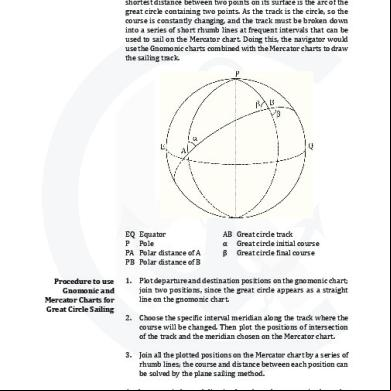
Great Circle Sailing Notes 495h4r
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Great Circle Sailing Notes as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 4,666
- Pages: 88
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing
GREAT CIRCLE SAILING Lindbergh Chart of the Great circle sailing chart of the North Atlantic Ocean 1926 SAK
1
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing A great circle is a circle which cuts the a sphere into two equal halves and its centre is coincident with the centre of the sphere.
SAK
2
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Plane ing through centre of the sphere
Great circle
SAK
3
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing The equator is a great circle. A Great circles cross the equator at two points 180° apart. All longitutes are great circle.
SAK
4
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing
SAK
5
SAK
6
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P
Show the great circles
SAK
7
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing PA, PB, AB is an arc of Great circle PAB is an spherical triangle O is the centre of the sphere The lenght of side AB is angle AOB Angle O is not equal to angle P
P
O
B
A
SAK
8
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P=Elevated Pole (i.e. pole chosen for the triangle) Angle P=D.Long from A to B (E or W)
B
Equator Side PB = Angular distance of B from the Elevated Pole 'B'
SAK
Vn
P
Side PA=Angular distance of A from the Elevated Pole 'P'. For example if elevated pole is North Pole and A is in north latitude then PA = 90°-LAT A. If elevated pole is North Pole and A is in south latitude then PA = 90° +LAT A. A
Vs Prime meridian 9
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing North elevated pole
SAK
11
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing North elevated pole
P
The elevated pole chosen can be in either hemisphere. SAK
12
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Equator South elevated pole
PB=90-Lat B
SAK
13
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing South elevated pole A
SAK
14
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing South elevated pole
SAK
15
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA P is Elevated Pole (i.e. pole chosen for the triangle) Angle P = D.Long from A to B (E or W) PA = Co Lat A PB = Co Lat B Equator
Vn
P
B
A
Vs Co Lat in the same hemisphere (90-Lat) Co lat in the opposite = hemisphere(90+Lat) SAK
Prime meridian 16
You may prefer to use the adjusted Marc St Hilaire
Formula Cos AB = Cos P x Cos Lat A x Cos Lat B ± Sin Lat A x Sin Lat B Vn
P
B
Equator
A
Vs (+ if A and B have same name) (- if A and B have different names) SAK
Prime meridian 17
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB) / (Sin PA x Sin AB) To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ (Sin PB x Sin AB) P
Vessel is sailing from A to B AB = distance PAB or angle A = initial course PBA or angle B = reciprocal of final SAK course
18
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing The principal advantage of calculating great circles this way is that once PA and PB have been
calculated, the rest can be left to the calculator and no ambiguity concerning sides or angles bigger or less than 90° will occur. When calculating spherical triangles it is best to convert all sides and angles into decimal angles. This can be done using the ° '" button on your calculator, or by dividing the minutes by 60. Always work to 3 decimal places of a degree when using decimal angles. SAK
19
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’
P
A
North elevated pole
PA = 90° – 34° 27’ PA = 55° 33’ B
Calculator Press 90 Press °’’’Press – Press 34 Press°’’’Press 27°’’’
SAK
20
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’ E North elevated pole PA = 90° – 34° 27’ PA = 55° 33’ = 55.55 PB = 90° + 41° 23’ PB = 131° 23’= 131.383
SAK
P
A
B
21
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’ E=105.733 PA = 55° 33’=55.55 PB = 131° 23’ = 131.383
P
A
B
Cos AB= Cos 105° 44’ x Sin 131° 23’ x Sin 55° 33’ + Cos 131° 23’ x Cos 55° 33’
Cos AB = - 0.541743104 Press shift Press cos Press Answer Press enter AB = 122.802 To convert degress Press shift Press °’’’ or Press °’’’ Press enter 122° 48’ 07”
Distance AB = 122.802 x 60 = 7368.1 mile. SAK
22
To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB) / (Sin PA x Sin AB) PA = 55° 33’ PB = 131° 23’ AB = 122° 48’ 07”
A
Becarefull when transferring the formula to the calculator! Use ( and ) or divide sin PA and Sin AB !
