Big Ati 1r6d2j
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Big Ati as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 27,287
- Pages: 73
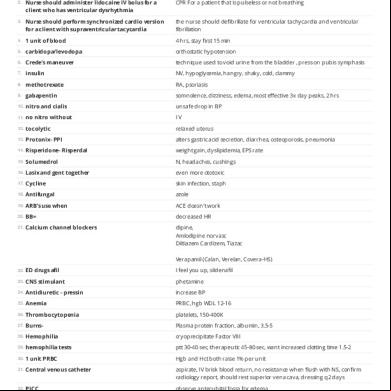
ATI: NCLEX Live Review Study online at quizlet.com/_253wzq 1.
bronchdilator
hyperglycemia, hypoK
2.
Nurse should ister lidocaine IV bolus for a client who has ventricular dysrhythmia
R For a patient that is pulseless or not breathing
3.
Nurse should perform synchronized cardio version for a client with supraventricular tacycardia
the nurse should defibrillate for ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation
4.
1 unit of blood
4 hrs, stay first 15 min
5.
carbidopa/levodopa
orthostatic hypotension
6.
Crede's maneuver
technique used to void urine from the bladder , press on pubis symphasis
7.
insulin
NV, hypoglycemia, hangry, shaky, cold, clammy
8.
methotrexate
RA, psoriasis
9.
gabapentin
somnolence, dizziness, edema, most effective 3x day peaks, 2 hrs
10.
nitro and cialis
unsafe drop in BP
11.
no nitro without
IV
12.
tocolytic
relaxed uterus
13.
Protonix- PPI
alters gastric acid secretion, diarrhea, osteoporosis, pneumonia
14.
Risperidone- Risperdal
weight gain, dyslipidemia, EPS rate
15.
Solumedrol
N, headaches, cushings
16.
Lasix and gent together
even more ototoxic
17.
Cycline
skin infection, staph
18.
Antifungal
azole
19.
ARB's use when
ACE doesn't work
20.
BB=
decreased HR
21.
Calcium channel blockers
dipine, Amlodipine norvasc Diltiazem Cardizem, Tiazac Verapamil (Calan, Verelan, Covera-HS)
22.
ED drugs afil
I feel you up, sildenafil
23.
CNS stimulant
phetamine
24.
Antidiuretic - pressin
increase BP
25.
Anemia
PRBC, hgb WDL 12-16
26.
Thrombocytopenia
platelets, 150-400K
27.
Burns-
Plasma protein fraction, albumin, 3.5-5
28.
Hemophilia
cryoprecipitate Factor VIII
29.
hemophilia tests
ptt 30-40 sec, therapeutic 45-80 sec, want increased clotting time 1.5-2
30.
1 unit PRBC
Hgb and Hct both raise 1% per unit
31.
Central venous catheter
aspirate, IV brisk blood return, no resistance when flush with NS, confirm radiology report, should rest superior vena cava, dressing q2 days
32.
PICC
observe antecubital fossa for edema
33.
Triple lumen
1 meds, 1 blood draw etc, complications- pneumothorax, air embolism
34.
triple lumen dwelling complications
occlusion, infection
35.
TPN
change tubing q 24 hrs, dc lipid infusion after 12 hrs, clean iv port before and after
36.
insulin given via IV
regular
37.
DI
ADH deficient, polyuria, can give desmopressin intranasally
38.
Lantus
glargine, lonely lantus doesn't play well with others
39.
another word for A1C
glycosylated hgb
40.
inject 10U reg then 20U NPH
roll nph, clean stoppers, inject 20U air into NPH, inject 10U air into regular, WD 10U reg, then 20U NPH
41.
lanoxin, digoxin
hypoK
42.
Ambien, zolpidem
caution in elderly, opposite effect
43.
MMR hold
allergy to gelatin or neomycin
44.
RH - mom
28 wks, 72h rs after birth rogham, baby should be RH +
45.
methylergonovine (Methergin)
stop contraction, hemorrhage
46.
aqua mephton
vit K
47.
statin take
at night
48.
glucophage / metformin
increase lactic acid levels
49.
glucocorticoid
osteoporitis, cushings, puffy moon face
50.
addison's
high and dry, hypoglycemia, dehydration, bronze skin
51.
budesonide formsterol
prevent asthma, COPD, GI upset, infection
52.
levothyroxine synthroid
take 30 min before breakfast
53.
flagyl and vancomycin
cdiffe
54.
give vanc and gent
over 1 hr
55.
fentanyl
duragesic, change 72 hrs, no heat over site
56.
lithium
0.6-1.2, fine tremors are normal, increase salt, thirst s/s toxicity, lithium and salt compete for binding sites
57.
Clozapine- clozaril
2nd gen antipsychotic, agranulocytosis- dangerously low WBC, constipation, othro Hypotn
58.
typical antispsychotic
SEATANS- sedation, EPS, antocholinergic, tradive dyskinesia, agranulocytosis, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, seizures
59.
atypical like clozaril
decrease risk of eps, weight gain, diabetes, dyslipidemia, agrnaulocytosis, ortho htn
60.
benzo od
romazicon flumazenil
61.
avoid tyramine with MAOI
phenelzine or Nardil
62.
tyramine food
bacon eggs liver, pepperoni, bologna, sausage, pickeld herring, anchovies, shrimp, caviar, yeast, chocolate, alcoholic drinks
63.
tyramine problems
hypertensive crisis, foods are pickled, aged, smoked, fermented, marinated
64.
new trach at bedside
bag valve, 20 set up, suction, two trach tubes
65.
weak legs
hypoK
66.
chron's
corticosteriods, cobblestone
67.
HHNS hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketonic syndrom
> 600 CBG, dehydration, low grade temp, confusion, headaches
68.
normal IOP
10-21
69.
Ulcerative colitis
starts @ rectum, increased risk cancer, more women than meb
70.
PVD
painless ulceration
71.
HyperK
peaked tented T- wave
72.
Cane COAL
cane opposite affected limb, cane stron side
73.
radiation
visitors 6 ft, 30 min day, sign on door, educate r/t isolation, save linens in room
74.
propofol milk of anesthesia
allergy to eggs pharm
75.
vaccines
don't give if egg allergy
76.
brudinskis sign
lay down, tilt neck chich to chest, makes knee/hip flex
77.
Kernigs sign
lay down bend knee AT 90 angle, can't straighten leg, hamstring tight, pain
78.
meningitis
headache, stiff neck, photophobia, seizure precautions, private room, dehydration
79.
test to see if amnio fluid or pee
fern or nitrizine test
80.
smallpox
, face to face, body fluids, aerosol, dever, red spot tongue, rash, most contagious
81.
sepsis
vascular changes, resp compromise, renal, CNS
82.
neonatal sepsis
low ax temp, lethargy, poor suck reflex
83.
nits
lindane no longer used, pretherin creme
84.
ED
can cause MI blood pools in penis
85.
external/internal hemmrhoid
streaks in stool
86.
3rd degree heart block
p & QRS not related
87.
problem after prolonged vomiting
hypoK
88.
parkland formula
4xkgxTBSA, 1st 1/2 in 8 hrs, rest remainint 16 hrs, deduct what previously given and look at time
89.
assess buttocks in traction
never side to side, lift buttocks
90.
AV fistula
use after several weeks, BP in opposite arm, feel thrill no heavy carrying
91.
metabolic imbalance
usually throwing up diarrhea
92.
abrupto placentia
rigid abdomen
93.
mastitis
keep feeding affected side
94.
serotonin antagonist- serotonin tron to the rescue
dolasetron, ondansetron
95.
Continuous bubbling in water seal chamber
means there is a leak
96.
Bubbling in suction chamber
means suction is working
97.
NEURO
...
98.
closed head injury
possible csf leak (yellow ring around a clear moist area seen on pillow)
99.
closed head injury with increaed I
instruct client to exhale when turning and moving in bed
100.
head trauma develops increased I
do this first-hyperventilate the pt(CO2 increased I-this will decrease CO2 and I) -trendelenburg position will increase I-not a good position
101.
subdural hematoma, reduce the I interventions
30 degrees semi fowler, trendelenburg contraindicated
102.
concussion discharge education
call dr if repeated episodes of vomiting occur-sign of I going up no dietary restrictions no activity restrictions unless HA develops for pain, can give acetaminophen, but not sedating drugs
103.
pt taking antipsychotic drugs develops NMS
early sign of this: muscle stiffness, fever, sweating, tremors late signs: dysphagia, unstable BP, respiratory depression -this is an emergency
104.
pt scheduled for CT scan
tell pt that he might experience slight discomfort not exposed to magnetic field
105.
post frontal craniotomy interventions
watch for increased I fluids restricted to 1-2 L per day space out activities, don't cluster provide Oxygen at 2 LPM-will prevent hypoxia which can lead to cerebral edema give Dexamethasone-reduce or prevent cerebral edema raise HOB at 30 degrees don't place in trendelenburg-can cause too much blood flow to the brain
106.
spinal cord injury-bladder management
urinate on a timed schedule, encourage fluids, no need to avoid carbonated drinksthey can have these
107.
suspected spinal cord injury, unconscious
avoid using chin-tilt maneuver during r r-2 breaths for q 30 compressions
108.
complete C7 transection
plan of care might include ventilatory lesions above C6-risk of respiratory paralysis C1-C8 injury-risk of quadriplegia
109.
stroke pt with L side weakness, in order to avoid disuse syndrome
use boots to prevent foot drop, assist pt with ive and active ROM,
110.
stroke major risk factor
hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, nonvalvular Afib
111.
MRI contraindication
pacemaker, cerebral aneurysm clips, metal implants, orthopedic hardware, intrauterine devices, pacemaker, internal surgical clips remove jewelry before give a mild sedative before, if pt is claustrophobic
112.
Myasthenia Gravis
fluctuating muscle weakness that worsens with effort and improves with rest weakness fatigue drooling ptosis oropharyngeal weakness have suction ready ister Pyridostigmine airway clearance-primary attention
113.
Parkinson
give Carbidopa/Levodopa semisolid, thickened food small frequent feedings bath bars recommended ROM and posture exercises
114.
Acute Bacterial Meningitis
complications: hearing impairment, photophobia-put pt in a dim light room no specific diet s/s: HA, fever, nuchal rigidity, altered mental status rapid onset-develops oper hrs to 2 days droplet precautions start to on empiric antimicrobial therapy asap
115.
Meningitis
altered cerebral perfusion from I and inflammation provide care for high I, seizures and hyperthermia fever HA nuchal rigidity Kernig's sign Brudzinski's sign-flexion of the hip and knee in response to forward flexion of the neck opisthotonos -no seizures
116.
infratentorial craniotomy for a brain tumor
keep HOB flat place a small pillow under the nape of the patient's neck to promote venous return and reduce I post any craniotomy monitor q 30 min for neuro check don't flex the neck post procedure-strict I&O maintained, strict fluid intake fluids at 175 ml/hr too much
117.
infratentorial craniotomy
elevate HOB at 30-45 degrees
118.
sustained severe brain injury
interventions are to maintain a low I elevate HOB relaxing atmosphere limit suction don't cluster activities don't discuss pt status at bed side
119.
MS
double vision visual loss impaired sensation mood swings impaired motor function and cerebellar function impaired urination male-sexual impotence weakness numbness of hands fatigue tremors s/s worsening over the past several months nystagmus scanning speech ataxia muscular weakness incontinence common between 20-40 yrs old women
120.
MS discharge instructions
exposure to heat and cold can exacerbate symptoms teach how to avoid fatigue, infections no restrictions in diet, just eat nutritious well balanced meals hard exercise not recommended but physical therapy yes it is recommended failure to store in bladder or failure to empty bladder-common problems constipation-most common bowel complaint
121.
MS manifestations
urinary retention hyperreflexia of the extremities intestinal obstruction ataxia decreased concentration constipation
122.
ALS
muscle weakness atrophy fasciculations dysphagia spasticity of the flexor muscles
123.
Parkinson's
mask like appearance to the face drooling slow speech shuffling gate
124.
GBS
risk for respiratory muscles weakness-paralysis
125.
Bell's palsy
7th cranial nerve priority: assess for pain experience soft diet apply an eye shield over the affected eye-corneal abrasion with Bell's Palsy
126.
trigeminal neuralgia
nerve V
127.
swallowing and speaking
nerve X
128.
facial muscle movement and taste
VII
129.
brain tumor
HA, vomiting, papiledema, seizures, changes in mental status, altered vision
130.
encephalitis
HA, fever, vomiting, menigeal signs
131.
cerebral arteriogram (angiogram of the blood vessels of the brain) (femoral artery access)
pt just came back, interventions: pressure dressing over the site for 4 hrs at least flat for 4 to 24 hrs, bed rest keep the affected extremity straight and immobilized 6 to 8 hrs before-NPO assess for weak pulses after give fluids to excrete dye
132.
lumbar puncture
lie flat after procedure for 4-6 hrs, depends on facility
133.
CN II (optic nerve) assessment
use a Snellen chart
134.
CN III-oculomotor, IV-trochlear and VI-abducens assessment
use penlight,note for nystagmus
135.
CN V (trigeminal nerve) assessment
corneal reflex
136.
CN VIII (acoustic nerve)
Weber test and Rinne test-assess conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
137.
cerebellar and vestibular function
Romberg test
138.
visual acuity
Rosenbaun test
139.
Tonometry
measures intraocular pressure
140.
Glascow Coma Scale
eye opening, motor response, verbal response coma=8 or less lowest score is 3=deep coma 15=perfect score
141.
head injury pt, in order to monitor hypothalamic function
assess urinary output and temperature
142.
brainstem
control of heart rate/ HR, resp rate/ RR
143.
TIA
temporary loss of cognitive function that will probably resolve warning sign of impending CVA brief period of neurologic deficit such as loss of vision, hemiparesis and slurred speech does not have long term neurologic deficits
144.
CVA
may cause long term deficits
145.
Meniere's disease
vertigo tinnitus hearing loss inner ear affected
146.
Acoustic neuroma
unilateral involvement progress without improvement
147.
MATERNITY/OB
...
148.
Carboprost
used in OB bleeding don't give in asthma-contraindicated AE-wheezing
149.
INFECTIOUS
...
150.
airborne
tb, rubeola, chickenpox, varicella door closed negative air pressure room mask-N95
151.
droplet
larger than 5 mcg door can remain open,the droplets are larger so they don't spread face mask for nurse distance between client and family pneumonia, meningococal meningitis
152.
wound infection-like MRSA Cdif RSV-young children secretions are not contained in these infections private room clean gloves when entering room if with surfaces in room-wear gown keep equipment in room
153.
chickenpox children
airborne, direct 2 days before rash appears they are contagious keep nails short no aspirin in kids
154.
rubella
droplet isolate these kids from pregnant women antipyretics and analgesics if its congenital rubella (newborn)--until 12 months old or until negative swabs at 3 months of age
155.
mononucleosis
flu like fever sore throat lymph nodes enlarged avoid with saliva 3 months adolescents risk for rupture spleen-no sports-danger of ruptured spleen
156.
tonsilitis
from strep infection->(risk for glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever) antibiotics
157.
TB
airborne-less than 5 mcg fatigue anorexia nightsweats low grade fever sputum purulent dyspnea x ray man 2 test/ppd-48-72 hrs induration (area hard, you feel the edges around it; greater than 10-pozitive-exposed and infected) immuncompromised patients-greater than 5-pozitive quatiferon tb gold-blood test-fater than sputum cultures-within 24 hrs results available-treatment earlier isolated 2-4 weeks if inpatient-isolated cannot work, isolated health dept notified teaching important dont isolate from family-impossible, already exposed, they should be tested and treated if necessary -teach to cover mouth when coughing and how to dispose tissues full range of meds-don't stop 3 negative sputum tests=go back to work Ethambutol Pyrazinamide-given to shorten treatment to 6 months assess for SE-client might stop meds-assess for nausea (take at night)
158.
Hepatitis
acute inflamatory jaundice RUQ pain tea color urine light color stool elevated ALT and AST A-fecal oral route, contaminated water or food B-parenteral, sexual C-bodily fluids mild or severe symptoms flu like symptoms rest liver to encourage regeneration, rest as much as possible, dont stop activities, but rest or standard precautions high carbs diet moderate fats and protein no alcohol careful with meds-break down in liver A-no treatment, just hand washing, their own towels no meds given, but in B,C-antivirals given
159.
Lyme
erythematous lesion-bulls eye flu like symtoms stage 2-cardiac and neuro problems stage 3-large t problems 3-4 weeks antibiotics
160.
syphillis
cupper color rash spread, mucus membranes congenital in baby Penicillin
161.
gonorrhea
thick disharge many times no symptoms in females-PID-sterility doxycycline, rocemphin
162.
genital herpes
painful vesicular genital lesions after outbreak, virus still there in skin, can reoccur with stress, menses spread to infants no vaginal birth sitz bath acyclovir-dont treat the virus, just decreases course pap spears oral antibiotics no sex-while lesions present use condoms in between
163.
chalamydia
urethritis-men thich discarge, odor-women mucus membrane Doxycycline
164.
