555 IC is low, Diode D1 get forward biased and capacitor C3 get charged through the D1. Capacitor C3 get charged up to the same voltage at the source, in our case 5v. Now when output at PIN 3 goes high, D1 get reverse biased and blocks the discharging of the capacitor C3, and at the same time D2 is forward biased and allow the capacitor C4 to charge. Now the capacitor C4 charges with the combined voltage of Capacitor C3 and the input source voltage, means 5v of capacitor C3 and 5v of input supply, so it charges up to 10v (twice the voltage of input source). But in practical we get output voltage less than the twice of input voltage, like in our case we get approx. 8.76v instead of 10v.
7. APPLICATIONS:
Cathode ray tubes. X- Ray systems. Lasser systems. Computer applications.
8. ADVANTAGES Construction is simple. Less cost & size. It doubles input voltage.
9. DISADVANTAGES However this circuit is very useful to generate higher voltage from a low power source, but this can only deliver up to 50mA current. So it should only be used for low current driven applications. Also the output voltage may be unstable, so a voltage regulator (IC78XX) of proper rating can be used regulation and smooth output. But voltage regulator IC itself consume some current, and reduce the deliverable current (must not exceed 70mA).
CONCLUSION
The 555 timer output voltage is made to through the voltage doubler for producing double output voltage. But, for maintaining good regulation and to
avoid output voltage from falling below the estimated level, we must restrict the load to less than 5mA. Thus, by eliminating the high current drawing loads we can avoid the poor voltage regulation. By adding more number of multiplier stages, we can obtain an output voltage that is equal to three to ten times the input voltage.
REFFERENCES 1. https://circuitdigest.com/electronic-circuits/voltage-doubler-circuit-diagram 2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage_doubler#CITEREFKindFeser2001 3. http://www.electroschematics.com/648/555-voltage-doubler/