B
Initial course N 120.8 E so Course = 120.8 T To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ (Sin PB x Sin AB) Final course S 70.8 E = 109.2 T
SAK
23
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35° 10’ N – 120° 45’ W to P (B) Aucland 36° 51’ S – 174° 49’ E.
To find Dlong: 120° 45’+ 174° 49’ = Ans 360°- Ans = 64° 26’ E Dlong= 64° 26’ E = 64°.433 E
A
B
SAK
24
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 90° - 35°10’ = 54° 50’ PB = 90°+ 36° 51’=126° 51’ Distance = 93° 37’.1 x 60 AB = 5617.1 mile.
SAK
A
B
25
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A)California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 54° 50’ PB = 126° 51’ AB = 93° 37’.1 a = N 133.67 W Initial Course C = 226°.3 T
SAK
A
B
26
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ Sin PB x Sin AB P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 54° 50’ PB = 126° 51’ AB = 93° 37’.1 b = N 47.63 E Recip Co or Final Co = S 47.53 W C = 227.6° T SAK
A
B
27
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Vertex Maximum Latitude that the great circle reaches is known as the vertex. Vertex north and Vertex south
P
Vn B
Vs
A
The latitude of the vertex equals the angle between the great circle and the equator at the intersection of the great circle and the equator. SAK
28
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Vertex of a Great Circle The vertex of a great circle is the maximum latitude point
of the great circle. The vertex has the following properties: There is a maximum latitude point in both the northern and southern hemispheres; these points have the same value of latitude (eg if northern vertex = 40°N then southern vertex = 40°S). The longitudes of the vertices are 180° apart (e.g. if one is in 20°W, the other is in 160°E). At the vertex the course on the great circle is exactly 090°T or 270°T, depending on whether you are proceeding towards the east or the west. This means that the angle between the great circle and the meridian at the vertex is always 90°. SAK
29
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
<90
Vertex before the start position SAK
30
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
Vertex between the start and end position SAK
31
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
Vertex After the final Position
SAK
32
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing
Rule: A and B less than 90° vertex between A and B A bigger than 90° , vertex before the A. B bigger than 90° , vertex after the B.
SAK
33
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Position of the Vertex and use of Napier's Rules
The basic form of Napier's Rules is used to resolve the following: Finding the position of the vertex of a great circle Solving the great circle legs of a composite great circle
Resolving any other right angled spherical triangle, be it terrestrial or celestial SAK
34
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) PV = Polar distance of V = (90° - Lat of V) VA = Arc of great circle. P
Vertex
V A
SAK
35
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
1
PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) PV = Polar distance of V = (90° - Lat of V) VA = Arc of great circle. P
Vertex
5
2
6 6
4 3
2
A
SAK
V
1
5
3 4
36
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
1
To find Lat. of vertex We know; A = Initial course and PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) P
Vertex
5
2
6 6
4 3
2
A
SAK
V
1
5
3 4
37
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Sine of middle part = Product of Tan of Adjacent Parts
Sine of middle part = Product of Cos of Opposite Parts Sin PV = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Cosine of a complementary angle is its sine e.g. Cos Co 30° = Sin 30°
Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA Lat of vertex SAK
38
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Sin mid part = Product of tan of adjacents. Sin Co PA = Tan Co A x Tan Co P Cos PA = 1 / Tan A x 1/ Tan P Multiple by Tan P Tan p x Cos PA = 1/Tan A Tan P = 1 / (Tan A x Cos PA) This gives us P, the D.Long between A and V, and hence the longitude of V. SAK
39
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To find the position of the vertex you will first have to find the great circle initial course angle A. This
will be found by the cosine rule We will then know two parts of the triangle and can find any other part. The parts we know are Angle A and the Co-Latitude of A (PA). We need to find PV (when taken from 90°, PV will give the latitude of the vertex), and angle VPA (the D.long between A and V) which is applied to the known longitude of A to give the longitude of the vertex. SAK
40
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A vessel sails on a great circle from A 40° 00'N 50° 00'W to B 43° 00'N 015° 00'W. Find the initial
course and the position of the vertex.