Hiv
aids-from deffective immune system from opportunistic infection: sarcoma contaminated blood or needles sexual placental transmission breast milk transmission prevention: no share of needles while drug use standard precautions in hospital high protein calorie diet of family and client important
165.
poison control
prevention toddlers-common victims meds in locked cabinets check with the eyes of a children don't take meds in front of them dont keep meds in purses accidental poison s/s-sudden change of child behaviour, empty container around the child have number available for poison control save vomitus and urine contrai to vomiting-unconscious child, petroleum base substances, corrosive substances poison control will decide what to do dont give a large amount of fluids-will increase absorption
166.
led
neuro affection irritability, increased i identify the source-nurse role homes built before 70's, oil based, pottery with oil based
167.
hazardous waste contamination
decontaminate-first thing prevent spread clean up contamination monitor personnel that has been exposed if you have a contaminated patient-dont know what they are contaminated with-first thing find out what they are contaminated with,
168.
hemophyllia
mom transmits gene to her son sex linked disorder 50% chance that mom will it to each children affected male gets the gene from mother and can transmit it only to the doughter
169.
laryngotracheobronchitis
inspiratory stridor and restlessness edema and inflammation of upper airways elevated RR
170.
night terrors
normal between 4-7
171.
otitis meds common meds
antihistamines steroids
172.
crushing meds for children
what do you crush or not crush
173.
infant
safe crib car seat-rear face, until 20 lbs, after front faced seat, back seat not front seat bath temperature small pieces toys-chicking child proof home plugs covered plants that are poisonous-don't keep these
174.
preschoolers and school age
safety helmet for bicycles-important bikes and scooters- ride on sidewalk sports safety-stay active cause of obesity, but have appropriate equipment, appropriate age group activities
175.
teenager
males-teach them how to deal with anger safety while driving-ask if they wear seatbelt 100% of the time, no cell phone drugs-teach about it
176.
adults safety
talk about guns exercise old adults-are they safe while ambulating? shoes-are they appropriate, walker-do they need one?, stairs-up and down correct, hand rails, don't carry things upstairs, do they have a way to someone in case they fall
177.
disaster planning
red-unstable, immediate attention yellow-stable, ca wait green-stable, can wait longer, the walking wounded black-fatal injuries, unstable ---use these colors only if system is overwhelemed-question will say it
178.
bioterrorismanthrax
cutaneous/skin-skin , no person to person, animal workers; standard precautions inhalation-spores; no person to person ; resp failure, shock, hemorrhagic shock-doxycycline
179.
Tetralogy of Fallow
Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis Ventricular septal defect
180.
...
Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis Ventricular septal defect
181.
infants
exploratory play
182.
todlers
imitation
183.
school age
working with otherrs groups, collaborative play hobbies
184.
erikson stages
infant-trust vs mistrust-stable caregiver toddlers-18m-3 yrs-autonomy vs shame and doubt-toilet training, walking, muscular coordination, they want to do things by themselves-autonomy preschool-3-6 yrs-initiative vs guilt-constant discovery school age-industry vs inferiority-tasks are imp-teams and groups are present-inferiority possible if role not met adolescence-12-20 yrs-peers more important than parents-think of careers start; disease-cannot fit in with the group; eg diabetic teenager cannot meet with friends and eat what they want young adulthood-20-25-commitment, family start 45-64 yrs-middle adulthood-generativity vs stagnation 65 and over-integrity vs despair-progressing towards the end of life-feeling that their life was meaningful
185.
screening tests
Denver test-birth to 6 years
186.
growth and development
...
187.
muscular developmet
screen routine infant for muscular development teach parents about milestones progression
188.
1-2 months
poor head control frequent feeding needed gain 5-7 oz weekly first few months
189.
3-4 monts
head control get up with head smile 4 m-loose reflexes become more social, eye
190.
5-6 m
double weight grasping objects weight slows down-4 oz a week turn from back to stomach-dont leave alone on changing table-teach parents
191.
7-8 m
stranger anxiety fear of stranger, wants mom 8 m-separation-stages -protest -dispair-they dont want to eat, play -denial-when parent comes back-ignore
192.
9-10 m
more mobile sitting position lift can say gaga.. respond with anger crawling starts possible 10m-pull to standing house baby proof cause now they are more mobile
193.
11-12 m
weight triple can sit from standing position wat with fingers babinski reflex changes from baby fanning injury, failure to thrive, development problems injury-most at risk small pieces things-choking dont give candy, nuts, hot dogs-small falls-risk for injury car seats-teach-completely restraint burns-outlets, cords failure to thrive-not enough growth, physical defects, not good parenting nutritional feeding has to be met age appropriate toys-nclex loves these toys should stimulate, also think safety, no sharp edges introduction of solid foods-variety but not too many at once, one q 2 weeks, starting with 6 m rice cereal-first, can mix with formula or breast milk no fruit juices in bottles-teeth problems finger foods-watch for choking
194.
15-18 m-todler
lots of vocabulary walking alone anterior fontanelle closes at 18 m tumb sucking 4 blocks together-15 m old tantrums-18 start-normal-until 2
195.
24-30 m
increase vocabulary tippytoe walk sphincter control-2 1/2 around that time 30 m-4 times birth weight they like push pull toys, stuffed animals, dolls negativism-they say no, dont ask yes/no questions -routine important safety-active so risk for injuries; mva's-most at risk, car seat safety, restraint seat drowning abuse
196.
3-5 yrspreschooler
3-vocabulary exploring-1500 words; brushing teeth; discipline, limits important 5 yrs-2500 words-identity play, play like mom and dad; love to play; housekeeping toys-stoves, cars; trycicles; tolerate separation from parents fear of death at this age; give a shot showing on a doll; help with increasing separation from parents
197.
7 yrs
boys play with boys girls play with boys
198.
9
seeking friends starting conflict with parents on the go
199.
10-12
love conversation choosing friends more selectively interested in other sex reading sowing construction sports bicycle industry vs inferiority-accomplishment important should be dry at night-no bed wetting at 12 void before bedtime, there are meds available for bed wetting
200.
Verapamil
SVT
201.
CVA
corneal abrasion
202.
permethrin
for head lice repeat the application of cream-rinse in 7 days if nits still present, repeated only at 7 days after first application comb hair daily with a nit comb clean clothing with very hot water and RID special detergent
203.
ceftriaxone
its a cephalosporin in pt for postop infection monitor tongue and oral cavity for growth of microorganisms
204.
hiatal hernia and reflux
less likely to wake up at night from heartburn if stomach is emty
205.
hypothyroidism
client very sensitive to narcotics, barbiturates, anesthetics-avoid narcotic sedatives
206.
type 2 diabetic pt going for surgery is subscribed insulin postop instead of his usually oral meds-why
being npo inhibits blood sugar control
207.
pneumothorax, chest tube
lung has re-expanded=the fluid in the water seal chamber does not fluctuate with respirations air leak=continuous bubbling in the water chamber, gentle bubbling is normal
208.
elderly type 1 diabetic
blood glucose tests are better than urine because the renal glucose threshold in elevated in elderly
209.
US at 32 weeks
getting gestational age
210.
amniocentesis
LS ratio to assess baby's lungs determines if there are any problems with spinal cord determines early problems with baby's blood
211.
tracheostomy
...
212.
allnurses random facts
1. barium swallow for 3 month old infant - npo for three hours 2. temporary pacemaker for mi client - increase cardiac output is the primary purpose 3. plasma cholesterol screening - only sips of water for 12 hours 4. reminiscing group - primary goal is to review and share their life experience with the group member 5. miller-abbott tube - removes fluid and gas in the small intestine; provides intestinal decompression 6. levin or salem stump - decompresses the stomach; prevent fluid and gas accumulation in the stomach 7. promethazine hcl (phenergan) - check patency of the patient's vein before of drug, extravasation will cause necrosis 8. insulin dependent diabetic, unable to urinate -- autonomic neuropathy 9. overdose of aspirin will produce parkinsons dse type sx 10. do not erythromycin to multiple sclerosis pt
213.
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
-antianxiety used to tx symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal
214.
terbutaline Brethine mag sulfate
tx for preterm labor
215.
Benzatropine (Cogentin)
-used to tx parkinsonian side effects of Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) (antipsychotic med)
216.
Methadone
hydrochloride-opiod analgesic; tx for narcotic withdrawal
217.
Nifedipine (Procardia)
antianginal med (CCB) decreases myocardial O2 demand.
218.
Digoxin
strengthens myocardial contractio0n & slows conduction thru AV node
219.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
inhibits prothrombin synthesis
220.
Aminocaproic acid (Amicar)
antifibrinolytic prevents recurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
221.
Lithium
tx manic phase of bipolar
222.
Nimodipine
CCB decreases spasm in cerebral blood vessels
223.
diltiazem
CCB inhibits Ca+ influx vascular smooth muscle reduces myocardial O2 demand &decreases force of ventricular contraction
224.
clotrimazole
antifungal; treats rashes.
225.
sphincter control
18 months
226.
Buerger's disease
digital sensitivity to cold intermittent claudication (pain with exercise)
227.
aging
nocturia increase need to frequent urination
228.
gastric ulcer
pain half and hr or 1 hr after a meal pain rarely at night, not helped by ingestion of food
229.
duodenal ulcer
pain at night, 2-3 hrs after a meal, prior to ingestion of a meal
230.
lumbra laminectomy
Educate about exercise to strengthen the abdominal muscle
231.
promethazine
extravasation of vein, iv
232.
tetrahydrozoline
contrai in angle closure glaucoma
233.
recurrent uti
limit milk ordered Mandelamine
234.
miller abot tube
used for decompression of onstruction
235.
aids pts
get dementia, many of them
236.
hypoparathyroidism
low calcium be ready to deal with dysrhythmiaa
237.
iv placement
not close to t
238.
rsv
...
239.
Bun
7-18 (older)
240.
Creatinine
0.7-1.4
241.
PT
9.5-12
242.
autonomic dysreflexia
...
243.
graves disease
heat intolerance metabolic rate increased
244.
tetracycline
use sunscreen outdoors
245.
propanolol
s/e bronchospasm
246.
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
npo-for several hrs lidocaine-numb the esophagus-risk for for aspiration possibly iv sedation
247.
Ankle brachial index
...
248.
Alteplase
...
249.
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
...
250.
Labs for Mi
...
251.
stress test
stop if pain
252.
Pepcid
report to dr if pt is about to be put on antiplatelets meds-it might not work
253.
Docusate
stool softner
254.
Omeprazole
makes the Clopidogrel not work
255.
30 months
able to jump
256.
18 months
walk up and down the stairs while holding self
257.
low K
risk for Dig toxicity call doc
258.
PSA
draw before digital rectal exam
259.
tube feeding
rinse the bag and change formula q 4 hrs
260.
ng tube, before feeding
check ph-3 is good-for the aspirated contents
261.
Ciprofloxacin
rash-stop drug and call dr
262.
iv K
if burning-decrease rate
263.
aPTT
1.5-2 x the therapeutic value is ok
264.
cerebellar tumor
losing balance easily
265.
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
can tell difference in taste
266.
CN VIII (acoustic)
loss of hearing temporal lobe (auditory center)
267.
gravity drip IV
piggy bag has to be higher than primary bag
268.
before giving dopamine iv
check iv patency risk for extravasation
269.
GEMFIBROZIL
...
270.
PERPHENAZINE
...
271.
TERBUTALINE
...
272.
ZIDOVUDINE
...
273.
PROCAINAMIDE
...
274.
PROCHLOPERAZINE
...
275.
BROMPHENIRAMINE
...
276.
PHENYLPROPANOLAMINE
...
277.
Random meds
Carbamazepine therapeutic serum level is 4 - 12 mcg/dL Cycloserine is an antituburculan and needs weekly drug levels foscarnet (Foscavir) can be toxic to kidneys so creatinine is monitored. Therapeutic serum digoxin is 0.5 - 2 mg/dL morphine is contraindicated in acute pancreatitis because is causes the spasms but the demerol is the drug of choice. Dantrium (dantroline) common drug kept in the OR for Malignant Hyperthermia No birth control pills with antiseizure meds....lowers the B's effects Metylergonovine-to contract uterus. before giving check BP. dont give if vascular diseases are present. MgSo4-CNS Deppressant and Anticonvulsant = normal range 4-7.5, effective if no seizures. Adverse reactions: Flushing, decrease in RR, Muscle weakness filgrastim (neupogen) - increase neutrophil count epoietin alfa (epogen) - increase rbc/erythrocytes 1. prozac, zoloft, paxil- tx of depression. 2. sodium nitroprusside- sheild from light. wrap in foil 3. cephalosporins- check for allergies to penicillins. pt could be hypersensitive. 4. pts recieving lasix should be assessed for tinnitus and hearing loss 5. anticoagulants cant dissolve a formed thrombus but tpas can. PVC's -Lidocaine Verapamil - treatment of supraventricular tachycardias, check heart rate Clomiphene- induces ovulation by changing hormonal effect on the ovary DO NOT give a pregnant laboring patient on methadone STADOL (precipitates withdrawal) contractions > 90 seconds, FHR < after contraction peak. . .turn off the pitocin [oxytocin] (if running) give O2 by tight face mask, reposition on left side, increase IV fluid rate, notify caregiver, document Aminoglycosides (gentamycin, etc.) affect 8th cranial nerve function (hearing) and are nephrotoxic he adverse effects of Anti psychotics can be ed using this: SHANCE S-SUNLIGHT SENSITIVITY( Use hats and sunscreen) H-HEPATOTOXICITY( Monitor LFT) A-AGRANULOCYTOSIS( Characterised by fever and sore throat) N-NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME( Characterised by fever and muscular rigidity) C-CIRCULATORY PROBLEMS( Leukopenia and orthostatic hypotension) E-EXTRA PYRAMIDAL SYMPTOMS( ister anticholinergics and anti parkinsonian agents) SVT - Adenosine Atrial Flutter - Anticoagulants Atrial Fibrillation - Beta Blockers, Digoxin PVC - Amiodarone Ventricular Tachycardia - Amiodarone
Ventricular Fibrillation - Defibrillation Torsades de Pointes - Magnesium Sulfate 1st Degree AV Block - No treatment usually 2nd Degree AV Block Type I - Atropine 2nd Degree AV Block Type II - Pacemaker 3rd Degree AV Block Complete - Emergent Pacemaker, Atropine, Epinephrine, Dopamine Sinus Bradycardia - Atropine or Epinephrine Sinus Tachycardia - Beta Adrenergic or Calcium Channel Blocker digoxin 05-2.0 ng/ml lithium 0.6-1.5 meq/l dilantin 10-20 mcg/dl theophylline 10-20 mcg/dl lithium 0.5-1.5 meq/l coumadin pt: 12-20 sec....therapeutic range 1.5-2 times the control inr: 2-3 heparin ptt: 30-60 sec...therapeutic range 1.5-2 times the control 278.
Electrolytes
Hyperkalemia = narrow, peaked T waves on cardiac monitor Hypokalemia = Peaked P, Flat T, Depressed ST and Prominent U HYPOCALCEMIA (not enough sedatives) + trouseau and + chovstek's sign incr DTR stridor, laryngospasm swallowing problem=aspiration ALDOSTERONE insufficiency -Hypo-Na-emia, Hyper-K-emia, hypo-Volemia. WHEN Na decrease, K increase addisons= hyponatremia, hypotension, decreased blood vol, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia cushings= hypernatremia, hypertension, incrased blood vol, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia 4. SIADH Na <120 Hx of lung cancer Specific gravity > 1.035 Diabetes Insipidus Na> 160 head injury Specific gravity <1.005
279.
Defense mechanisms
phobias include projection and displacement
280.
Delegation Rule of Thumb?
DO NOT delegate what you can EAT! E - evaluate A - assess T - teach
281.
VV and AA?
EleVate Veins; dAngle Arteries for better perfusion
282.
Apgar Scoring?
A= appearance (color all pink, pink and blue, blue [pale]) P= pulse (>100, < 100, absent) G= grimace (cough, grimace, no response) A= activity (flexed, flaccid, limp) R= respirations (strong cry, weak cry, absent)
283.
Airborne Transmission?
My - Measles Chicken - Chicken Pox/Varicella Hez - Herpez Zoster/Shingles TB
284.
Protocol for Airborne Transmission?
Private Room - negative pressure with 6-12 air exchanges/hr Mask, N95 for TB
285.
Droplet Precautions Transmission?
DROPLET think of SPIDERMAN! S - sepsis S - scarlet fever S - streptococcal pharyngitis P - parvovirus B19 P - pneumonia P - pertussis I - influenza D - diptheria (pharyngeal) E - epiglottitis R - rubella M - mumps M - meningitis M - mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia An - Adenovirus
286.
Protocol for Droplet Precautions?
Private Room or cohort mask
287.
transmission precautions
PRECAUTION MRS.WEE M - multidrug resistant organism R - respiratory infection S - skin infections * W - wound infxn E - enteric infxn - clostridium difficile E - eye infxn - conjunctivitis
288.
What to do in the case of- an Air/Pulmonary Embolism?
S&S: chest pain, difficulty breathing, tachycardia, pale/cyanotic, sense of impending doom --> turn pt to left side and lower the head of the bed.
289.
What to do in the case of- A woman in labor with UnReassuring FHR?
(late decels, decreased variability, fetal bradycardia, etc) --> turn on left side (and give O2, stop Pitocin, increase IV fluids)
290.
What to do in the case of tube feeding with decreased LOC?
position pt on right side promotes emptying of the stomach with the HOB elevated to prevent aspiration
291.
During epidural puncture?
Side lying
292.
After lumbar puncture?
e (and also oil-based Myelogram)--> pt lies in flat supine (to prevent headache and leaking of CSF)
293.
What to in the case of- Pt with heat stroke?
Lie flat with legs elevated
294.
During CBI (continuous bladder irrigation)
(CBI) --> catheter is taped to thigh so leg should be kept straight. No other positioning restrictions.
295.
After Myringotomy?
Position on the side of the AFFECTED EAR after surgery to allow drainage of secretions
296.
After Cataract surgery?
pt will sleep on unaffected side with a night shield for 1-4 weeks.
297.
After Thyroidectomy?
low or semi-Fowler's, head, neck and shoulders.
