Mee255 Industrial Economics 2p611g
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Mee255 Industrial Economics as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 449
- Pages: 1
12/20/2016
MEE255 Version No Pre requisite Objectives
Expected Outcomes
Ramanujam R Outlook Web App
INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS
3
0
0
3
Nil 1. To familiarize students with a broad range of the methods and models applied by economists in the analysis of firms and industries. 2. To ensure that students who take the course will, by working extensively with theoretical models, acquire analytical skills that are transferable to other kinds of intellectual problems. Upon completion of the course students should:
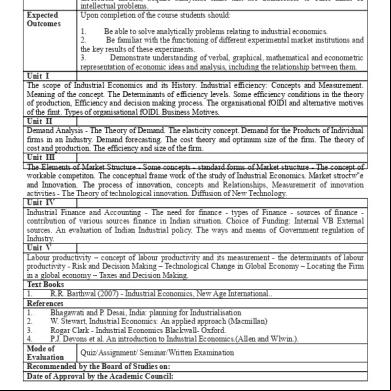
1. Be able to solve analytically problems relating to industrial economics. 2. Be familiar with the functioning of different experimental market institutions and the key results of these experiments. 3. Demonstrate understanding of verbal, graphical, mathematical and econometric representation of economic ideas and analysis, including the relationship between them. Unit I The scope of Industrial Economics and its History. Industrial efficiency: Concepts and Measurement. Meaning of the concept. The Determinants of efficiency levels. Some efficiency conditions in the theory of production, Efficiency and decision making process. The organisational fOlDl and alternative motives of the fimt. Types of organisational fOlDl. Business Motives. Unit II Demand Analysis The Theory of Demand. The elasticity concept. Demand for the Products of Individual firms in an Industry. Demand forecasting. The cost theory and optimum size of the firm. The theory of cost and production. The efficiency and size of the firm. Unit III The Elements of Market Structure Some concepts standard forms of Market structure The concept of workable competiton. The conceptual frame work of the study of Industrial Economics. Market stroctw"e and Innovation. The process of innovation, concepts and Relationships, Measuremerit of innovation activities The Theory of technological innovation. Diffusion of New Technology. Unit IV Industrial Finance and ing The need for finance types of Finance sources of finance contribution of various sources finance in Indian situation. Choice of Funding: Internal VB External sources. An evaluation of Indian Industrial policy. The ways and means of Government regulation of Industry. Unit V Labour productivity – concept of labour productivity and its measurement the determinants of labour productivity Risk and Decision Making – Technological Change in Global Economy – Locating the Firm in a global economy – Taxes and Decision Making. Text Books 1. R.R. Barthwal (2007) Industrial Economics, New Age International.. References 1. Bhagawati and P. Desai, India: planning for Industrialisation 2. W. Stewart, Industrial Economics: An applied approach (Macmillan) 3. Rogar Clark Industrial Economics Blackwall Oxford. 4. P.J. Devons et al. An introduction to Industrial Economics.(Allen and Wlwin.). Mode of Quiz/Assignment/ Seminar/Written Examination Evaluation Recommended by the Board of Studies on: Date of Approval by the Academic Council:
https://webmail.vit.ac.in/owa/#path=/mail
1/1
MEE255 Version No Pre requisite Objectives
Expected Outcomes
Ramanujam R Outlook Web App
INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS
3
0
0
3
Nil 1. To familiarize students with a broad range of the methods and models applied by economists in the analysis of firms and industries. 2. To ensure that students who take the course will, by working extensively with theoretical models, acquire analytical skills that are transferable to other kinds of intellectual problems. Upon completion of the course students should:
1. Be able to solve analytically problems relating to industrial economics. 2. Be familiar with the functioning of different experimental market institutions and the key results of these experiments. 3. Demonstrate understanding of verbal, graphical, mathematical and econometric representation of economic ideas and analysis, including the relationship between them. Unit I The scope of Industrial Economics and its History. Industrial efficiency: Concepts and Measurement. Meaning of the concept. The Determinants of efficiency levels. Some efficiency conditions in the theory of production, Efficiency and decision making process. The organisational fOlDl and alternative motives of the fimt. Types of organisational fOlDl. Business Motives. Unit II Demand Analysis The Theory of Demand. The elasticity concept. Demand for the Products of Individual firms in an Industry. Demand forecasting. The cost theory and optimum size of the firm. The theory of cost and production. The efficiency and size of the firm. Unit III The Elements of Market Structure Some concepts standard forms of Market structure The concept of workable competiton. The conceptual frame work of the study of Industrial Economics. Market stroctw"e and Innovation. The process of innovation, concepts and Relationships, Measuremerit of innovation activities The Theory of technological innovation. Diffusion of New Technology. Unit IV Industrial Finance and ing The need for finance types of Finance sources of finance contribution of various sources finance in Indian situation. Choice of Funding: Internal VB External sources. An evaluation of Indian Industrial policy. The ways and means of Government regulation of Industry. Unit V Labour productivity – concept of labour productivity and its measurement the determinants of labour productivity Risk and Decision Making – Technological Change in Global Economy – Locating the Firm in a global economy – Taxes and Decision Making. Text Books 1. R.R. Barthwal (2007) Industrial Economics, New Age International.. References 1. Bhagawati and P. Desai, India: planning for Industrialisation 2. W. Stewart, Industrial Economics: An applied approach (Macmillan) 3. Rogar Clark Industrial Economics Blackwall Oxford. 4. P.J. Devons et al. An introduction to Industrial Economics.(Allen and Wlwin.). Mode of Quiz/Assignment/ Seminar/Written Examination Evaluation Recommended by the Board of Studies on: Date of Approval by the Academic Council:
https://webmail.vit.ac.in/owa/#path=/mail
1/1