SAK
41
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A vessel sails on a great circle from A 40° 00'N 50° 00'W to B 43° 00'N 015° 00'W. Find the initial
course and the position of the vertex. First find AB and initial course D.Long = 35° E = P PA = 50° PB = 47° Cos AB= Cos 35xSin47xSin50+Cos47xCos50 26° 11’ 36’’ AB=1571.6 mile SAK
42
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Initial course PA = 50° PB = 47° AB= 26° 11’ 36’’ Cos A = (Cos PB-Cos PAxCos AB)/(SinPAxSinAB) Course = N 71,87 E Course = 71,87° T
SAK
43
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules PA = 50°
P
PB = 47° AB= 26° 11’ 36’’
50
Initial Course = 71,87 T
71,87
Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA PV = 46,72= 46 43’ 12” Lat of vertex = 90- 46 43’ 12” Lat of vertex = 43° 16’ 48” N SAK
V
A
44
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Initial course P PA = 50° PB = 47° 50 AB= 26° 11’ 36’’ Course = 71,87 T 71,87 V Lat of vertex = 43° 16’ 48” N A Tan P = 1 / Tan A x Cos PA P = D.Long=26° 59’ 38” E Long of vertex = 50W- 26° 59’ 38” E=23° 00’ 22” W SAK
45
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Solution of right-angled spherical triangles to find
latitudes of intermediate points along great circle tracks. In practice, a GC route is approximated by following a succession of rhumb lines between points on the GC. We can use Napier's Rules to find these intermediate points.
SAK
46
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P PA = Co Lat A
PV = Co Lat V
LV L
V
A
We know PV and P (the D.long from V to longitude of L). We need to find PL, and hence Lat L. Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacents Sin Co P = Tan PV x Tan Co PL Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV Cos P = Tan PV x Tan Lat L Cos P / Tan PV = Tan Lat L SAK
47
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Wellington (A) 41° 38' S 175° 28'
E to Panama (B) 07°24'N 079° 55 'W Find also the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the great circle in longitude 140°W
SAK
48
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Wellington (A) 41° 38' S 175° 28'
E to Panama (B) 07°24'N 079° 55 'W Draw the sketch
SAK
49
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Draw the sketch B 7° 24'N
SAK
50
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = PB = P =
SAK
51
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 55 'W South elevated pole PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ = D.long= 104° 37’ E
Long A : 175° 28' E Long B : 079° 55 'W Dlong : 255 23 W 360 D.Long : 104° 37’ E
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA
AB = ? SAK
52
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ Cos AB = Cos 104 37x Sin 48 22 x Sin 97 24+Cos 48 22x Cos 97 24 AB=105.819*60=6349.2 mile=105° 49’ 10” SAK
53
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E; B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819°=6349.2 To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB
Initial course:
SAK
54
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819°
B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W
Course: Cos A= (Cos PB-CosPAxCosAB) / Sin PA x Sin AB A = 85.828 (angle) Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T
SAK
55
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T
Cos B= (Cos PA-CosPBxCosAB) / Sin PB x Sin AB A = 48.738 (angle) Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
SAK
56
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
SAK
57
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° A= S 85.8 E , B= N 48.7 E Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
Latitute of vertex: Sin Mid Part= Cos opposite parts Sin PV = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA Sin PV = Sin 85.828 x Sin 48° 22’ PV = 48.196° Lat V = 90-48.196 = 41.804 = 41 48.2 S SAK
58
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
Longitute of vertex: Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co PA = Tan Co A x Tan Co P Cos PA = 1 / Tan A x 1 / Tan P Tan P = 1 / (Tan A x Cos PA) P = 6.266° or 6° 15’ 57” Longitude of vertex = 175° 28'E + 6°15'.9E = 181°43'.9E or 178° 16'.1W Longitute : 178° 16’.1 W SAK
59
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To calculate the latitude of a point on the great circle in 140°W. In triangle VPL: The polar angle P is 178° 16.1 W - 140°W =38°16.6’ or 38.268 PV = 48.196° Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co P = Tan PV x Tan PL Cos P = Tan PV x (1/Tan Lat L) Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV Tan L = 0.70208 Lat of point is 35.072° or 35° 04'.3S in longitude 140° West SAK
60
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To calculate the latitude of a point on the great circle in 85°W In triangle VPL: The polar angle P is 178° 16MW-85°W = 93° 16'.1 or 93.268° PV = 48.196° Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV = 0.05098 Lat of point is-2.918° S =2.918°N =2° 55’.1 N in longitude 85°W (- sign means go to the opposite latitude from the pole used in the calculation.)