298.
Infant with Spina Bifida?
position prone (on abdomen) so that sac does not rupture
299.
Buck's Traction?
(skin traction) --> elevate foot of bed for counter-traction
300.
After Total Hip Replacement?
don't sleep on operated side, don't flex hip more than 4560 degrees, don't elevate HOB more than 45 degrees. Maintain hip abduction by separating thighs with pillows.
301.
Prolapsed Cord?
knee-chest position or Trendelenburg
302.
Infant with Cleft lip?
position on back or in infant seat to prevent trauma to suture line. While feeding, hold in upright position.
303.
To prevent dumping syndrome?
(post-operative ulcer/stomach surgeries) --> eat in reclining position, lie down after meals for 20-30 minutes (also restrict fluids during meals, low CHO and fiber diet, small frequent meals)
304.
Above the knee amputation?
elevate for first 24 hours on pillow, position prone daily to provide for hip extension.
305.
Below the knee amputation?
foot of bed elevated for first 24 hours, position prone daily to provide for hip extension.
306.
Detached Retina?
area of detachment should be in the dependent position-- dependent meaning ed by something
307.
Enema positioning?
position pt in left side-lying (Sim's) with knee flexed
308.
After Supratentorial Surgery?
(incision behind hairline) --> elevate HOB 30-45 degrees
309.
After Infratentorial Surgery?
(incision at nape of neck)--> position pt flat and lateral on either side.
310.
During internal radiation?
on bedrest while implant in place
311.
Autonomic Dysreflexia/ Hyperreflexia?
S&S: pounding headache, profuse sweating, nasal congestion, goose flesh, bradycardia, hypertension place client in sitting position elevate HOB first before any other implementation.
312.
Shock?
bedrest with extremities elevated 20 degrees, knees straight, head slightly elevated (modified Trendelenburg)
313.
Head Injury?
elevate HOB 30 degrees to decrease intracranial pressure
314.
Peritoneal Dialysis when outflow is inadequate?
turn pt from side to side BEFORE checking for kinks in tubing (according to Kaplan)
315.
Lumbar Puncture?
AFTER the procedure, the client should be placed in the supine position for 4 to 12 hrs as prescribed. (Saunders 3rd ed p. 229)
316.
The difference between Myasthenia Gravis, Myastenia Crisis, and Cholinergic Crisis?
Myasthenia Gravis: worsens with exercise and improves with rest. Myasthenia Crisis: a positive reaction to Tensilon--will improve symptoms Cholinergic Crisis: caused by excessive medication-stop med-giving Tensilon will make it worse
317.
Prior to liver biopsy?
Its important to be aware of the lab result for prothrombin time
318.
From the ass? From the Mouth?
From the a** (diarrhea)= metabolic acidosis From the mouth (vomitus)=metabolic alkalosis
319.
Myxedema/ hypothroidism?
slowed physical and mental function, sensitivity to cold, dry skin and hair
320.
Graves disease/ Hyperthyroidism?
accelerated physical and mental function; sensitivity to heat, fine/soft hair
321.
Thyroid storm?
increased temp, pulse and HTN
322.
Post Thyroidectomy?
semi-Fowler's, prevent ncek flexion/hyperextension, trach at bedside
323.
Hypo-parathyroid?
CATS - convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasms, stridor (decreased calcium), high Ca, low phosphorus diet
324.
Hyperparathyroid?
fatigue, muscle weakness, renal calculi, back and t pain (increased calcium), low Ca, high phosphorus diet
325.
Hypovolemia?
incrased temp, rapid/weak pulse, increase respiration, hypotension, anxiety, urine specific gravity >1.030
326.
Hypervolemia?
bounding pulse, SOB, dyspnea, rares/crackles, peripheral edema, HTN, urine specific gravity <1.010; Semi-Fowler's
327.
Diabetes Insipidus?
(decreased ADH): excessive urine output and thirst, dehydration, weakness, ister Pitressin
328.
SIADH?
(increased ADH): change in LOC, decreased deep tendon reflexes, tachycardia, n/v/a, HA; ister Declomycin, diuretics
329.
HypoKalemia?
muscle ewakness, dysrhythmias, increase K (raisins, bananas, apricots, oranges, beans, potatoes, carrots, celery)
330.
HyperKalemia?
MURDER - muscle weakness, urine (oliguria/anuria), respiratory depression, decreased cardiac contractility, ECG changes, reflexes
331.
Hyponatremia?
nausea, muscle cramps, increased I, muscular twitching, convulsion; osmotic diuretics, fluids
332.
Hypernatremia?
increased temp, weakness, disorientation/delusions, hypotension, tachycardia; hypotonic solution
333.
Hypocalemia?
CATS - convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasms and stridor
334.
Hypercalemia?
muscle weakness, lack of coordination, abdominal pain, confusion, absent tendon reflexes, sedative effect on CNS
335.
HypoMg?
tremors, tetany, seizures, dyrshythmias, depression, confusion, dysphagia; dig toxicity
336.
HyperMg?
depresses the CNS, hypotension, facial flushing, muscle ewakness, absent deep tendon reflexes, shallow respirations, emergency
337.
Addisons?
hypoNa, hyperK, hypoglycemia, dark pigmentation, decreased resistance to stress, fractures, alopecia, weight loss, GI distress
338.
Cushings?
hyperNa, hypoK, hyperglycemia, prone to infection, muscle wasting, weakness, edema, HTN, hirsutism, moonface/buffalo hump
339.
Addisonian Crisis?
n/v, confusion, abdominal pain, extreme weakness, hypoglycemia, dehydration, decreased BP
340.
Pheochromocytoma?
hypersecretion of epi/norepi, persistent HTN, increased HR, hyperglycemia, diaphoresis, tremor, pounding HA; avoid stress, frequent bating and rest breaks, avoid cold and stimulating foods, surgery to remove tumor
341.
NMS?
-NMS is like S&M; -you get hot (hyperpyrexia) -stiff (increased muscle tone) -sweaty (diaphoresis) -BP, pulse, and respirations go up & -you start to drool
342.
Dangerous thing to get during pregnancy?
I kept forgetting which was dangerous when you're pregnant; regular measles (rubeola), or German measles (rubella), so : -never get pregnant with a German (rubella)
343.
Tetraology of Fallot?
Tetralogy of fallot; HOPS Think DROP(child drops to floor or squats) or POSH Defect, septal Right Ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorts Pulmonary stenosis
344.
Autonomic Dysreflexia?
Autonomic dysreflexia: potentially life threatening emergency - elevate head of bed to 90 degree - loosen constrictive clothing - assess for bladder distention and bowel impaction (triger) - ister antihypertensive meds (may cause stroke, MI, seisure )
345.
FHR patterns in ob?
Have trouble ing fhr patterns in OB? Think VEAL CHOP VC EH AO LP V = variable decels; C = cord compression caused E = early decels; H = head compression caused A = accels; O = okay, not a problem! L = late decels = placental insufficiency, can't fill
346.
For cord compression in OB?
For cord compression, place the mother in the TRENDELENBERG position because this removes pressure of the presenting part off the cord. (If her head is down, the baby is no longer being pulled out of hte body by gravity) If the cord is prolapsed, cover it with sterile saline gauze to prevent drying of the cord and to minimize infection.
347.
Late Decels?
For late decels, turn the mother to her left side, to allow more blood flow to the placenta.
348.
Before Epidural?
Hydration is a big priority!
349.
Major risks of epidural?
Hypotension and bradypnea / bradycardia are major risks and emergencies.
350.
OB secret?
NEVER check the monitor or a machine as a first action. Always assess the patient first; for exmaple listen to the fetal heart tones with a stethoscope in NCLEX land. Sometimes it's hard to tell who to check on first, the mother or the baby; it's usually easy to tell the right answer if the mother or baby involves a machine. If you're not sure who to check first, and one of the choices involves the machine, that's the wrong answer.
351.
Hearing the baby in OB?
If the baby is a posterior presentation, the sounds are heard at the sides. If the baby is anterior, the sounds are heard closer to midline, between teh umbilicus and where you would listen to a posterior presentation. If the baby is breech, the sounds are high up in the fundus near the umbilicus. If the baby is vertex, they are a little bit above the symphysis pubis.
352.
Ventilator Alarms?
HOLD High alarm- Obstruction due to incr. secretions, kink, pt. coughs, gag or bites Low press alarm- Disconnection or leak in ventilatior or in pt. airway cuff, pt. stops spontaneous breathing
353.
To blood sugar?
hot and dry-sugar high (hyperglycemia) cold and clammy-need some candy (hypoglycemia)
354.
I and Shock have?
I AND SHOCK HAVE OPPOSITE V/S I-increased BP, decreased pulse, decreased resp. shock- decreased BP, increased pulse, increased resp.
355.
Cor Pulmonae?
right sided heart failure caused by left ventricular failure (so pick edema, jvd, if it is a choice.)
356.
Heroin withdrawl in a neonate?
Irritable, and poor sucking
357.
Jews?
No meat and milk together
358.
Brachial Pulse?
Pulse area r on infant
359.
What to check children for at age 12 months?
always check lead posioning levels
360.
Sources of potassium?
Bananas, potatoes, citrus fruits
361.
What is obtained before starting any iv antibiotic?
Cultures
362.
Why would a pt with leukemia have epistaxis?
b/c of low platelets
363.
Best way to warm a newborn?
skin to skin on mom with a blanket
364.
When a pt comes in and she is in active labor?
nurses FIRST action is to listen to fetal rate/tone
365.
How to treat phobic disorders?
systematic desensitization
366.
Best way to tube feed or feed kids?
small frequent is better than large
367.
With lower amputations?
place in prone position
368.
LVN/LPN cant?
Handle any blood
369.
Cardinal signs of ARDS?
Cardinal sign of ARDS is hypoxemia (low oxygen level in tissues).
370.
Best indicator of dehydration?
weight
371.
Besides sodium, water also follows?
Glucose
372.
Use of cold and hot?
Use cold for acute pain (sprained ankle) and heat for chronic pain (arthritis)
373.
Guided imagery is great for?
CHRONIC pain
374.
When patient is in distress?
Med istration is rarely a good choice
375.
Pneumonia?
pneumonia, fever and chills are usually present. For the elderly confusion is often present.
376.
COPD and Pneumonia?
COPD is chronic, pneumonia is acute. Emphysema and bronchitis are both COPD. in COPD patients the baroreceptors that detect the CO2 level are destroyed. Therefore, O2 level must be low because high O2 concentration blows the patient's stimulus for breathing.
377.
4 options for cancer?
chemo, radiation, surgery, allow to die with dignity.
378.
Nuetropenic patients?
no live vaccines, no fresh fruits, no flowers should be used for neutropenic patients.
379.
Where are chest tubes placed?
chest tubes are placed in the pleural space.
380.
Diff between angina and MI?
angina (low oxygen to heart tissues) = no dead heart tissues. MI= dead heart tissue present.
381.
Preload and Afterload?
Preload affects amount of blood that goes to the R ventricle. Afterload is the resistance the blood has to overcome when leaving the heart.
382.
CABG?
for a CABG operation when the great saphenous vein is taken it is turned inside out due to the valves that are inside.
383.
1 tsp= how many ml ?
1 t (teaspoon)= 5 ml
384.
1 tablespoon = how many ml?
1 T(tablespoon)= 3 t = 15 ml
385.
How many oz in a ml?
30 ml = 1 oz
386.
1 cup= how many oz?
1 cup= 8 oz
387.
1 quart = how many pints?
1 quart = 2 pints
388.
1 pint = how many cups?
1 pint= 2 cups
389.
1 gr= how many mg?
1 gr (grain)= 60 mg
390.
1 g = how many mg?
1 gram = 1000 mg
391.
1 kg= how many pounds?
2.2
392.
1 lb = how many ozs?
one pound equals 16 0z
393.
Temp conversion?
* To convert Centigrade to F. F= C+40, multiply 9/5 and substract 40 * To convert Fahrenheit to C. C= F+40, multiply 5/9 and substract 40.
394.
After Endoscopy?
after endoscopy check gag reflex.
395.
TPN is given in ?
TPN(total parenteral nutrition) given in subclavian line.
396.
Low Residue diet?
low residue diet means low fiver
397.
Diverticulitis?
diverticulitis (inflammation of the diverticulum in the colon) pain is around LL quadrant.
398.
Appendicitis
Appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix) pain is in RL quadrant with rebound tenderness.
399.
Cause of Ascites?
portal hypotension + albuminemia= Ascites.
400.
Who produces insulin?
beta cells of pancreas produce insulin
401.
s3 heart sound is normal? not?
Normal in CHF from the squishin'.. NOT normal in an MI patient
402.
Signs observed in hypocalemia?
Trousseau and Tchovoski signs observed in hypocalcemia
403.
DKA?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)= when body is breaking down fat instead of sugar for energy. Fats leave ketones (acids) that cause pH to decrease. 71. DKA is rare in diabetes mellitus type II because there is enough insulin to prevent breakdown of fats.
404.
s/s of a fat embolism?
petechiae. Treated with heparin.
405.
Knee replacement?
for knee replacement use continuous ive motion machine.
406.
Glaucoma patients loose?
glaucoma patients lose peripheral vision. Treated with meds
407.
c02 builds up and causes?
Co2 causes vasoconstriction.
408.
Where are most spinal cord injuries?
most spinal cord injuries are at the cervical or lumbar regions
409.
autonomic dysreflexia
autonomic dysreflexia ( life threatening inhibited sympathetic response of nervous system to a noxious stimulus- patients with spinal cord injuries at T-7 or above is usually caused by a full bladder.
410.
Myasthenia gravis?
myasthenia gravis= decrease in receptor sites for acetylcholine. Since smallest concentration of ACTH receptors are in cranial nerves, expect fatigue and weakness in eye, mastication, pharyngeal muscles.
411.
Guillian Barre?
Guillain-Barre syndrome= ascending paralysis. Keep eye on respiratory system.
412.
Parkisons?
parkinson's = RAT: rigidity, akinesia (loss of muscle mvt), tremors. Treat with levodopa.
413.
TIA?
TIA (transient ischemic attack) mini stroke with no dead brain tissue
414.
CVA?
CVA (cerebrovascular accident) is with dead brain tissue.
415.
Hodgkins disease?
Hodgkin's disease= cancer of lymph is very curable in early stage.
416.
Rule of nines?
Rule of NINES for burns Head and Neck= 9% Each upper ext= 9% Each lower ext= 18% Front trunk= 18% Back trunk= 18% Genitalia= 1%
417.
Peds weight ?
Birth weight doubles by 6 month and triple by 1 year of age.
418.
Dig rule for kids?
if HR is <100 do not give dig to children.
419.
First sign of cystic fibrosis?
first sign of cystic fibrosis may be meconium ileus at birth. Baby is inconsolable, do not eat, not ing meconium.
420.
Heart Defects?
heart defects. for cyanotic -3T's( Tof, Truncys arteriosus, Transposition of the great vessels). Prevent blood from going to heart. If problem does not fix or cannot be corrected surgically, CHF will occur following by death. 94. with R side cardiac
421.
Heart problems?
with R side cardiac cath=look for valve problems with L side in adults look for coronary complications
422.
What disease leads to cardiac valve malfunctions?
Rhematic fever
423.
Cerebral palsy?
poor muscle control due to birth injuries and/or decrease oxygen to brain tissues
424.
I?
I (intracranial pressure) should be <2. measure head circonference.
425.
Signs to look for in meningitis?
for Meningitis check for Kernig's/ Brudzinski's signs.
426.
Wilms tumor?
Wilm's tumor is usually encapsulated above the kidneys causing flank pain.
427.
Facts about hemophilia?
It is X-linked. Mother es the disease to her son
428.
What happens when phenylalanine increases?
brain problems occur
429.
Bucks traction =
knee immobility
430.
Russel Traction =
femur or lower leg instability
431.
Dunlap traction=
Skeletal or skin
432.
Bryant's traction=
Children <3yoa, <35 lbs with femur fx
433.
How to put on traction?
Place the apparatus first then place the weight (der)
434.
Where should placenta be?
Upper part of the uterus
435.
Eclampsia is a ?
seizure>
436.
A patient with vertical c- section will likely have?
another c section with any more kids
437.
Amniocentesis is performed? and why?
perform amniocentesis before 20 weeks gestation to check for cardiac and pulmonary abnormalities.
438.
Rh?
mothers receive rhogam to protect next baby.
439.
Fontanelles?
anterior fontanelle closes by 18 months. Posterior 6 to 8 weeks.
440.
caput succedaneum=
caput succedaneum= diffuse edema of the fetal scalp that crosses the suture lines. Swelling reabsorbs within 1 to 3 days.
441.
Pathological jaundice?
pathological jaundice= occurs before 24hrs and last7 days. Physiological jaundice occurs after 24 hours.
442.
Diff between placenta previa and placenta abrupto?
placenta previa = there is no pain, there is bleeding. Placenta abruption = pain, but no bleeding.
443.
Bethamethasone?
bethamethasone (celestone)=surfactant. Med for lung expansion.
444.
Dystocia?
dystocia= baby cannot make it down to canal
445.
Therapies?
milieu therapy= taking care of patient/environment cognitive therapy= counseling crisis intervention=short term.
446.
Rule of thumb for obsessions/distractions?
Osession is to thought. Compulsion is to action
447.
Rule of thumb for assisting pysch patients?
if patients have hallucinations redirect them. In delusions distract them.
448.
Alzheimers?
Alzheimer's disease is a chronic, progressive, degenerative cognitive disorder that s for more than 60% of all dementias
449.
Hyperthyroidism?
HYPERthyroidism think of MICHAEL JACKSON in THRILLER! SKINNY, NERVOUS, BULDGING EYES, Up all night, heart beating fast
450.
Awesome ing for cranial nerves?
Cranial Nerves: *I am sorry if this vulgar for some, but hey, it sticks Sensory=S Motor=M Both=B Oh (Olfactory I) Some Oh (Optic II) Say Oh (Oculomotor III) Marry To (Trochlear IV) Money Touch (Trigeminal V) But And (Abducens VI) My Feel (Facial VII) Brother A (Auditory VIII) Says Girls (Glossopharyngeal IX) Big Vagina (Vagus X) Bras And (Accessory XI) Matter Hymen (Hypoglassal XII) More
451.
Hypernatremia? SALT?
Hyper natremia (greater than 145) SALT! Skin flushed Agitation Low grade fever Thirst
452.
Developmental milestones?
Developmental 2-3 months: turns head side to side 4-5 months: grasps, switch & roll 6-7 months: sit at 6 and waves bye-bye 8-9 months: stands straight at eight 10-11 months: belly to butt (phrase has 10 letters) 12-13 months: twelve and up, drink from a cup
453.
Hepatitis?
Hepatitis Hepatitis: -ends in a VOWEL, comes from the BOWEL (Hep A) Hepatitis B=Blood and Bodily fluids Hepatitis C is just like B
454.
Apgar scores/scoring?
Apgar measures HR,RR,Muscle tone, Reflexes,Skin color each 0-2 point. 8-10 OK. 0-3 RESUSCITATE.
455.
Cute way to glascow coma?
GLASGOW COMA SCALE. EYES, VERBAL,MOTOR! It is similar to measuring dating skills...max 15 points -one can do it if below 8 you are in Coma. So, to start dating you gotta open your EYES first, if you albe to do that spontaneously and use them correctly to SEE whom you dating you earn 4. But if she has to scream on you to make you open them it is only 3....and 1 you dont care to open even if she tries to hurt you. if you get good EYE (4 points) then move to VERBAL. talk to her/ him! if you can do that You are really ORIENTED in situation she/he uncontiously gives you 4 points! if you like her try not to be CONFUSED (3), and of cause do not use INAPPROPRIATE WORDS (3), she will not like it)), try not to RESPOND WITH INCOMPREHENSIBLE SOUNDS (2), if you do not like herjust show no VERBAL RESPONSE(1) Since you've got EYE and VERBAL you can MOVE now using your Motor Response Points. THis is VERY important since Good moves give you 6!
456.
What to do for addisons/cushings?
Addison's disease (need to "add" hormone) Cushing's syndrome (have extra "cushion" of hormones)
457.
Dumping syndrome?
Dumping syndrome: increase fat and protein, small frequent meals, lie down after meal to decrease peristalsis, wait 1 hr after meals to drink.
458.
Blood typing?
For blood types: "O" is the universal donor ( "o" in donor) "AB" is the universal receipient
459.
Gross things to about nurses with herpes!!!!
Disseminated Herpes Zoster is AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS, as to Localized Herpes Zoster is PRECAUTIONS. A nurse with a localized herpes zoster CAN care for patients as long as the patients are NOT immunosuppressed and the lesions must be covered!
460.
Birth control- Diaphram?
Diaphragm must stay in place 6 hours after intercourse. They are also fitted so must be refitted if you lose or gain a significant amount of weight.
461.
Cushing ulcers and cushings triad?
Cushings ulcers r/t BRAIN injury *Cushings triad r/t I in BRAIN (htn, bradycard, irr. resp)
462.
Thyroid storm and myxedema?
Thyroid storm is HOT (hyperthermia) *Myxedema coma is COLD (hypothermia)
463.
Nondairy sources of calcium?
Non dairy sources of calcium include RHUBARB, SARDINES, COLLARD GREENS
464.
Whats petaling?
You can petal the rough edges of a plaster cast with tape to avoid skin irritation.
465.
How do you teach someone to reduce back aches?
With low back aches, bend knees to relieve
466.
Koplick's spots?
* Koplick's spots are red spots with blue center characteristic of PRODROMAL stage of Measles. Usually in mouth.
467.
Pancreatitis pts>?
* Pancreatitis patients but them in fetal position, NPO, gut rest, prepare antecubital site for PICC cuz they'll probably be getting TPN/Lipids
468.
Trendelenberg's test?
Trendelenburg test - for varicose veins. If they fill proximally = varicosity.
469.
What can't you give to immunosupressed pts?
Yogurt has live cultures- dont give to immunosuppressed pt
470.
How to itch under a cast?
Itching under cast area- cool air via blow dryer, ice pack for 10- 15 minutes. NEVER use qtip or anything to scratch area
471.
Murphy's sign?
Murphy's sign - pain with palpation of gall bladder area seen with cholecystitis
472.
Cullens sign?
Cullen's sign - ecchymosis in umbilical area, seen with pancreatitis
473.
Turner's sign?
Turner's sign - flank grayish blue (turn around to see your flanks) pancreatitis
474.
Mcburney's point?
McBurney's Point - pain in RLQ indicative of appendicitis--RLQ - appendicitis, watch for peritonitis
475.
Pain in the LLQ indicative of?
LLQ - diverticulitis , low residue, no seeds, nuts, peas
476.
Guthrie test?
Guthrie Test - Tests for PKU, baby should have eaten source of protein first
477.
Shilling test?
Shilling Test - test for pernicious anemia/ how well one absorbs Vit b12
478.
Allen's test?
Allen's test - occlude both ulnar and radial artery until hand blanches then release ulnar. If the hand pinks up, ulnar artery is good and you can carry on with ABG/radial stick as planned. ABGS must be put on ice and whisked to the lab.
479.
Tenkhoff cath?
oIt's ok to have abdominal craps, blood tinged outflow and leaking around site if the Peritoneal Dialysis cath (tenkhoff) was placed in the last 1-2 wks. Cloudy outflow NEVER NORMAL.
480.
Meconium stained protocol?
oAmniotic fluid yellow with particles = meconium stained`
481.
Hyper reflexive? Absent reflexsive?
oHyper reflexes (upper motor neuron issue "your reflexes are over the top") oAbsent reflexes (lower motor neuron issue)
482.
When is Rhogam given and how?
oRhogam : given at 28 weeks, 72 hours post partum, IM. Only given to Rh NEGATIVE mother.
483.
Coomb's test?
Also if indirect Coomb's test is positive, don't need to give Rhogam cuz she has antibody only give if negative coombs
484.
Order of assessment?
Order of assessment: Inspection, Palpation, Percussion and Ausculation. EXCEPT with abdomen cuz you don't wanna mess with the bowels and their sounds so you Inspect, Auscultate, Percuss then Palpate (same with kids, I suppose since you wanna go from least invasive to most invasive sine they will cry BLOOD MURDER ! Gotta love them kids !)
485.
Latex allergies?
Latex allergies => Assess for allergies to bananas, apricots, cherries, grapes, kiwis, ion fruit, avocados, chestnuts, tomatoes, peaches
486.
ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ( ALS ) is a condition in which there is a degeneration of motor neurons in both the upper & lower motor neuron systems.
487.
TEF?
Transesophageal Fistula (TEF) - esophagus doesn't fully develop (this is a surgical emergency) The 3 C's of TEF in the newborn: 1) Choking 2) Coughing 3) Cyanosis
488.
MMR SHot?
The MMR vaccine is given SQ not IM.
489.
Color codes?
Red--unstable, ie, occluded airway, actively bleeding, see first Yellow---stable, can wait up to an hour for treatment, ie burns, see second Green---stable, can wait even longer to be seen, "walking wounded" Black--unstable clients that will probably not make it, need comfort measures
490.
Greeks?
Greek heritage - they put an amulet or any other use of protective charms around their baby's neck to avoid "evil eye" or envy of others
491.
4 year olds?
4 year old kids cannot interpret TIME. Need to explain time in relationship to a known COMMON EVENT (eg: "Mom will be back after supper").
492.
Hep B vaccine always ask?
Anaphylactic reaction to baker's yeast is contraindication for Hep B vaccine.
493.
Flu shot always ask?
allergic to eggs??? (Tristan D. ) !
494.
Before giving MMR>?
** Ask for anaphylactic rxn to eggs or neomycin before MMR
495.
If kid has a cold?
**If kid has cold, can still give immunizations
496.
SARS?
**SARS (severe acute resp syndrome) airborne + (just like varicella)
497.
Disease precautions?
** Hepatitis A is precautions ** Tetanus, Hepatitis B, HIV are STANDARD precautions
498.
Willam's position?
** William's position - Semi Fowlers with knees flexed (inc. knee gatch) to relieve lower back pain.
499.
Signs of a hip fracture?
SIGNS of a Fractured hip: EXTERNAL ROTATION, SHORTENING, ADDUCTION
500.
S/S of a fat embolism?
Fat Embolism: Blood tinged sputum (r/t inflammation), inc ESR, respiratory alkalosis (not acidosis r/t tachypnea), hypocalcemia,increased serum lipids, "snow storm" effect on CXR.
501.
Complications of mechanical ventilation?
Complications of Mechanical Ventilation: Pneumothorax, Ulcers
502.
Paget's disease?
Paget's Disease - tinnitus, bone pain, enlargement of bone, thick bones.
503.
Intravenous Pylogram requires?
** IVP requires bowel prep so they can visualize the bladder better
504.
ACID ash diet?
Acid Ash diet - cheese, corn, cranberries, plums, prunes, meat, poultry, pastry, bread
505.
Alkaline Ash diet?
Alk Ash diet- milk, veggies, rhubarb, salmon
506.
Orange tag in pysch
Orange tag in triage is non emergent Psych
507.
Greenstick fracture?
Greenstick fractures, usually seen in kids bone breaks on one side and bends on the other
508.
Side effects of thyroid hormones?
Insomnia is a side effect of thyroid hormones. Saunders confirms it. Makes sense though!Increased met. rate, your body is "too busy to sleep" as opposed to the folks with hypothyroidism who may report somnolence (dec. met rate, body is slow and sleepy).
509.
Botox?
** BOTOX for strabismus. Patch the GOOD eye so that the weaker eye can get stronger. Found a cool link about its use in peds pt with strabismus. I had to look it up cuz I heard it was important ah hem ah hem
510.
Tidal volume?
** TIDAL VOLUME is 7 - 10ml / kg
511.
COPD patients?
** COPD patients : 2LNC or less (hypoxic NOT hypercapnic drive), Pa02 of 60ish and Sa02 90% is normal for them b/c they are chronic CO2 retainers. ...
512.
Stranger Danger>?!?
Stranger anxiety is greatest 7 - 9 months, Separation anxiety peaks in toddlerhood
513.
Lymes mostly found in
Lymes is found mostly in Conneticuts
514.
Asthma and arthritis best excercise?
swimming
515.
What is a bad sign in asthma?
intercostal retractions=bad!
516.
ABG drawin?
When drawing an ABG, you need to put the blood in a heparinized tube, make sure there are no bubbles, put on ice immediately after drawing, with a lable indicating if the pt was on room air or how many liters of O2. to preform the Allen's Test prior to doing an ABG to check for sufficient blood flow
517.
Before a pft?
Before going for Pulmonary Fuction Tests (PFT's), a pt's bronchodilators will be with-held and they are not allowed to smoke for 4 hrs prior
518.
For a lung biopsy?
For a lung biopsy, position pt lying on side of bed or with arms raised up on pillows over bedside table, have pt hold breath in midexpiration, chest x-ray done immediately afterwards to check for complication of pneumothorax, sterile dressing applied
519.
For a lumbar puncture?
For a lumbar puncture, pt is positioned in lateral recumbent fetal position, keep pt flat for 2-3 hrs afterwards, sterile dressing, frequent neuro assessments
520.
For an EEG test?
EEG, hold meds for 24-48 hrs prior, no caffine or cigarettes for 24 hrs prior, pt can eat, pt must stay awake night before exam, pt may be asked to hyperventilate and watch a bright flashing light, after EEG, assess pt for seizures, pt's will be at increased risk
521.
Munchhausen Syndrome?
-Munchausen Syndrome is a psychiatric disorder that causes an individual to self-inflict injury or illness or to fabricate symptoms of physical or mental illness, in order to receive medical care or hospitalization. In a variation of the disorder, Munchausen by proxy (MSBP), an individual, typically a mother, intentionally causes or fabricates illness in a child or other person under her care.
522.
MS?
-Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic, progressive disease with demyelinating lesions in the CNS which affect the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. Motor S/S: limb weakness, paralysis, slow speech Sensory S/S: numbness, tingling, tinnitus Cerebral S/S: nystagmus, ataxia, dysphagia, dysarthria
523.
Huntington's Chorea?
Huntington's Chorea: 50% genetic, autosomal dominant disorder S/S: chorea --> writhing, twisting, movements of face, limbs and body -gait deteriorates to no ambulation -no cure, just palliative care
524.
Shift to the left means?
WBC shift to the left in a patient with pyelonephritis neutrophils kick in to fight infection
525.
How to Dx a AAA?
Definitive diagnosis for abd. aortic aneurysm (AAA) --> CT scan
526.
Uremic Fetor?
Uremic fetor --> smell urine on the breath
527.
Hirschsprungs?
-Hirschsprung's --> bile is lower obstruction, no bile is upper obstruction; ribbon like stools.
528.
No Cantalope?
Thank you, I finally realize why a person shouldn't have cantaloupe before a occult stool test, because cantaloupe is high in vit c and vit c causes a false + for occult blood. Now I just need to figure out why they can't have fish.
529.
Penis Problems?
Hypospadias: abnormality in which urethral meatus is located on the ventral (back) surface of the penis anywhere from the corona to the perineum ( hypo, low (for lower side or under side) Epispadias: opening of the urethra on the dorsal (front) surface of the penis Priapism: painful erection lasting longer than 6 hrs.
530.
When you see coffee brown emesis think?>
Peptic ulcer
531.
For PVD ?
For PVD DAVE (Legs are Dependent forArterial & for Venous Elevated)
532.
Traction rule?
Never release traction unless you have an order from an MD to do so
533.
Halo?
Questions about a halo? safety first, have a screwdriver nearby.
534.
Compartment syndrome?
compartment syndrome is an emergency situation. Paresthesias and increased pain are classic symptoms. Neuromuscular damage is irreversible 4-6 hours after onset.
535.
Behavior/Developmental-Peds
Behavior motivated by need to avoid anxiety and satisfy needs 1. Infancy 0-18 months others will satisy needs 2. childhood >6yrs learn to delay need gratification 3. juvenile 6-9 years learn to relate to peers 4. preadolescence 9-12 yrs learns to relate to friends of of opposite sex 5. early adolescence12-14yrs:learn independence and how to relate to opposite sex 6. late adolecence 14-21yrs: develop intimate relationship with person of opposite sex is this not about communication?....
536.
Fetal alcohol sydrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome -upturned nose -flat nasal bridge -thin upper lip -SGA
537.
Immunizations rules?
vastus lateralis is IM istration site for 6month infants For toddlers above 18 months ventrogluteal The deltoid and gluteus maximus are appropriate sites for children`
538.
Eyes?
OU- both eyes OS- left eye OD- right eye ( dominent Right eye- just a tip to )
539.
Cane walking?
1. COAL (cane walking): C - cane O - opposite A - affected L - leg
540.
In depth- Color codes??
Red- Immediate: Injuries are life threatening but survivable with minimal intervention. Ex: hemothrax, tension pneumothorax, unstable chest and abdominal wounds, INCOMPLETE amputations, OPEN fx's of long bones, and 2nd/3rd degree burn with 15%-40% of total body surface, etc. Yellow- Delayed: Injuries are significant and require medical care, but can wait hrs without threat to life or limb. Ex: Stable abd wounds without evidence of hemorrhage, fx requiring open reduction, debridement, external fixation, most eye and CNS injuries, etc. Green- Minimal: Injuries are minor and tx can be delayed to hrs or days . Individuals in this group should be moved away from the main triage area. Ex: upper extremity fx, minor burns, sprains, sm. lacerations, behavior disorders. Black- Expectant: Injuries are extensive and chances of survival are unlikely. Seperate but dont abandoned, comfort measures if possible. Ex: Unresponsive, spinal cord injuries, woulds with anatomical organs, 2nd/3rd degree burn with 60% of body surface area , seizures, profound shock with multipe injuries, no pulse, b.p, pupils fixed or dilated.
541.
Thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis prep- Take v.s., shave area around needle insertion, position patient with arms on pillow on over bed table or lying on side, no more than 1000cc at a one time. Post- listen for bilateral breath sounds, v.s., check leakage, sterile dressing.
542.
Cath lab?
Cardiac cath- npo 8-12hr, empty bladder, pulses, tell pt may feel heat palpitations or desire to cough with dye injection. Post- Vital signs keep leg straight bedrest 6-8hr.
543.
MRI?
MRI- claustrophobia, no metal, assess pacemaker
544.
Cerebral angio prep?
cerebral angio prep- well hydrated, lie flat, sire shaved, pulses marked post- keep flat 12-14hr, check site, pulses,force fluids.
545.
More info on lumbar puncture?
Lumbar puncture- fetal postion. post- nuero assess q15-30 until stable, flat2-3hr, encourage fluids, oral anlgesics for headache, observe dressing
546.
More info on EEG?
EEG- no sleep the night before, meals not withheld, no stimulants for 24hr before, tranquilizer/stimulant meds held 24-48hr before, may be asked to hyperventilate 3-4min and watch a bright flashing light.
547.
Myelogram?
Myelogram- Npo 4-6hr, allergy hx, phenothiazines, cns depressants, and stimulants withheld 48hr prior, table will be moved to various postions during test. Post- neuro q2-4, water soluble HOB up, oil soluble HOB down, oral analgesics for h/a, encourage po fluids, assess for distended bladder, inspect site.