SAK
61
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Dondra Head, South of Sri Lanka 05° 48' N 80° 36' E to Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia 34° 26' S 115° 04' E. Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 100°E
SAK
62
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test P A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E A PA=90- 05° 48‘N = 84° 12’ PB=90+34° 26'S = 124° 26’ D.Long= 115° 04' E- 80° 36' E =34° 28’ E or 34.467
B
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA
AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile
SAK
63
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=90- 05° 48‘N = 84° 12’ A PB=90+34° 26'S = 124° 26’ D.Long= 115° 04' E- 80° 36' E =34° 28’ E or 34.467 AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile
P
B
To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB
A=N143.5E Course= 143.5 T SAK
64
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ A D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.5E Course= 143.5 T
P
B
To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ Sin PB x Sin AB B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T
SAK
65
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 V AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.5E Inital Course= 143.5 T B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T Where is vertex?
SAK
P
A
B
66
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 V AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.52E Inital Course= 143.5 T B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T pAv=180-143.52=36.48
P
A
AV
B
PV
pAv ☺
vPa PA
☺ SAK
67
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test 2. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Fastnet Island 51°16'N 9° 3 6 'W to Mona age 18°28'N 67° 3 2 ' W .Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 20°W 3. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Strait of Magellan 52° 23' S 68° 18' W to Cape Town 33° 53'S 18° 2 0 ' E. Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 0°E 4. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Durban 29° 53'S 31° 0 4 ' E to Fremantle 32° 04'S 115° 2 6 ' E Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 100°E SAK
68
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing It is not always possible or desirable to travel along a great circle for some of the following reasons.
The great circle track may through high latitudes where weather is likely to be rough and the ship may encounter large waves and swell. The great circle track may over land. The saving of distance is small in low latitudes, or
if the course is nearly north/south. A great circle track may take the ship into head winds and adverse currents. SAK
69
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Composite great circle sailing means travelling between two places by the shortest route with the restriction of not going north or south of a limiting latitude. P
V1
A
V2
B SAK
70
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts or Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposite Parts
V1
P
A
To find the longitude of V, by finding D.long 'P' Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co P = Tan PV1 x Tan Co PA Cos P = Tan PV1 / Tan PA SAK
71
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Similarly, in the second triangle:
Cos P = Tan PV2 / Tan PB to find the longitude of V2
SAK
72
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing To find initial course A
Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposites Sin PV1 = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Sin PV1 = Sin A x Sin PA Sin A = Sin PV1 / Sin PA
SAK
73
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing To find distance AV Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposites Sin Co PA = Cos PV1 x Cos AV1 Cos PA = Cos PV1 x Cos AV1
Cos AV1 = Cos PA / Cos PV1
SAK
74
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing-Example Find the distance from Durban to Fremantle by composite great circle course using 35° S as the,
limiting latitude. Find also the initial and final courses.
SAK
75
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Find the distance from Durban to Fremantle by composite great circle course using 35° S as the, limiting latitude. Find also the initial and final courses.
A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
76
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
77
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
78
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
79
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
80
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
81
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
82
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
83
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
84
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
85
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
86
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
87
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
88
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
89
GREAT CIRCLE SAILING Lindbergh Chart of the Great circle sailing chart of the North Atlantic Ocean 1926 SAK
1
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing A great circle is a circle which cuts the a sphere into two equal halves and its centre is coincident with the centre of the sphere.
SAK
2
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Plane ing through centre of the sphere
Great circle
SAK
3
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing The equator is a great circle. A Great circles cross the equator at two points 180° apart. All longitutes are great circle.