548.
Liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy- vit k , npo morning of exam 6hr, give sedative, Teach pt that he will be asked to hold breath for 5-10sec, supine postion, lateral with upper arms elevated. Post- postion on right side, frequent v.s., report severe ab pain stat, no heavy lifting 1wk.
549.
Paracentesis?
Paracentesis- semi fowlers or upright on edge of bed, empty bladder. Post- v.s., report elevated temp, observe for signs of hypovolemia.
550.
Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy- CO2 used to enhances visual, general anesthesia, foley. Post- walk patient to decrease CO2 build up used for procedure.
551.
Sengstaken blakemore tube ?
Sengstaken blakemore tube used for tx of esophageal varices, keep scissors at bedside.
552.
Hemovac?
Hemovac- used after mastectomy, empty when full or q8hr, remove plug, empty contents, place on flat surface, cleanse opening and plug with alcohol sponge, compress evacuator completely to remove air, release plug, check system for operation.
553.
Common S/S of PTB?
Common Signs and Symptoms 01. PTB - low-grade afternoon fever.
554.
Common S/S of pneumonia?
Rusty sputum
555.
Common S/S of asthma
Wheezing on EXPIRATION
556.
Common S/S of emphysema?
Barrel chest
557.
Common S/S of Kawasaki syndrome?
Strawberry tongue
558.
Common S/S of pernicious anemia
red beefy tongue
559.
Common S/S of down syndrome
protruding tongue
560.
Common S/S of Cholera?
Rice watery stool
561.
Common S/S of Malaria?
Stepladder like fever with chills
562.
Common S/S of Thypohiod
Rose spots on abdomen
563.
Common S/S of Diptheria?
Psuedo membrane formation
564.
Common S/S of measles?
Kopliks spots
565.
Common S/S of SLE?
Butterfly rashes
566.
Common S/S of Liver cirrhoisis?
Spider like varices- Varices can be in stomach, esophagus or the skin! They are just spider/varicose veins! Ithcy on the skin
567.
Common S/S of leprosy?
Lioning face
568.
Common S/S of Bulimia?
chipmunk face
569.
Common S/S of appendicitis
rebound tenderness
570.
Common S/S of Dengue
petechiae or + Herman's sign
571.
Common S/S of Meningitis?
Kernigs Sign (leg flex then leg pain on extension) Brudinzski sign (neck flex= lower leg flex)
572.
Common S/S of Tetany?
Risus Sardonicus
573.
Common S/S of pancreatitis?
Cullens sign ( ecchymosis of umbilicus) (+) Grey Turner spots
574.
Common S/S of pyloric stenosis?
olive like mass
575.
Common s/s of PDA
Machine like murmur
576.
Common S/S of addisions?
bronze like skin pigmentation
577.
Common S/S of Cushings syndrome?
Moon face appearance and buffalo hump
578.
Common S/S of Intusseption?
Sausage shaped mass , Dance sign (empty portion of RLQ)
579.
Common S/S of MS>?
Charcot's Triad (IAN)
580.
Common S/S of MG?
Descending muscle weakness
581.
Common S/S of guillian Barre Syndrome
Ascending muscle paralysis.. dont confuse with MG
582.
Common S/S of chicken pox?
Vesicular rash (central to distal) dew drop on rose petal
583.
Common S/S of LTB?
inspiratory stridor.. LTB = croup!!!!
584.
Common S/S of TEF?
4 C'S- Coughing, Choking, Cyanosis and continuous droolings
585.
Common S/S of epiglottitis?
3 D'S --Drooling, Dysphonia, Dysphagia
586.
Common S/S of Hodgkins Disease/Lymphoma?
Painless, progressive englargement of spleen and lymph tissues, and Reedstenberg cells!
587.
Common S/S of Infectious Mononucleosis?
Hallmark= Sore throat, cervical lymph adenopathy, fever
588.
Common S/S of parkinsons?
Pilling rolling tremors
589.
Cmmon S/S Fibrin Hyalin?
Expiratory grunt-- Causes Infant respiratory distress!
590.
Common S/S of cystic fibrosis?
Salty skin
591.
Common S/S of DKA
Kussmauls breathing (deep rapid RR)
592.
Common S/S of Bladder Cancer?
painless hematuria... CA=Cancer ! Duhh
593.
Common S/S of BPH?
reduced size and force of urine
594.
Common S/S of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Nilosky's sign (seperation of epidermis caused by rubbibng of the skin)
595.
Common S/S of retinal detachment?
Visual floaters, flashes of light, curtain vision
596.
Common S/S of glaucoma?
Painful vision loss, tunnel/gun barrel/ halo vision (peripheral vision loss)
597.
Common S/S of Cataract?
PainLESS vision loss, opacity of lens, blurring of the vision
598.
Common S.S of Retino Blastoma?
Cat's eye reflex (grayish discoloration of the pupil)
599.
Common S/S Acromegaly?
Coarse facial features
600.
Common S/S Duchennes Muscular Dystrophy?
Gower's sign (use of the hands to push ones self from the floor_) Looks EXACTLY like the Pilates Downward dog!!!!!!!
601.
Common S/S of GERD?
Barrets Esophagus (erosion of the lower portion of the esophageal mucosa)
602.
Common S/S Hepatic Encephalopathy ?
Flapping tremors
603.
Common S/S of Hydrocephalosis?
Bossing Sign (prominent forehead)
604.
Common S/S of Increased I?
HYPERTENSION, BRADYpnea, BRADYcardia (cushings triad)!
605.
Common S/S of Shock?
HYPERtension TACHYpnea and TACHYcardia
606.
Common S/S Meniere's Disease?
Vertigo, Tinnitus
607.
Common S/S of Cystitis?
Burning on urination
608.
Common S/S of hypocalcemia?
Chvostek and Trosseaus sign! Also hypomag!
609.
Common S/S of Ulcerative Colitis?
Recurrent bloody diarrhea
610.
Common S/S of Lyme's disease
Bull's eye rash
611.
Common S/S of Basilar Fracture?
Ottorhea
612.
Common S/S of orbital fracture?
Battles Sign and Racoon's eyes
613.
Osteomyeltitis?
Osteomyletitis is an infectious bone dz. Give blood cultures and antibiotics, then if necessary surgery to drain abscess.
614.
Nephrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome s/s edema + hypotension. Turn and reposition (risk for impaired skin integrity)
615.
Renal impairment labs?
Renal impairment: serum creatinine elevated and urine clearance decreased
616.
Normal Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin Neonates 18-27 3 mos 10.6-16.5 3 yrs 9.4-15.5 10 yrs 10.7-15.5
617.
Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis: take vs q 4 hrs + daily weights
618.
Age 4=5 year shots?
Age 4 to 5 yrs child needs DPT/MMR/OPV
619.
Cystic fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis give diet low fat, high sodium, fat soluble vitamins ADEK. Aerosal bronchodilators, mucolytics and pancreatic enzymes.
620.
More info on droplet precautions?
Droplet Precautions:sepsis, scarlet fever, streptococcal pharyngitis, parovirus B19, pnuemonia, pertusis, influenza, diptheria, epiglottis, rubella, mumps, meningitis, mycoplasma and adenovirus. Door open, 3 ft distance, private room or cohort, mask
621.
Meningeal irriatation>?
Meningeal irritation S/s nuchal rigidity, positive Brudzinski + Kernig signs and PHOTOPHOBIA too!
622.
Babinski sign?
toes curl= GREAT Toes fan = BAD
623.
GTT for preggos?
Glucose Tolerance Test for preggies result of 140 or highter needs further evaluation.
624.
Cranial nerves for Assessing extraocular eye movements?
3,4,6
625.
Stomas?
Stomas dusky stoma means poor blood supply, protruding means prolapsed, sharp pain + rigidity means peritonitis, mucus in ileal conduit is expected.
626.
Tension Pneumothorax?
Trachea shifts to the opposite side
627.
Change in color is ?
a LATE sign! Always~!
628.
Incentive Spirometry steps?
Incentive Spirometry steps:1) Sit upright 2) Exhale 3) Insert mouthpiece 4) Inhale for 3 seconds, and then HOLD for 10 seconds
629.
MRSA and VRSA precautions?
*MRSA - precaution ONLY *VRSA - AND airborne precaution (Private room, door closed, negative pressure)
630.
Thrombocyopenia- bleeding precautions
*Thrombocytopenia -Bleeding precautions! 1)Soft bristled toothbrush 2)No insertion of anything! (c/i suppositories, douche)
631.
Burn Degrees?
1st Degree - Red and Painful 2nd Degree - Blisters 3rd Degree - No Pain because of blocked and burned nerves
632.
Menieres's disease?
*Meniere's Disease - diuretics to decrease endolymph in the cochlea, restrict Na, lay on affected ear when in bed. Triad: 1)Vertigo 2)Tinnitus 3)N/V
633.
Gastric ulcer pain
*Gastric Ulcer pain occurs 30 minutes to 90 minutes after eating, not at night, and doesn't go away with food
634.
Med that can't be infused Intra osseously?
One medication that cannot be istered by intraosseous infusion is isoproterenol, a beta agonist.
635.
Sickle cell crisis?
During sickle cell crisis there are two interventions to prioritize: fluids and pain relief.
636.
Glomerulonephritis considerations
With glomerulonephritis you should consider blood pressure to be your most important assessment parameter. Dietary restrictions you can expect include fluids, protein, sodium, and potassium.
637.
Labs for congenital heart disease?
yesterday when I mentioned how congenital cardiac defects result in hypoxia which the body attempts to compensate for (influx of immature rbc's)? Labs ing this would show increased hematocrit, hemoglobin, and rbc count.
638.
Kidneys and ears?
Did you know there is an association between low-set ears and renal anomalies? Now you know what to look for if down's isn't there to choose. (just to expand on it a little, the kidneys and ears develop around the same time in utero. Hence, they're shaped similarly. Which is why when doing an assessment of a neonate, if the nurse notices low set or asymmetrical ears, there is good reason to investigate renal functioning. Knowing that the kidneys and ears are similar shapes helped me this).
639.
School aged kids and five year olds?
School-age kids (5 and up) are old enough, and should have an explanation of what will happen a week before surgery such as tonsillectomy.
640.
What if a toddler says no to medication?
If you gave a toddler a choice about taking medicine and he says no, you should leave the room and come back in five minutes, because to a toddler it is another episode. Next time, don't ask.
641.
First sign of pyloric stenosis in a baby?
The first sign of pyloric stenosis in a baby is mild vomiting that progresses to projectile vomiting. Later you may be able to palpate a mass, the baby will seem hungry often, and may spit up after feedings.
642.
Kawasaki disease causes?
We know Kawasaki disease causes a heart problem, but what specifically? Coronary artery aneurysms d/t the inflammation of blood vessels.
643.
A child with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt
A child with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt will have a small upper-abdominal incision. This is where the shunt is guided into the abdominal cavity, and tunneled under the skin up to the ventricles. You should watch for abdominal distention, since fluid from the ventricles will be redirected to the peritoneum. You should also watch for signs of increasing intracranial pressure, such as irritability, bulging fontanels, and high-pitched cry in an infant. In a toddler watch lack of appetite and headache. Careful on a bed position question! Bed-position after shunt placement is flat, so fluid doesn't reduce too rapidly. If you see s/s of increasing i, then raise the hob to 15-30 degrees.
644.
What could cause bronchopulmonary dysplasia?
What could cause bronchopulmonary dysplasia? Dysplasia means abnormality or alteration. Mechanical ventilation can cause it. Premature newborns with immature lungs are ventilated and over time it damages the lungs. Other causes could be infection, pneumonia, or other conditions that cause inflammation or scarring.
645.
How do children less than one breathe?
It is essential to maintain nasal patency with children < 1 yr. because they are obligatory nasal breathers.
646.
Milk for kids?
Watch out for questions suggesting a child drinks more than 3-4 cups of milk each day. (Milks good, right?) Too much milk reduces intake of other essential nutrients, especially iron. Watch for anemia with milk-aholics. And don't let that mother put anything but water in that kid's bottle during naps/over-night. Juice or milk will rott that kids teeth right out of his head.
647.
Traction in kids?
What traction is used in a school-age kid with a femur or tibial fracture with extensive skin damage? Ninety, ninety. Huh? I never heard of it either. The name refers to the angles of the ts. A pin is placed in the distal part of the broken bone, and the lower extremity is in a boot cast. The rest is the normal pulleys and ropes you're used to visualizing with balanced suspension. While we're talking about traction, a kid's hinder should clear the bed when in Bryant's traction (also used for femurs and congenial hip for young kids).
648.
Yeast infection in a babys mouth?
If you can remove the white patches from the mouth of a baby it is just formula. If you can't, its candidiasis.
649.
MMR and Varicella?
Just know the MMR and Varicella immunizations come later (15 months).
650.
Cryptoorchidism?
Undescended testis or cryptorchidism is a known risk factor for testicular cancer later in life. Start teaching boys testicular self exam around 12, because most cases occur during adolescence.
651.
Maslow for a guy who lost his house in a fire?
- A guy loses his house in a fire. Priority is using community resources to find shelter, before assisting with feelings about the tremendous loss. (Maslow).
652.
Kids pain relief in NCLEX land?
No aspirin with kids b/c it is associated with Reye's Syndrome, and also no nsaids such as ibuprofen. Give Tylenol.
653.
How will CSF look in meningitis?
CSF in meningitis will have high protein, and low glucose.
654.
Suctioning is good--except
No nasotracheal suctioning with head injury or skull fracture.
655.
Peds positioning for GERD?
Position prone w hob elevated with gerd. In almost every other case, though, you better lay that kid on his back (Back To Sleep - SIDS).
656.
When instilling eardrops?
Pull pinna down and back for kids < 3 yrs. when instilling eardrops.
657.
Kids with RSV?>
Kids with RSV; no lenses or pregnant nurses in rooms where ribavirin is being istered by hoot, tent, etc.
658.
Positioning with pneaumonia?
Positioning with pneumonia - lay on the affected side to splint and reduce pain. But if you are trying to reduce congestion the sick lung goes up. (Ever had a stuffy nose, and you lay with the stuff side up and it clears?)
659.
TB test confirmation?
A positive ppd confirms infection, not just exposure. A sputum test will confirm active disease.
660.
Asthmas and wheezers?
Coughing w/o other s/s is suggestive of asthma. Speaking of asthma, watch out if your wheezer stops wheezing. It could mean he is worsening.
661.
What treats tet spells?
Tet spells treated with morphine.
662.
Group-A strep?
Group-a strep precedes rheumatic fever. Chorea is part of this sickness (grimacing, sudden body movements, etc.) and it embarrasses kids. They have t pain. Watch for elevated antistreptolysin O to be elevated. Penicillin!
663.
Tylenol poisioining ?
Tylenol poisoning - liver failure possible for about 4 days. Close observation required during this time-frame, as well as tx with Mucomyst.
664.
Radioactive iodine?
Radioactive iodine - The key word here is flush. Flush substance out of body w/3-4 liters/day for 2 days, and flush the toilet twice after using for 2 days. Limit w/patient to 30 minutes/day. No pregnant visitors/nurses, and no kids.
665.
Main hypersensitivity for antiplatelet drugs?
broncospasm (anaphylaxis)
666.
Common sites for metastatsis?
liver, brain, lung, bone, and lymph
667.
Orthostatis is verfied by?
a drop in presssure with increasing heart rate... Orthostatis= orthostatic hypotension
668.
Bence Jones protein in urine?
confirms multiple myeloma
669.
How do you treat a small bowel obstruction?
Don't fall for 'reestablishing a normal bowel pattern' as a priority with small bowel obstruction. Because the patient can't take in oral fluids 'maintaining fluid balance' comes first.
670.
G tube and J tubes are usually?
Other than initially to test tolerance, G-tube and J-tube feedings are usually given as continuous feedings.
671.
Side rail rules?
Four side-rails up can be considered a form of restraint. Even in LTC facility when a client is a fall risk, keep lower rails down, and one side of bed against the wall, lowest position, wheels locked.
672.
Post spleenectomy?
Pneumovax 23 gets istered post splenectomy to prevent pneumococcal sepsis.
673.
Potassium lab importance?
Let's say every answer in front of you is an abnormal value. If potassium is there you can bet it is a problem they want you to identify, because values outside of normal can be life threatening. Normal potassium is 3.5-5.0. Even a bun of 50 doesn't override a potassium of 3.0 in a renal patient in priority.
674.
Every new ission needs?
You will ask every new ission if he has an advance directive, and if not you will explain it, and he will have the option to sign or not.
675.
Potassium and acid base balance?
A little trick regarding potassium: ALKALOSIS: K is LOW Acidosis is just the opposite: K is High The vital sign you should check first with high potassium is pulse (due to dysrhythmias).
676.
What is bleeding considered in ADPIE?
Bleeding is part of the 'circulation' assessment of the ABCD's in an emergent situation. Therefore, if airway and breathing are ed for, a compound fracture requires assessment before Glasgow coma scale and a neuro check (D=disability, or neuro check)
677.
What to do in a sucking stab wound?
The immediate intervention after a sucking stab wound is to dress the wound and tape it on three sides which allows air to escape. Do not use an occlusive dressing, which could convert the wound from open pneumo to closed one, and a tension pneumothorax is worse situation. After that get your chest tube tray, labs, iv.
678.
What to do if your patients chest tube accidently getes removed?
An occulsive dressing is used
679.
Labs in DKA>?
Serum acetone and serum ketones rise in DKA. As you treat the acidosis and dehydration expect the potassium to drop rapidly, so be ready, with potassium replacement. Fluids are the most important intervention with HHNS as well as DKA, so get fluids going first. With HHNS there is no ketosis, and no acidosis. Potassium is low in HHNS (d/t diuresis).
680.
Decorticate and Decerebrate?
Decorticate positioning in response to pain = Cortex involvement. Decerebrate in response to pain = Cerebellar, brain stem involvement
681.
Other S/S of MS?
Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, vision changes, fatigue and spasticity are all symptoms of MS
682.
After removal of the pituitary gland what should you watch for?
After removal of the pituitary gland you must watch for hypocortisolism and temporary diabetes insipidus.
683.
After appendectomy?
position on the RIGHT side with legs flexed
684.
Hirschsprungs is dx how?
Hirschsprung's diagnosed with rectal biopsy looking for absence of ganglionic cells. Cardinal sign in infants is failure to meconium, and later the classic ribbon-like and foul smelling stools.
685.
More info on intussception?
Intussusception common in kids with CF. Obstruction may cause fecal emesis, currant jellylike stools (blood and mucus). A barium enema may be used to hydrostatically reduce the telescoping. Resolution is obvious, with onset of bowel movements.
686.
Omphalocele?
With omphalocele and gastroschisis (herniation of abdominal contents) dress with loose saline dressing covered with plastic wrap, and keep eye on temp. Kid can lose heat quickly.
687.
Hydrocele?
After a hydrocele repair provide ice bags and scrotal .
688.
PKU ?
No phenylalanine with a kid positive for PKU (no meat no dairy no aspartme
689.
When to test urine for ketones and glucose?
Second voided urine most accurate when testing for ketones and glucose.
690.
Nepphrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria (looks dark and frothy) caused by glomerular damage. Corticosteroids are the mainstay. Generalized edema common.
691.
Western blot test?
A positive Western blot in a child <18 months (presence of HIV antibodies) indicates only that the mother is infected. Two or more positive p24 antigen tests will confirm HIV in kids <18 months. The p24 can be used at any age.
692.
Kids with HIV?
For HIV kids avoid OPV and Varicella vaccinations (live), but give Pneumococcal and influenza. MMR is avoided only if the kid is severely immunocompromised. Parents should wear gloves for care, not kiss kids on the mouth, and not share eating utensils.
693.
What will alter the accuracy of o2 sats?
Hypotension and vasoconstricting meds
694.
Room air is?
Ambient air (room air) contains 21 % o2
695.
The first s/s of ards?
The first sign of ARDS is increased respirations. Later comes dyspnea, retractions, air hunger, cyanosis.
696.
PCWP
Normal PCWP (pulm capillary wedge pressure) is 8-13. Readings of 18-20 are considered high.
697.
First sign of pe?
First sign of PE is sudden chest pain, followed by dyspnea and tachypnea.
698.
Carbon dioxide narcosis?
High potassium is expected with carbon dioxide narcosis (hydrogen floods the cell forcing potassium out). Carbon dioxide narcosis causes increased intracranial pressure.
699.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis?
Pulmonary sarcoidosis leads to right sided heart failure..Sarcidosis is basically scar tissue build up
700.
NG tube rules?
An NG tube can be irrigated with cola, and should be taught to family when a client is going home with an NG tube.
701.
If your patient starts seeing bugs?
If your normally lucid patient starts seeing bugs you better check his respiratory status first. The first sign of hypoxia is restlessness, followed by agitation, and things go downhill from there all the way to delirium, hallucinations, and coma. So check the o2 stat, and get abg's if possible.
702.
Cold stress in a newborn?
The biggest concern with cold stress and the newborn is respiratory distress.
703.
A preggo in a minus station?
If your laboring mom's water breaks and she is any minus station you better know there is a risk of prolapsed cord.
704.
R in a five year old?
In a five-year old breathe once for every 5 compressions doing r.
705.
After Gtube placement?
After g-tube placement the stomach contents are drained by gravity for 24 hours before it can be used for feedings.
706.
Cephalhematoma (caput succinidanium)?
Cephalhematoma (caput succinidanium) resolves on its own in a few days. This is the type of edema that crosses the suture lines.
707.
Hep A precautions?
During the acute stage of Hep-A gown and gloves are required. In the convalescent stage it is no longer contagious.
708.
More labs suggestive of renal failure?
Low magnesium and high creatinine signal renal failure.
709.
Hightest priority for RA?
Pain is usually the highest priority with RA
710.
TB health risk?
If a TB patient is unable/unwilling to comply with tx they may need supervision (direct observation). TB is a public health risk.
711.
Highest priortiy in status elipticus?
Level of consciousness is the most important assessment parameter with status epilepticus.
712.
Crackles most likely are?
Crackles suggest pneumonia, which is likely to be accompanied by hypoxia, which would manifest itself as mental confusion, etc.
713.
Anorexia sucks because?
Absence of menstruation leads to osteoporosis in the anorexic.
714.
Low crit/hemoglobin?
A patient with a low hemoglobin and/or hematocrit should be evaluated for signs of bleeding, such as dark stools.
715.
More IVP info?
A laxative is given the night before an IVP in order to better visualize the organs.
716.
Pt with edema and walking?
A patient with liver cirrhosis and edema may ambulate, then sit with legs elevated to try to mobilize the edema.
717.
High priority in Addisons?
Managing stress in a patient with adrenal insufficiency (Addison's) is paramount, because if the adrenal glands are stressed further it could result in Addisonian crisis. While we're on Addison's, blood pressure is the most important assessment parameter, as it causes severe hypotension.
718.
Pancreatitis prioritys?
After pain relief, cough and deep breathe is important in pancreatitis, because of fluid pushing up in the diaphragm.
719.
Likely cause of cardiac arrest in child?
Prolonged hypoxemia is a likely cause of cardiac arrest in a child.
720.
What can also cause an s3 heart sound?
Fluid volume overload caused by IVC fluids infusing too quickly (or whatever reason) and CHF can cause an S3
721.
coarctation of the aaorta causes?
Coarctation of the aorta causes increased blood flow and bounding pulses in the arms
722.
If you THINK a patient has new HTN?
A newly diagnosed hypertension patient should have BP assessed in both arms
723.
Depression manifests itself?
Depression often manifests itself in somatic ways, such as psychomotor retardation, gi complaints, and pain.
724.
Chief concern in CF
Respiratory problems!
725.
More info on TB testing a positive result?
speaking of TB... PPD is positive if area of induration is: >5 mm in an immunocompromised patient >10 mm in a normal patient >15 mm in a patient who lives in an area where TB is very rare.
726.
Hba1c?
HbA1c - test to assess how well blood sugars have been controlled over the past 90-120 days. 46 corresponds to a blood sugar of 70-110; 7 is ideal for a diabetic and corresponds to a blood sugar of 130.
727.
Most accurate way to test kids for medication accuracy?
BSA is considered the most accurate method for medication dosing with kids. (I though it was weight, but apparently not)
728.
Placement of a wheelchair?
Place a wheelchair parallel to the bed on the side of weakness
729.
If you see a nurse make a mistake? Chain of command?
If one nurse discovers another nurse has made a mistake it is always appropriate to speak to her before going to management. If the situation persists, then take it higher.
730.
Besides meds and congenital problems .. what can lead to decreased preload ?
Sepsis and anaphylaxis (along with the obvious hemorrhaging) reduce circulating volume by way of increased capillary permeability, which leads to reduced preload (volume in the left ventricle at the end of diastole). This is a toughie...think about it.
731.
Nitrazine paper?
Amniotic fluid is alkaline, and turns nitrazine paper blue. Urine and normal vaginal discharge are acidic, and turn it pink.
732.
STD= gonnorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a reportable disease
733.
Crutch use?
the phrase "step up" when picturing a person going up stairs with crutches. The good leg goes up first, followed by the crutches and the bad leg. The opposite happens going down. The crutches go first, followed by the good leg.
734.
MORE info on DKA? ugh!
While treating DKA, bringing the glucose down too far and too fast can result in increased intracranial pressure d/t water being pulled into the CSF. Polyuria is common with the hypercalcemia caused by hyperparathyroidism.
735.
Nonfat milk?
Nonfat milk reduces reflux by increasing lower esophageal sphincter pressure
736.
Gerd again?
Patients with GERD should lay on their left side with the HOB elevated 30 degrees.
737.
To prevent dumping syndrome?
Unusual positional tip - Low-fowlers recommended during meals to prevent dumping syndrome. Limit fluids while eating.
738.
Emphysema?
In emphysema the stimulus to breathe is low PO2, not increased PCO2 like the rest of us, so don't slam them with oxygen. Encourage pursed-lip breathing which promotes CO2 elimination, encourage up to 3000mL/day fluids, high-fowlers and leaning forward.
739.
Kernigs sign?
One of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis is Kernig's sign. Severe stiffness of the hamstrings causes an inability to straighten the leg when the hip is flexed to 90 degrees.
740.
Brudzinski's sign?
One of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis is Brudzinski's sign. Severe neck stiffness causes a patient's hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed ( The kid knees will fly up and he lift his bum off the table cause it hurts his neck)
741.
Phenalalanine?
It is an amino acid that is BAD for people with PKU. It is found in food only and is also found in aspartame
742.
Vertical C section?
Used in plus sized women or risky or emergency c sections. less chance of harm for the baby
743.
Dystocia?
Just means a difficult or abnormal delivery or birth... example.. shoulder dystocia
744.
Peritoneal dialysis?
On the other hand, peritoneal dialysis does not require that the patient's blood be pumped outside of his body. Instead, the blood is cleaned while still inside the body. The organs in the abdomen are surrounded by the peritoneum, which is a membrane that allows waste products to through it. Peritoneal dialysis uses a Tenckhoff catheter to run the dialysis fluid, a sugar solution with some salts, into the abdominal, or peritoneal, cavity. This allows the patient's blood to be filtered without pumping it through a dialysis machine. A Tenkhoff catheter is usually used in peritoneal dialysis
745.
Why would somone who is allergic to latex be allergic to food too?
CROSS REACTION! People who have a latex allergy may be allergic to some foods, as well. This is called a cross reaction. When this happens, your body responds with the same allergic symptoms that you would have if you were exposed to latex. Cross reactions differ from one person to another. Someone may have a reaction to all the foods noted to cause cross reaction while another may have no reaction at all. Likewise, if you are allergic to any of these foods, you may also be allergic to latex: •apples, bananas, kiwi, peaches, plums, figs, grapes, melons, papaya, ion fruit, cherries, nectarines, pears, pineapple and strawberries; •carrots, celery, raw potatoes, avocados and tomatoes; •chestnuts and hazelnuts; •wheat and rye.
746.
Acid/ ASH diet?
The acid ash diet has nothing to do with weight loss. It is a diet intended for health and may be prescribed by your physician to control illness or disease. Once your liver has metabolized the food you ingest, it leaves a mineral deposit, known as ash, which can be acidic or alkaline depending on its effect on the pH of your urine. Eating foods that create an acid ash may help to balance your system or create a hostile environment to inhibit bacterial growth. .... Acid/ ash diet is used to BALANCE the acid/alkaline ash in the body... Ash wiill affect the urinary system and even the nervous system. Imbalance will be diet modified
747.
PTB means?
Pumonary tuberculosis
748.
Psuedomembrane in DIptheria?
Diptheria is an upper respiratory tract infection. It is characterized by sore throat, low fever and the psuedomembrane! Which is just a capsule around the tonsils that you can see with your penlight... It just looks like a whiteish yellow capsule around the tonisils
749.
SLE?
Systemic Lupus Ethramoutus.... (Lupus)
750.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Hermans sign= flushes and redness of skin with lighter color at the center of the rash.... It is a disease that comes from tropical and subtropical areas that are spread by misquotos
751.
Risus Sardonicus?
Risus sardonicus is a highly characteristic, abnormal, sustained spasm of the facial muscles that appears to produce grinning--- From Tetany! Sad and scary looking! Never Google image it again, Megan! Nightmares!
752.
Grey Turners sign?
Purple bruises around the belly button... Pancreatitis!
753.
PDA?
patent ductuous arteriousus in infants! Valve doesn't close!
754.
Dance Sign?
Dance's sign: RUQ mass (intussusception) with RLQ empty space (movement of cecum out of normal position).
755.
Charcots sign?
A. Charcot's triad for multiple sclerosis 1. Nystagmus 2. Intention tremor 3. Scanning or staccato speech
756.
MG and Guillian Barre?
Opposites! Nursing connection! Think about it!
757.
Chvostek and Trosseaus sign
Chvostek= Tapping on the face above the cheek bone will cause spams! Trosseaus= using a BP cuff and inflating it, and it will cause spasms of the wrist
758.
VRSA?
Staph infection that is resistant to Vancomycin treatement! Worse than MRSA
759.
Tet spells?
Children with tetralogy of Fallot may develop "tet spells". The precise mechanism of these episodes is in doubt, but presumably results from a transient increase in resistance to blood flow to the lungs with increased preferential flow of desaturated blood to the body. Tet spells are characterized by a sudden, marked increase in cyanosis followed by syncope, and may result in hypoxic brain injury and death. Older children will often squat during a tet spell, which increases systemic vascular resistance and allows for a temporary reversal of the shunt.
760.
HHNS Vs DKA
· Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a condition of DKA=insulin deficiency resulting in acidemia due to altered metabolism. · Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) is primarily a disorder of dehydration due to hyperglycemia
761.
Pancreatitis
NPO, TPN May be used
762.
Diverticulitis
Clear liquids to high fiber
763.
Cholecystis
Low-fat diet
764.
Liver disease
Decreased protein intake
765.
Celiac disease
Avoid glutens
766.
Nausea and vomiting
Clear liquids
767.
Gout
Avoid purines
768.
Dumping syndrome
Small frequent meals
769.
GERD
Avoid large meals, eating late, alcohol caffeine
770.
Monitor for digoxin
Potassium
771.
Monitor for acetaminophen
Temperature
772.
Monitor for glipizide
Blood glucose
773.
Monitor for morphine
Respiratory rate
774.
Monitor for prednisone
Delayed wound healing
775.
Monitor for warfarin
INR
776.
Monitor for zolpidem
Sleep patterens
777.
Monitor for Olanzapine
Mood
778.
Monitor for Levoflaxacin
Culture and sensitivity
779.
Erikson stage 0-1, posterior fontanelle closes at 2 to 3 months, 1 to 5 m grasp rattle 6 m transfer between hands, 8-9 m uses pincer grasps, nine months bangs toys together, 3 m holds head, 5-6 m rolls, 9m sits up on own, 12 m stands alone
Trust vs mistrust, meet social and developemental needs
780.
Erikson stage 1-3, feeds self, anterior fentanyl closes, steady gait, draw stick figure, potty train, need routines and rituals
Autonomy vs shame and doubt, provide acceptable options
781.
Erikson stage 3-6, hopping, draws shapes, walking heel to toe
Initiative vs. guilt, provide age appropriate activities, stranger danger
782.
Erikson stage 6-12 or games, rides bicycle, build models, organize sports, puzzles games, video games
Industry vs inferiority, encourage participation in care
783.
Erikson stage 12-20 pure activities, music interest, career training, sexual maturiation, STI's, pregnancy, substance abuse
Identity vs role confusion, Provide groups of same age
784.
Erikson stage 20-35 leaves families and seeks relationships, growth ends childbearing, established career,
Intimacy vs isolation, provide private time with partner
785.
Erikson stage 35-65 bouncing life, aging parent, adult children, grandchildren, career transition, retirement, menopause, osteoporosis, decrease in visual and hearing
Generativity vs stagnation
786.
Erikson stage 65+, decreased skin elasticity, decreased cough reflects, lower cardiac output, peridontal disease
Integrity vs despair, use personal items were not home
787.
Antidote for opoids
Naloxone
788.
Antidote for warfarin
Vitamin K
789.
Antidote for acetaminophen
Acetylcystiene
790.
Antidote for heparin
Protamine sulfate
791.
Antidote for benzodiazepine
Flumaxenil
792.
Antidote for digitalis
Digoxin immune fab
793.
Antidote for lead
Succimer
794.
Antidote for magnesium
Calcium gluconate
795.
When mixed with regular insulin draw this medication up last, 4-6 hr peak time
NPH
796.
Have client eat as soon as this medication is given
Lispro
797.
Hold this medication 48 hours before and after use of contrast dye
Metformin
798.
Given subcutaneously and has no peak time
Glargine
799.
May be used to lower potassium levels, can be given IV, also for DKA
Regular insulin
800.
Type of solution for TPN
Hypertonic
801.
Routes TPN can be given
Picc line, tunneled catheter
802.
TPN is prepared how often
Daily
803.
TPN is hung every_ hours
24
804.
Standard precaution requirements
Nothing, gloves prn
805.
precaution requirements (body fluids)
Gloves and gown
806.
Droplet precaution requirements (air)
Mask
807.
Airborne precaution requirements (air)
Mask
808.
Normal sodium level
135-145
809.
Normal potassium level
3.5-5
810.
Normal calcium level
9-10.5
811.
Normal carbon dioxide level
35-45
812.
Normal hydrochloride level
21-28
813.
Normal hemoglobin level
14-18
814.
Normal Hct level
37-52%
815.
Normal WBC level
5,000-10,000
816.
Normal cholesterol level
<200
817.
Normal platelets
150,000-400,000 (enoxaparin sodium)
818.
Normal P T
11-12.5 sec, rx: 1.5-2x (Coumadin)
819.
normal aptt
30-40 sec rx 1.5-2x (heparin)
820.
Normal INR
0.7-1.8, rx 2-3x (Coumadin)
821.
Normal glucose fasting
70-105
822.