SAK
4
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing
SAK
5
SAK
6
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P
Show the great circles
SAK
7
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing PA, PB, AB is an arc of Great circle PAB is an spherical triangle O is the centre of the sphere The lenght of side AB is angle AOB Angle O is not equal to angle P
P
O
B
A
SAK
8
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P=Elevated Pole (i.e. pole chosen for the triangle) Angle P=D.Long from A to B (E or W)
B
Equator Side PB = Angular distance of B from the Elevated Pole 'B'
SAK
Vn
P
Side PA=Angular distance of A from the Elevated Pole 'P'. For example if elevated pole is North Pole and A is in north latitude then PA = 90°-LAT A. If elevated pole is North Pole and A is in south latitude then PA = 90° +LAT A. A
Vs Prime meridian 9
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing North elevated pole
SAK
11
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing North elevated pole
P
The elevated pole chosen can be in either hemisphere. SAK
12
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Equator South elevated pole
PB=90-Lat B
SAK
13
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing South elevated pole A
SAK
14
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing South elevated pole
SAK
15
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA P is Elevated Pole (i.e. pole chosen for the triangle) Angle P = D.Long from A to B (E or W) PA = Co Lat A PB = Co Lat B Equator
Vn
P
B
A
Vs Co Lat in the same hemisphere (90-Lat) Co lat in the opposite = hemisphere(90+Lat) SAK
Prime meridian 16
You may prefer to use the adjusted Marc St Hilaire
Formula Cos AB = Cos P x Cos Lat A x Cos Lat B ± Sin Lat A x Sin Lat B Vn
P
B
Equator
A
Vs (+ if A and B have same name) (- if A and B have different names) SAK
Prime meridian 17
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB) / (Sin PA x Sin AB) To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ (Sin PB x Sin AB) P
Vessel is sailing from A to B AB = distance PAB or angle A = initial course PBA or angle B = reciprocal of final SAK course
18
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing The principal advantage of calculating great circles this way is that once PA and PB have been
calculated, the rest can be left to the calculator and no ambiguity concerning sides or angles bigger or less than 90° will occur. When calculating spherical triangles it is best to convert all sides and angles into decimal angles. This can be done using the ° '" button on your calculator, or by dividing the minutes by 60. Always work to 3 decimal places of a degree when using decimal angles. SAK
19
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’
P
A
North elevated pole
PA = 90° – 34° 27’ PA = 55° 33’ B
Calculator Press 90 Press °’’’Press – Press 34 Press°’’’Press 27°’’’
SAK
20
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’ E North elevated pole PA = 90° – 34° 27’ PA = 55° 33’ = 55.55 PB = 90° + 41° 23’ PB = 131° 23’= 131.383
SAK
P
A
B
21
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA Lat A = 34° 27’ N Lat B = 41° 23’ S D.Long = 105° 44’ E=105.733 PA = 55° 33’=55.55 PB = 131° 23’ = 131.383
P
A
B
Cos AB= Cos 105° 44’ x Sin 131° 23’ x Sin 55° 33’ + Cos 131° 23’ x Cos 55° 33’
Cos AB = - 0.541743104 Press shift Press cos Press Answer Press enter AB = 122.802 To convert degress Press shift Press °’’’ or Press °’’’ Press enter 122° 48’ 07”
Distance AB = 122.802 x 60 = 7368.1 mile. SAK
22
To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB) / (Sin PA x Sin AB) PA = 55° 33’ PB = 131° 23’ AB = 122° 48’ 07”
A
Becarefull when transferring the formula to the calculator! Use ( and ) or divide sin PA and Sin AB !
B
Initial course N 120.8 E so Course = 120.8 T To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ (Sin PB x Sin AB) Final course S 70.8 E = 109.2 T
SAK
23
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing-Example Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35° 10’ N – 120° 45’ W to P (B) Aucland 36° 51’ S – 174° 49’ E.
To find Dlong: 120° 45’+ 174° 49’ = Ans 360°- Ans = 64° 26’ E Dlong= 64° 26’ E = 64°.433 E
A
B
SAK
24
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 90° - 35°10’ = 54° 50’ PB = 90°+ 36° 51’=126° 51’ Distance = 93° 37’.1 x 60 AB = 5617.1 mile.