Normal HbA1c (glycosylated hgb)
4-6%
823.
Normal BUN level
10-20
824.
Normal creatinine level
0.5-1.2
825.
Arterial supply
Goes down in legs
826.
Venous supply
Goes up in legs
827.
Red tag
Emergent
828.
Yellow tag
Urgent within 1 to 2 hours
829.
Green tag
Non-urgent 2 to 4 hours
830.
Black tag
Not seen don't have survival potential
831.
LPNs cannot what
Evaluate Assess teach, can reinforce or reteach, iv therapy, blood therapy rhogam
832.
Medication to hold prior to ECT
Dilantin or other medications that alter brain activity
833.
How long post surgery to be on blood thinners
30 days
834.
Priority if chest tube comes out
Cover with Vaseline soaked gauze
835.
Ebola
Hemorrhagic fever, w/ out symptoms quarenteen for 21 days
836.
System affected by methotrexate (steroid)
Immune system, decreased white blood cells and decreased platelets
837.
System affected by sodium levels
Neurological system, seizures occur with low levels
838.
Anti-cholinergic drugs side effects
No see no Pee no stool no drool
839.
Versed
Pt cannot sign for anything after recieving
840.
16 y.o can be a majority if
Married, emancipated, or has child
841.
ED triage
Treat most severe injury first
842.
Mass casualty triage
Do the greatest good for the greatest number
843.
Magnesium
drip needs to have one-to-one, due to side effects (absent deep tendon reflexes), monitor BP, resp, DTR, used for preclampsia
844.
Meningitis
symptoms: Headache, Stiff neck and photosynthesis, Diagnostics: spinal fluid (lumbar puncture) blood cultures, Prevention: Hand washing, immunization, Assessments: Brudzinski (pain with Head to breast bone) Kernigs (Pain with knee up to chest) Living in close spaces can cause this.
845.
Priority for MI
Apply oxygen first
846.
2 pt gait
Partial weight-bearing on extremity walking with crutches right leg left crutch as if they were skiing
847.
3 pt gait
Nonweightbearing swing through crutches
848.
4 pt gait
Stability partial weight-bearing on both extremities right leg right crutch
849.
Walker
Step into it, arm's-length away, don't pull self up with device
850.
Cane
Always on the strong side
851.
Up stairs
Strong leg first
852.
Down stairs
Weak leg first
853.
Yogurt
Form of calcium for lactose intolerant patients
854.
Diet for Christianity
Don't eat meat on ash Wednesday or Fridays of light may have days of fasting
855.
Diet for Buddhism
Avoid beef pork seafood
856.
Judaism diet (Muslims)
Kosher- can't mix milk and meat no pork avoid fish that don't have scales
857.
Hinduism diet
No beef, may fast, many are vegetarian
858.
Interventions for dumping syndrome
Lay down after eating, avoid drinking one hour before and one hour after eating, avoid sugar and milk
859.
Interventions for eternal nutrition
Start slow increase rate every 8 to 12 hours, greater than 100 residue fluid hold fluid, head of bed 30° or higher, assess for signs of intolerance, first feeding have x-ray every other check pH.
860.
Lithium toxicity
Can occur if greater than two
861.
Zolpidem
(Ambien) sleepwalk and cannot
862.
Side affects of anti-psychotics (typical)
Sedation, EPS, and anti-cholinergic effects
863.
Adverse affects of antipsychotics
Tardive dyskinesia,such as thumb rolling And eye emovements, Agranulocytosis, neuroleptic malignment syndrome, siezures
864.
Risedronate
Don't lay down right away
865.
Fentanyl patch
Remove with temperature, one for three days, don't put heating pad over it
866.
Gentamicin
Don't use if damage to kidneys when used with furosemide can cause hearing loss at high doses
867.
Amoxicillin
Be aware with cephalosporins allergy
868.
Ceftriaxone
Can create C diff
869.
Adverse effects
Life-threatening
870.
varenicline
Only use up to 12 weeks for smoking cessation
871.
Calcium channel blocker's, beta blockers, ARBs, ace inhibitors
Blood-pressure medications
872.
Calcium channel blocker's side effects
Bradycardia, decreased contractility, peripheral edema
873.
Ace inhibitor side effects
Dry hacking cough, angioedema
874.
20 gauge catheter
Can be used for packed RBCs, dextrose 5%, 9% sodium chloride, not used for TPN, amirodone, vancomycin
875.
Clean wound with _ before getting culture
Saline or sterile water
876.
V tach
First action drug Amerodone then lidocaine then prepare for cardioversion
877.
CAGE
Screening tool for alcoholism, cutdown use of alcohol, ever felt anger when people tell you to cut down, ever feel guilty about how much you drink, eye-opener to quit
878.
Wilms tumor
On adrenal gland needs to be removed prior to bursting
879.
1 pound
3500 calories
880.
Intropic agents
Increases myocardial contraction, and cardiac output, digoxin, dopamine, dubotamine
881.
Digoxin toxicity
Halos around everything, <6
882.
Dopamine and dubotamine
Monitor heart rate urine output and blood pressure
883.
BNP
Diagnostic test for CHF, normal is lower than 100, 100 to 300 heart failure is possible, 300 to 600 heart failure is mild, 600-900 moderate heart failure, severe hf > 900
884.
Packed RBCs
Treat anemia, monitor hemoglobin
885.
Platelets
Treats thrombocytopenia, monitor platelets
886.
Plasma
Treats Burns, monitor albumin, 3.5-5
887.
Factor 8
Treats hemophilia, monitor ptt
888.
1 unit of blood
Expect 1g/dl increase in hgb ex. 7.8-8.8
889.
Kidneys
Monitor I&O, electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, Hgb, BP (BUN & creatinine increases with kidney failure)
890.
Complications with central lines
Pneumothorax, air embolism, occlusion, infection, with air embolism lay on left side and Trendelenburg position with insertion
891.
Hyperthyroidism
PTU & Tapazole, or remove thyroid (calcium at bedside) Think of Tigger orange and hyper
892.
Hypothyroidism
Levothyroxine, Think of eeyore, slow moving, depressed
893.
Affected system of potassium
Cardiac, cardiac arrest with severe levels
894.
Insulin withdrawal when mixing
Clear to cloudy (regular-NPH)
895.
Oxytocin
Monitor fhr, contractions, BP, hr, rr
896.
Quetiaphine fulmarate
Bipolar, monitor for suicidal thinking, dizziness, leukopenia
897.
Risperidone
Bipolar, monitor for sedation insomnia pseudoparkinsonism,
898.
Lithium carbonate
Bipolar, no levels of lithium,
899.
SSRI
Antidepressant that blocks reuptake of serotonin
900.
SNRI and tricyclics
Antidepressant that box reuptake of serotonin and norepinepherine
901.
MAOI
Focus on diet
902.
Atypical antidepressants
Selectively inhibits dopamine and stimulates CNS, side effects: seizures psychotic symptoms, Buproprion
903.
Developing cancer with birth control
Only with smoking
904.
Naegeles rule
1st day menstrual cycle-3 months, +7 days
905.
First stage of labor
Latent 0 to 3 cm, active 4 to 7, transition 8 to 10,
906.
Second stage of labor
Pushing stage
907.
Third stage of labor
Delivery of placenta
908.
Fourth stage of labor
Bonding with newborn
909.
Taking in phase
It's all about me
910.
Taking hold phase
It's all about the baby
911.
Letting go phase
Getting back to the new normal
912.
Anemia side effects
Weakness paler fatigue
913.
Anemia interventions
Food sources that contain red meat, organ meat, egg yolks, leafy green vegetables, use z track method for Iran dextran
914.
Blood compatibility
this by what factor they have a or B or both AB or neither o patient doesn't have that factor they can't receive the blood,
915.
Hemophilia signs and symptoms
Risk for bleeding, Hematomas, G.I. and G you bleeding, brain hemorrhage, and bleeding mucous membranes
916.
Hemophilia nursing interventions
Assess for t pain, monitor vitals, onister factor replacement, avoid injections and NSAIDs, assess LOC and bleeding
917.
MI diagnostic labs
Troponins
918.
Sickle cell anemia and crisis
Most common in African Americans, blood comes and causes severe pain, oxygen is limited to the cells of the body because cells cannot carry oxygen as well, don't do well in cold weather or high altitude
919.
Signs and symptoms of sickle cell anemia
Anemia, hypoxic damaged tissue, dehydration, susceptibility to infection, knowledge deficit and powerlessness
920.
Nursing interventions for sickle cell anemia
Oxygen as needed, manage pain, and her vitals, monitor H&H, Mr. fluids as needed, assess for signs and symptoms of infection, teach self-care, causes and prevention of crisis
921.
Cervical cancer
Contributing factors: HPV/ multiple partners, manifestations: abnormal bleeding, Dianosing: pap/DNA test, prevention: Gardisil
922.
Breast cancer
Contributing factors: family history, lifestyle, Manifestations: Lumps, thickening, Diagnosing: mammogram, Prevention: Diet, weight, excercise
923.
When is a colposcopy used?
abnormal pap test
924.
Stable angina
pt is awake and doing something when having chest pain. Pain is able to be treated with first nitro
925.
Unstable angina/ preinfarction
Moving around but not relieved with nitro.
926.
Prinemetal/ Coronary spasm
Sound asleep and woken up by pain in chest
927.
Protocol for American Heart Association regarding MI
Sit down take a nitro, wait 5 min, call 911, take another nitro, wait 5 min and take final nitro.
928.
Nursing interventions for MI
Morphine (decreases preload & afterload) Oxygen (First, treats ischemic myocardium) Nitro (increases coronary perfusion) Aspirin- (decreases clot formation) MONA
929.
Aortic femoral By (restoring blood supply to blocked area) interventions
peripheral pulses, skin temp, anticoags, avoid crossing legs, monitor site, KEEP BP LOW
930.
Heart sounds mnemonic
Ape to man Aortic, pulmonic, erbs point, tricuspid, mitral
931.
Where do I listen to S2?
aortic and pulmonic
932.
Where do I listen to S1?
tricuspid and mitral
933.
S3 and S4 sounds
kentucky (going into CHF) Tennessee (Angina)
934.
Angioplasty
NI: cardiac diet, check vitals every 15 min, cardiac monitor, pressure @ site. Complications: dysrhithmias, bleeding, hypovolemia
935.
P wave
atrium are contracting
936.
QRS
ventricles contract
937.
T wave
ventricles relax, Don't want PVC's to hit T wave
938.
Cardioversion
Use with unstable v tach, machine synchronizes with the heart rhythm because you do not want to hit the t wave
939.
v fib
whole ventricles are shaking like jello and not firing
940.
Common heart rhythm with anemia
Sinus tachycardia
941.
Left sided heart failure
Fluid backs up into lungs, crackles in lungs, dyspnea
942.
Right sided heart failure
Fluid backs up into heart, S3 gallop, peripheral edema
943.
Normal pulmonary wedge pressure
4-12
944.
Heart failure
NI: O2, fowlers, lung sounds, I&O, fluid restriction, daily weights, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, digitalis
945.
DKA
Symptoms include: kussmaul respirations, fruity breath
946.
Thyroidectomy
Check for positive Chvotesek sign
947.
Hyponatremia
Causes: Diuretics, renal disease, Treatment: SIADH, Symptoms: confusion-> seizures, muscle weakness, cramping
948.
Hypernatremia
Causes: Water deficit, Cushings, Symptoms: Confusion->siezures, muscle weakness
949.
Hypokalemia
Causes: Diuretics, corticosteriods, suctioning, diarhea. Symptoms: muscle weakness, shallow respirations, Dysrrhithmias
950.
Hyperkalemia
Causes: salt substitutes, renal failure, packed RBCs, Addisons Symptoms: Dysrhythmias, peaked T waves
951.
Addisons
Low cortisol
952.
Cushings
High cortisol (steroid symptoms)
953.
Kayexalate enema
pulls off potassium
954.
Hypocalcemia
Causes: hypoparathyroidism, renal failure, malabsorption Symptoms: Changes in HR, prolonged ST, tetany, changes in LOC, siezures
955.
Hypercalcemia
Causes: Hyperthyroidism, Excessive intake Symptoms: Dysrhithmias, cardiac arrest
956.
Isotonic
No fluid crosses the cell membrane 0.9%NS
957.
Hypotonic
fluid moves into the cell 0.45% NS
958.
Hypertonic
fluid moves out of the cell D5 NS
959.
Cirrhoises
Symptoms: hypertension, esophageal carices, clotting abnormalities, hepate encephalopathy, ascites, peritonitis. NI: Assess fluid balance, assess bleeding, safety precaustions, high calorie diet, fluid restrictions, low protien
960.
Rule of 9's
Each arm= 9%, Anterior leg=9%, Posterior leg=9% Head=9%, Back=18% Chest=18%, Perineum=1%
961.
Parkland formula
used for determining amount of lactated ringersfor burn patient. Begin time at time of burn. ister through central line and have foley cath. 4mL x kg x %TBSA= 1/2 total in first 8 hrs, 1/2 in remaining 16 hours
962.
Head injury
Signs: Changes in LOC, Increased I, Brady, tachypnea, hypo/hypertension, hyperthermia, bradycardia, posturing. Interventions: Assess neurostatus w/ glascow coma scale (higher the better), I & O, Elevate HOB, monitor electrolytes, decrease stimulation, monitor I, vitals, nutritional .
963.
Spinal shock
occurs right away, hypotension,
964.
Autnomic dyreflexia
Spinal injury, can occur after several weeks only in T6 or higher, hypertension, flushing, headache Treatment: lower BP and treat cause.
965.
Cervical spine
Top 8, worry about breathing
966.
Thoracic spine
Middle 12, quadroplegic
967.
Lumbar spine
Bottom 5, paraplegic
968.
Spinal cord injury
Intervention: Immobilization, assess respiratory status, assess vital signs, institue bowel sounds and bladder program, prevent DVT, urinary retention, constipation, skin break down.
969.
VEAL CHOP MINE
Menomic for decelerations Variable Cord compression Move patient Early Head compression Identify labor progress Accelearate Okay No action Late Placental insufficiency Execute STAT
970.
Precalampsia
NI: Monitor BP, protein in urine, weight, watch edema eclampsia occurs with seixures
971.
Uncompensated
pH is off and 1 other is off
972.
Partially compensated
pH is off as well as other two are off
973.
fully compensated
pH is normal other two are off
974.
Metabolic alkalosis
Vomiting loose acid and left with base
975.
Metabolic acidosis
Diarrhea loose base and left with acid
976.
High pressure with mechanical ventilation
NI: assess for need to suction, pt needs tomlet machine breath for them.
977.
Low pressure with mechanical ventilation
check tubes for leaks
978.
Cancer internal radiation
NI: visitors should maintain 6 feet away and visit no longer then 30 min, staff needs a dosimeter badge.
979.
Carseat
Middle of backseat for 2 years or 20 lbs
980.
Donning order
Gown-Mask- goggles-gloves-enter
981.
Doffing order
gloves- gown- goggles-mask
982.
Nasal Cannula
1-6 L/min over 2 needs humidifyer
983.
Simple face mask
6-8L/ min
984.
Venturi face mask
4-8L/min
985.
Non- Rebreather
12L/min
986.
RSV
contagious for 1 week after antibiotic
987.
C-Diff and VRE
use soap and water
988.
Droplet (infections)
measles, influenza, can cohort
989.
Airborne(infections)
chicken pox, TB, cant cohort
990.
(infections)
MRSA, C-diff can cohort
991.
Abuse phases
Tension building-> battering-> honeymoon-> tension building
992.
PTSD
symptoms are delayed, assess for irritibility, difficulty sleeping and concentration, decrease excessive stimulus, help evaluate coping mechanisms
993.
Bipolar disorder
Depression and mania, inflated self esteem, flight of ideas, buying sprees, decreased needs for sleep, coexist with substance abuse.
994.
Borderline personality disorder
Manipulative behavior
995.
Depression
R/f: female, unmarried, low socialeconomic class, postpartum period, medical illness, early child hood trauma. Symptoms: Insomnia, anergia, feelings of worthlessness decreased concentration.
996.
Grief
Denial-> Anger-> Bargaining-> Depression-> Acceptance
997.
Cluster A
Paranoid, schizoid, Schizotypal
998.
Cluster B
Antisocial, Borderline, Histronic, Narcissistic
999.
Cluster C
Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive Compulsive
1000.
When patient hears voices
"What are the voices saying to your?"
1001.
What does clubbing of the fingers mean?
chronic hypoxia
1002.
Cap refill reveals what?
end-organ perfusion
1003.
#1 thing to do with edema
elevate
1004.
Where to check for skin turgor?
Adult - chest child - abdomen/thigh
1005.
HR over what is tachycardic
100
1006.
In acid/base balance, poop is? vomit is?
Poop is base Vomit is acid
1007.
Where is apex of heart found
6th intercostal space mid-axillary
1008.
Where is PMI found
4th intercostal space mid-clavicular
1009.
Where is 6 month fetal heart rate found
halfway between umbilicus and symphysis pubis
1010.
What cannot be taken with CCBs
Grapefruit juice
1011.
What does digoxin do
Makes the heart pump harder
1012.
How many cc's is 1 ounce
30 cc (30 ml)
1013.
LPN ramifications
No vents, can't do initial assessment, can't do initial teaching, can't discharge Can take phone orders, can do f/u assessment, can do reinforcement teaching, can do dry dressings
1014.
Hurts with eating/feels better with eating
Hurts with eating = gastritis Feels better with eating = PUD
1015.
Zantac and -dines are what?
H2 blocker
1016.
Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, and Protonix are what?
PPI
1017.
What to do with metabolic acidosis
...