SAK
A
B
25
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A)California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 54° 50’ PB = 126° 51’ AB = 93° 37’.1 a = N 133.67 W Initial Course C = 226°.3 T
SAK
A
B
26
Find the initial and final course and total distance from; (A) California 35 10 N – 120 45 W to (B) Aucland 36 51 S – 174 49 E. To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ Sin PB x Sin AB P
P = 64° 26’ PA = 54° 50’ PB = 126° 51’ AB = 93° 37’.1 b = N 47.63 E Recip Co or Final Co = S 47.53 W C = 227.6° T SAK
A
B
27
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Vertex Maximum Latitude that the great circle reaches is known as the vertex. Vertex north and Vertex south
P
Vn B
Vs
A
The latitude of the vertex equals the angle between the great circle and the equator at the intersection of the great circle and the equator. SAK
28
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Vertex of a Great Circle The vertex of a great circle is the maximum latitude point
of the great circle. The vertex has the following properties: There is a maximum latitude point in both the northern and southern hemispheres; these points have the same value of latitude (eg if northern vertex = 40°N then southern vertex = 40°S). The longitudes of the vertices are 180° apart (e.g. if one is in 20°W, the other is in 160°E). At the vertex the course on the great circle is exactly 090°T or 270°T, depending on whether you are proceeding towards the east or the west. This means that the angle between the great circle and the meridian at the vertex is always 90°. SAK
29
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
<90
Vertex before the start position SAK
30
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
Vertex between the start and end position SAK
31
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing Sailing A to B
Vertex After the final Position
SAK
32
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing
Rule: A and B less than 90° vertex between A and B A bigger than 90° , vertex before the A. B bigger than 90° , vertex after the B.
SAK
33
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Position of the Vertex and use of Napier's Rules
The basic form of Napier's Rules is used to resolve the following: Finding the position of the vertex of a great circle Solving the great circle legs of a composite great circle
Resolving any other right angled spherical triangle, be it terrestrial or celestial SAK
34
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) PV = Polar distance of V = (90° - Lat of V) VA = Arc of great circle. P
Vertex
V A
SAK
35
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
1
PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) PV = Polar distance of V = (90° - Lat of V) VA = Arc of great circle. P
Vertex
5
2
6 6
4 3
2
A
SAK
V
1
5
3 4
36
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
1
To find Lat. of vertex We know; A = Initial course and PA = Polar distance of A = (90° - Lat of A) P
Vertex
5
2
6 6
4 3
2
A
SAK
V
1
5
3 4
37
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Sine of middle part = Product of Tan of Adjacent Parts
Sine of middle part = Product of Cos of Opposite Parts Sin PV = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Cosine of a complementary angle is its sine e.g. Cos Co 30° = Sin 30°
Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA Lat of vertex SAK
38
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Sin mid part = Product of tan of adjacents. Sin Co PA = Tan Co A x Tan Co P Cos PA = 1 / Tan A x 1/ Tan P Multiple by Tan P Tan p x Cos PA = 1/Tan A Tan P = 1 / (Tan A x Cos PA) This gives us P, the D.Long between A and V, and hence the longitude of V. SAK
39
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To find the position of the vertex you will first have to find the great circle initial course angle A. This
will be found by the cosine rule We will then know two parts of the triangle and can find any other part. The parts we know are Angle A and the Co-Latitude of A (PA). We need to find PV (when taken from 90°, PV will give the latitude of the vertex), and angle VPA (the D.long between A and V) which is applied to the known longitude of A to give the longitude of the vertex. SAK
40
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A vessel sails on a great circle from A 40° 00'N 50° 00'W to B 43° 00'N 015° 00'W. Find the initial
course and the position of the vertex.
SAK
41
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A vessel sails on a great circle from A 40° 00'N 50° 00'W to B 43° 00'N 015° 00'W. Find the initial
course and the position of the vertex. First find AB and initial course D.Long = 35° E = P PA = 50° PB = 47° Cos AB= Cos 35xSin47xSin50+Cos47xCos50 26° 11’ 36’’ AB=1571.6 mile SAK
42
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Initial course PA = 50° PB = 47° AB= 26° 11’ 36’’ Cos A = (Cos PB-Cos PAxCos AB)/(SinPAxSinAB) Course = N 71,87 E Course = 71,87° T
SAK
43
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules PA = 50°
P
PB = 47° AB= 26° 11’ 36’’
50
Initial Course = 71,87 T
71,87
Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA PV = 46,72= 46 43’ 12” Lat of vertex = 90- 46 43’ 12” Lat of vertex = 43° 16’ 48” N SAK
V
A
44
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Initial course P PA = 50° PB = 47° 50 AB= 26° 11’ 36’’ Course = 71,87 T 71,87 V Lat of vertex = 43° 16’ 48” N A Tan P = 1 / Tan A x Cos PA P = D.Long=26° 59’ 38” E Long of vertex = 50W- 26° 59’ 38” E=23° 00’ 22” W SAK
45
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Solution of right-angled spherical triangles to find
latitudes of intermediate points along great circle tracks. In practice, a GC route is approximated by following a succession of rhumb lines between points on the GC. We can use Napier's Rules to find these intermediate points.
SAK
46
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing P PA = Co Lat A
PV = Co Lat V
LV L
V
A
We know PV and P (the D.long from V to longitude of L). We need to find PL, and hence Lat L. Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacents Sin Co P = Tan PV x Tan Co PL Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV Cos P = Tan PV x Tan Lat L Cos P / Tan PV = Tan Lat L SAK
47
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Wellington (A) 41° 38' S 175° 28'
E to Panama (B) 07°24'N 079° 55 'W Find also the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the great circle in longitude 140°W
SAK
48
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Wellington (A) 41° 38' S 175° 28'
E to Panama (B) 07°24'N 079° 55 'W Draw the sketch
SAK
49
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules Draw the sketch B 7° 24'N
SAK
50
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = PB = P =
SAK
51
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 55 'W South elevated pole PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ = D.long= 104° 37’ E
Long A : 175° 28' E Long B : 079° 55 'W Dlong : 255 23 W 360 D.Long : 104° 37’ E
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA
AB = ? SAK
52
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ Cos AB = Cos 104 37x Sin 48 22 x Sin 97 24+Cos 48 22x Cos 97 24 AB=105.819*60=6349.2 mile=105° 49’ 10” SAK
53
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E; B =07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819°=6349.2 To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB
Initial course:
SAK
54
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819°
B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W
Course: Cos A= (Cos PB-CosPAxCosAB) / Sin PA x Sin AB A = 85.828 (angle) Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T
SAK
55
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T
Cos B= (Cos PA-CosPBxCosAB) / Sin PB x Sin AB A = 48.738 (angle) Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
SAK
56
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules
SAK
57
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° A= S 85.8 E , B= N 48.7 E Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
Latitute of vertex: Sin Mid Part= Cos opposite parts Sin PV = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Sin PV = Sin A x Sin PA Sin PV = Sin 85.828 x Sin 48° 22’ PV = 48.196° Lat V = 90-48.196 = 41.804 = 41 48.2 S SAK
58
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules A =41° 38' S 175° 28' E ; B=07°24'N 079° 5 5 'W PA = 48° 22’ PB = 97° 24’ P = 104° 37’ AB=105° 49’ 10”=105.819° Intial course = S 85.8 E = 180-85.8= 094.2 T Final course= N 48.7 E= 048.7 T
Longitute of vertex: Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co PA = Tan Co A x Tan Co P Cos PA = 1 / Tan A x 1 / Tan P Tan P = 1 / (Tan A x Cos PA) P = 6.266° or 6° 15’ 57” Longitude of vertex = 175° 28'E + 6°15'.9E = 181°43'.9E or 178° 16'.1W Longitute : 178° 16’.1 W SAK
59
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To calculate the latitude of a point on the great circle in 140°W. In triangle VPL: The polar angle P is 178° 16.1 W - 140°W =38°16.6’ or 38.268 PV = 48.196° Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co P = Tan PV x Tan PL Cos P = Tan PV x (1/Tan Lat L) Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV Tan L = 0.70208 Lat of point is 35.072° or 35° 04'.3S in longitude 140° West SAK
60
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Napier's Rules To calculate the latitude of a point on the great circle in 85°W In triangle VPL: The polar angle P is 178° 16MW-85°W = 93° 16'.1 or 93.268° PV = 48.196° Tan Lat L = Cos P / Tan PV = 0.05098 Lat of point is-2.918° S =2.918°N =2° 55’.1 N in longitude 85°W (- sign means go to the opposite latitude from the pole used in the calculation.)
SAK
61
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Dondra Head, South of Sri Lanka 05° 48' N 80° 36' E to Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia 34° 26' S 115° 04' E. Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 100°E
SAK
62
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test P A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E A PA=90- 05° 48‘N = 84° 12’ PB=90+34° 26'S = 124° 26’ D.Long= 115° 04' E- 80° 36' E =34° 28’ E or 34.467
B
To find distance AB: Cos AB = Cos P x Sin PB x Sin PA + Cos PB x Cos PA
AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile
SAK
63
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=90- 05° 48‘N = 84° 12’ A PB=90+34° 26'S = 124° 26’ D.Long= 115° 04' E- 80° 36' E =34° 28’ E or 34.467 AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile
P
B
To find initial course A; Cos A = (Cos PB - Cos PA x Cos AB )/ Sin PA x Sin AB
A=N143.5E Course= 143.5 T SAK
64
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ A D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.5E Course= 143.5 T
P
B
To find final course – reciprocal of B; Cos B = (Cos PA - Cos PB x Cos AB )/ Sin PB x Sin AB B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T
SAK
65
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 V AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.5E Inital Course= 143.5 T B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T Where is vertex?
SAK
P
A
B
66
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test A=05° 48' N 80° 36' E ; B= 34° 26' S 115° 04' E PA=84° 12’ PB= 124° 26’ D.Long=34° 28’ E or 34.467 V AB=51.729°=x60=3103.7 mile A=N143.52E Inital Course= 143.5 T B=45.817° Final course=S45.817°E or 134.2° T pAv=180-143.52=36.48
P
A
AV
B
PV
pAv ☺
vPa PA
☺ SAK
67
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Great circle sailing- Self assessment test 2. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Fastnet Island 51°16'N 9° 3 6 'W to Mona age 18°28'N 67° 3 2 ' W .Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 20°W 3. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Strait of Magellan 52° 23' S 68° 18' W to Cape Town 33° 53'S 18° 2 0 ' E. Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 0°E 4. Find the great circle distance and the initial and final courses from Durban 29° 53'S 31° 0 4 ' E to Fremantle 32° 04'S 115° 2 6 ' E Find the position of the vertex and the latitude of a point on the track in longitude 100°E SAK
68
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing It is not always possible or desirable to travel along a great circle for some of the following reasons.
The great circle track may through high latitudes where weather is likely to be rough and the ship may encounter large waves and swell. The great circle track may over land. The saving of distance is small in low latitudes, or
if the course is nearly north/south. A great circle track may take the ship into head winds and adverse currents. SAK
69
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Composite great circle sailing means travelling between two places by the shortest route with the restriction of not going north or south of a limiting latitude. P
V1
A
V2
B SAK
70
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts or Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposite Parts
V1
P
A
To find the longitude of V, by finding D.long 'P' Sin Mid Part = Tan Adjacent Parts Sin Co P = Tan PV1 x Tan Co PA Cos P = Tan PV1 / Tan PA SAK
71
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Similarly, in the second triangle:
Cos P = Tan PV2 / Tan PB to find the longitude of V2
SAK
72
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing To find initial course A
Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposites Sin PV1 = Cos Co A x Cos Co PA Sin PV1 = Sin A x Sin PA Sin A = Sin PV1 / Sin PA
SAK
73
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing To find distance AV Sin Mid Part = Cos Opposites Sin Co PA = Cos PV1 x Cos AV1 Cos PA = Cos PV1 x Cos AV1
Cos AV1 = Cos PA / Cos PV1
SAK
74
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing-Example Find the distance from Durban to Fremantle by composite great circle course using 35° S as the,
limiting latitude. Find also the initial and final courses.
SAK
75
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing Find the distance from Durban to Fremantle by composite great circle course using 35° S as the, limiting latitude. Find also the initial and final courses.
A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
76
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
77
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
78
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
79
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
80
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
81
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing A
Lat: 29 53 S
Long: 31 04 E
PA=60 07
PA=60.117
B
Lat: 32 04 S
Lonf: 115 26 E
PB=57 56
PA=57.933
D.Long
84 22 E
PV=55
PV=55.000
SAK
82
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
83
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
84
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
85
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
86
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
87
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
88
DECK 122 (NAVIGATION-II) Composite GC sailing
SAK
89