1018.
What to do with metabolic alkalosis
...
1019.
What to do with respiratory acidosis
...
1020.
What to do with respiratory alkalosis
...
1021.
Aquamephytin
vitamin K
1022.
secretes vitamin K
liver
1023.
secretes bile
liver
1024.
bile stores
gallbladder
1025.
S/S of hepatitis
jaundice, foamy-tea colored urine (bile in urine - bile is soap), clay colored stool (no bile in stool)
1026.
Hepatitis needs in diet
increased protein and decreased fat
1027.
ESLD is caused by..
Liver dying, has lots of scar tissue, closing off biliary tree (same symptoms as hepatitis, but will not regenerate)
1028.
ESLD needs in diet
decreased protein (this creates more ammonia)
1029.
Secretes amylase/lipase
Pancrease
1030.
Crohn's
diarrhea inflammation of entire colon tx = anti-inflammatory drugs (steroids) malnourished
1031.
Ulcerative colitis
bloody diarrhea No steroids tx = complete removal of lg bowel w/ ileostomy malnourished
1032.
Why no morphine with bowel surgery or biliary pain
morphine can cause spasm at sphincter of Odi Give Demerol
1033.
RA
inflammatory response red, hot, swollen, bad deformities anti-inflammatories (NSAID, steroids) Rest t when inflamed
1034.
OA
t is wearing out - DJD Pain meds (tylenol, NSAIDS, narcotics) likes temp extremes (hot better) Keep t moving even when painful or will freeze
1035.
weight bearing for hip replacement
TOUCH weight bearing
1036.
weight bearing for hip fracture
NON weight bearing
1037.
Instructions when taking Fosamax
Empty stomach sit up for 30 minutes
1038.
Anterior pituitary gland
Growth hormone Too much = acromegaly Too little = Dwarfism
1039.
Posterior pituitary gland
ADH Too much = SIADH Too little = DI (DDAVP)
1040.
Thyroid gland
T3/T4 Too much = Increased metabolism (Graves) Too little = Decreased metabolism (thick nails, course hair, myxedema coma)
1041.
Parathyroid gland
Calcium Too much = hypercalcemia (somnolent) - tx diuretics/dialysis Too little = hypocalcemia (jittery, seizure, mouth tetany)
1042.
Adrenal gland
glucocorticoids Too much = like too many steroids (weight gain, increase infection, increase glucose, skinny limbs, moon face, buffalo hump) Too little = Addison's disease - tx is life long steroids (which causes Cushings)
1043.
Addisonian crisis
Not enough steroids Bronze pigment to skin d/t mineral corticoid steroids
1044.
Pancreas
Insulin Too much = hyperglycemia (dry, hot) Too little = hypoglycemia (pale, cold, clammy)
1045.
Diet for renal patient
Low protein, fluid restriction, low potassium, low phosphorus Phosphate binder given with meals
1046.
Bronchodilators
increased oxygen demand-myocardial
1047.
Intermittent claudication
think arterial vs venous-this is arterial-position leg dependently
1048.
arterial
skin shines
1049.
arterial issues
put your legs down-so blood flows down-like an A (artery)
1050.
venous issues
like a V-put them up-so blood can go up
1051.
Heart Failure
-pumping issue; give Lasix and Digoxin (help with pumping)
1052.
V tach
electrical conduction system issue
1053.
INFILTRATION
IV site painful and swollen
1054.
blood reaction
send blood and tubing to the lab
1055.
New Trach
DO NOT remove the ties before cleaning the tracheostomy-wrong-stoma is not formed yetrisk of stoma closing and airway impacted
1056.
all tracheostomies
dont cut the gauze; need a pre cut gauze
1057.
C3 spinal fracture
airway is your issue
1058.
if you see a presenting part for a baby for a labor pt in ER
prepare delivery room-priority
1059.
pt found on the floor
assess vital signs and LOC first, not injuries assessment first (if pt was conscious before the fall-vitals will tell us the most about the client; unconscious pt would not have been found on the floor-they cannot get up-most likely they rails are up)
1060.
NCLEX wont test
chemo drugs
1061.
NCLEX will test
Eriksson but not Piaget, high pressure alarms
1062.
obese client that vomits after surgery-will increase pressure in the abdomen, at more risk for
Adhehicence
1063.
Disaster prioritization
Priority pt-pt with burns on the face, with respiratory stridor; fixed pupil and agonal respirations-will not live, so not a priority
1064.
LPN
can give report during a transfer can take VS in a transfusion client, after RN has stayed with client for first 15 min or the necessary initial time
1065.
pt after MVA on balanced suspension traction
disorientation is a priority; not shallow respirations
1066.
ECT
before: withhold Dilantin; Atropine IS given- for its anticholinergic effects-will lower the secretions in the mouth; ECT causes seizures-we don't want them to have fluids in mouth-risk for aspiration; Methohexital- possible given for amesthesia; also Succinylcholine-possible given
1067.
knee arthroplasty-1 week ago
post op-for 4 to 6 weeks blood thinners are given throughout the recovery; also if pt was on blood thinners prior to arthroplasty, he won't be taken off these meds, because they are lying down (postop) so they are at risk for cloths; they won't be taking NSAIDs-they are on blood thinners; Motrin vs Lortab?
1068.
pt that had a catheter in before, now catheter is out and pt cannot peeintervention
assessment FIRST-so do a bladder scan first; (full bladder-dull sounds when you percuss); anesthesia can cause decreases ability to urinate
1069.
if chest tube is disconnected
immerse the end of chest tube in a bottle of sterile water-this will prevent the air going into the chestcreates a water sill
1070.
new dx of RA-Methotrexate order
this drug is used in CA patients as well-but its not a chemo drug associated with this drug: WBC low- possible 1200, stomatitis-sores and difficulty in the mouth-hard to eat, fever above 101 can be caused (fever is only above 101 F), increased urine specific gravity-they are not eating or drinking-dehydration occurs; low platelets; also pts are advised to take Folic Acid with this drug-it causes a depletion of dolic acid
1071.
three point crutches
unaffected leg first, then crutches 6 inches forward
1072.
2 point leg
R foot and the L crutch go first together; L foot and the R crutch after at same time-m0ve the other ones
1073.
swing through gait
crutches forward, lift both feet and swing forward
1074.
Tetralogy of Fallot
4 issues here: ventricular septal defect, right ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonic stenosis, overriding aorta, there is a whole in the septum; this will impact blood getting around the body
1075.
TPN pt- to prevent fluid volume deficit
monitor glucose q 4-6 hrs-if the glucose is up-dehydration (osmotic diuresis)
1076.
incident reports
risk management investigates these, they are not shared with non involved staff, include description of incidents in the reports
1077.
medication reconciliation
contains documented meds taken by client, comparrison of current and past meds list; this list is done at any change in care..not only at ission and discharge; the purpose is to avoid errors of duplication, missing some meds etc; also the pharmacy has a role in this, not only the RN
1078.
Autocratic manager
"do this, don't ask any questions"; employees have little to say; these managers are good in critical situations
1079.
Laissez Faire manager
disorganized floor, chaotic environment, employees make the decisions
1080.
Democratic manager
decisions are made as a group , employees ARE asked their opinions
1081.
UAP
CANNOT encourage to share feelings-this requires therapeutic communications-RN has the skills to do this CANNOT get a urine specimen from a indwelling catheter-this is sterile CAN assist with ambulating the client; CAN empty the suction container, but RN has to assess the fluid collected
1082.
LPN
CANNOT ister Rogham-its a blood product; they CAN hang the second bag for TPN, not the first one-RN they CANNOT do anything with titration they CANNOT stick the pt-no IV's start CAN hang a piggy pag as long as its not a titration and as long as its a second bag; always RN has to hang the first bag; LPN CAN give IM injections, they CAN hang the bag of fluid; when LPN hangs the second bag, she does not need the RN there CAN do wound care-dressing changes, irrigations, sterile techniques CAN listen for the lung sounds-for data collection only-not as an assessment-RN will go in there and listen to those heart sounds
1083.
UAP
new ission or post of fresh pt-RN has to do the vitals, not the UAP CAN do specimen collection but not something that require sterile specimens
1084.
IV antibiotics
30 min window
1085.
antidiarrheals
always PRN
1086.
acute glomerulonephritis
can lead to acute kidney failure-watch for decreased urine output
1087.
these CAN be disclosed/reported to DMV
uncontrolled seizure disorder of a school bus driver, if it is not controlled dx of TB or HIV someone with a gun in the hospital can be called to the cups right away
1088.
nonmaleficence
do not insert a contaminated catheter in after not sterile anymore
1089.
implied consent
unless you have a DNR, you do everything for them
1090.
living will WITHOUT a DNR order
you have resuccitate in a code
1091.
in an outbreak for STD's
tell sexually active students to trace outbreaks-in a high school (when addressing the community outbreak)
1092.
phone triage for a client exposed to EBOLA-client has no symptoms
tell client: "we will have to notify the health dept, HIPPA does not apply in this case"
1093.
Fire disaster
evacuate the ones can ambulate first-smoke kills before fire
1094.
NCLEX
increased number of questions about religions and cultures practices
1095.
when you need a translator
call a certified one; no family member should translate-HIPPA
1096.
Ebola
report immediately-fever, epistaxis, vomiting
1097.
AMA client
no need to call security but DO inform about possible complications if they leave
1098.
Amiodarone
should be given through a central line, not peripherally- because ph < 5
1099.
Vacomyocin
ph is <5-not given peripherally but PICC line ok
1100.
TPN
not given peripherally
1101.
narcotics (eg. Morphine)
can be taken out without a witness signature BUT needs second nurse when wasting it never take out a narcotic if drower count is incorrect LPN CAN sign a waste for narcotics
1102.
SEIZURES (precautions before a seizure, after an aura)
roll them on their side only if they lost consciousness; if not they CAN maintain their airway time it during a seizure-needs to be documented after: report it, document, determine LOC postdictal state: drowsy; ok for them to sleep on their side
1103.
chemo treatment
if it spills you call the biohazard, not the housekeeping-you put them at danger (not the housekeeping, not the laundry department) incident report done as well
1104.
smoking client on non smoking campus
give hime a patch
1105.
cane use left side weakness
cane opposite affected leg (COLL)-move cane and the bad leg forward first
1106.
crutches
arms flexed; 2-3 inches to underarmed cannot rest on crutches (underarm)
1107.
Parkinson client
walker with wheels-not ok for this client-safety problem should use the walker with tennis balls-he is shuffling he needs smooth sole shoes- not the non skid ones-he will fall
1108.
Shingles and TB
cannot share room
1109.
neutropenic pt
needs private room
1110.
DONT isolate
an HIV pt UNLESS he is neutropenic or he has an opportunistic infections
1111.
private room
productive cough and possible TB rash with possible varicella only airborne needs private room C-dif is -does not need private room but its recommended (its only in the stool-only way to get it-if you touch the stool)
1112.
Laryngectomy client with fresh trach, Hep C and HIV
need gloves, gown, mask, googles-all of these needed because the new tracheostomy
1113.
client with MRSA + client who's post op total knee replacement
you dont want them in the same room-knee rejection risk-MRSA might get in the knee
1114.
mammogram
after 40 annually
1115.
colorectal exam
should start at age of 50
1116.
prostate
discuss with p at 50
1117.
pap test
every 3 years starting at 21 if there is an abnormal pap->annual exam recommended
1118.
vaginal exam
has to be done annual in all patients
1119.
analgesia
cold and hot
1120.
hot
relaxes
1121.
emergency numbers
should be next to the phone, not the exit door
1122.
progressive macular degeneration
room free of clutter call light within rich
1123.
fall history
have bed alarm for client
1124.
purulent exudate drainage from wound
clean site first with sterile saline and water place specimen in biohazard bag
1125.
who is at risk for falls
over 65 yrs old bifocal glasses pt on Lasix
1126.
hypotonic pulls fluid INTO the cell
hypertonic pulls it OUT of the cell
1127.
to check for JVD
place in semi fowler
1128.
if you see JVD when client is standing
CHF R side
1129.
Calculate output
Assume-0.5 ml per kg output per hour if we dont know the weight then is 30 ml per hr
1130.
the lower the Na it goes
the higher the risk for seizures it is
1131.
kidney function decreased
creatinine increased
1132.
hyperventilation
blowing out CO2-give rebreather bag-client is in respiratory alkalosis
1133.
Atropine
metabolic acidosis
1134.
Narcan
risk for respiratory acidosis-they are not breathing
1135.
pt on Zofran
risk for metabolic alkalosis-they are vomiting
1136.
Insulin
metabolic acidosis-K is high
1137.
Dilaudid
respiratory acidosis or alkalosis
1138.
sputum specimen
collect in the morning- also provide oral care for this pt
1139.
bronchoscopy
they are looking for lung cancer assess gag reflex asks client if he has night sweats-lung CA pts has this particular symptom
1140.
Quantiferon Gold-TB
blood test definitive for TB results within 24 hrs ask for night sweats
1141.
Thoracentesis
place a chest tube in the room- pt at risk for pneumothorax during procedure check lung sounds on that side
1142.
pulmonary hygiene
T turn and cough bronchodilators steroids use bronchodilator first
1143.
suctioning
3 rounds before you hyper oxygenate again, max 15 secs rounds suction on exiting
1144.
TB
mucopurulent sputum, low grade fever, chest tightness, decreased appetite
1145.
chronic bronchitis
copious sputum cough for few months
1146.
emphysema
pursed lip breathing
1147.
asthma
bronchospasms careful with beta blockers
1148.
lung cancer
non specific s/s
1149.
pneumonia
pleuritic chest pain-that does not go down when you sit/lay down, movement hurts
1150.
anginal pain
pain goes away when you lay down
1151.
pneumothorax
O2 decreases, put pt on O2, semi high fowler position; give anxiolytics- if anxious they won't be breathing ok; give analgesics- because it hurts chest tube placed as well
1152.
Chest tubes components
right container-this is the drainage water seal-middle-red suction bubbles on the left if no bubbling- possible kick in the tube if drainage becomes purulent-check for fever, check when CBC was done last time, look at the insertion side for infection in case of crackles-these are in the pleural space-crackles mean fluid; check to see if a chest xray was done this morning 1153.
intubated client
nurse should do frequent hand wash provide oral decontamination clean oral suction device turn client q 2 hrs high fowler
1154.
preop clients
might take half of insulin
1155.
post op
respiratory, circulation, neuro, GU, GI, pain-these are all impaired by the surgery
1156.
dehisscence
put some stitches on high fowler
1157.
evisceration
lay pt down, bend knees, call for help, cover with sterile dressing 1158.
acute cholecystitis
low fat diet have rich in HDL food sources
1159.
NG tube
with x-ray first, gastric ph later empty when 1.5 to 3/4 full check residual in continuous feeding-check in q 4 hrs; if less than 100 ml-put it back; if more than 200-call provider; if more than 200 is taken out-metabolic alkalosis risk meds through NG tube are given liquid, if crushed you give the meds 1 at a time-you don't know how they interact when crushed and mixed in all together-also flush in between you don't give extended release meds through ng tube-they need liquid or non extended released
1160.
GERD
prokinetic agents- Reglan
1161.
Peptic ulcer
...
1162.
IBS
diarrhea and constipation LLQ pain cramps
1163.
Inflammatory bowel disorders (UC and Crohn's)
give immune modulators with the Ulcerative colitis-stool gets into the tissues?
1164.
Diverticulitis
they always have diverticulosis, but if something gets in a diverticula-then it becomes diverticulitis fluids only, rest the bowel later-low fiber and after, transition to high fiber
1165.
Dumping syndrome
dizziness, sweating, tachicardia post bariatric surgery-avoid lactose and high concentrated sugar, high fat and protein foods, turn to the L side not supine
1166.
Bariatric clients
they are obese- so high risk clients
1167.
Colostomy care teaching
include cranberry juice and yogurt to the diet-this will help with the odor empty bag when one third full clip hair surrounding the peristomal site
1168.
post up stoma care
pink and red is good the further in the colon the stoma is, the more solid the stool is emotional , lots of teaching required they will have an NG tube initially in for feeding stoma care and assessment-priorities
1169.
pancreatitis
need for intervention: 1.042 Urine specific gravity-severe dehydration (osmotic diuresis-started on TPN, sugar elevates) amylase, lipase, related to the exocrine function of the endocrine system
1170.
acute pancreatitis
possible hypocalcemia (Tressou sign)-hand spasms occurs during blood pressure monitoring with the auto digestion-Ca ends up in the bloodstream
1171.
Cirrhosis
low protein diet bleeding-esophageal varices they are breaking down protein-so they have high ammonia-this is toxic to neuro system
1172.
Hepatitis
liver impairment
1173.
Pancreatitis-malnutrition
put them far away from nurses station-so when food comes the smell wont create pancreatic enzymes
1174.
pancreatic cancer
immunosuppression present treatment: Whipple procedure and chemo many times its mehtastazied
1175.
OA
weather changes-barometric pressure chronic unilateral pain pain worsen after activity
1176.
Rheumatoid A
bilateral t inflammation morning stiffness and pain
1177.
Gout
men usually get it cannot put pressure on foot during acute episode multiple tophi excruciating pain with acute episode bed rest, avoid touch, increase fluids Allopurinol
1178.
SIADH
low sodium level seizure precautions
1179.
Arterial line
...
1180.
Clonidine
change position slowly, this is a BP drug take at night in case of a cough->don't stop the med, just call the dr
1181.
VTac
obtain VS don't defibrillate but cardiovert (if hemodynamically stable don't cardiovert) check carotid pulse give Amiodarone
1182.
Progressive MS
get rest and avoid stress major personality changes need speech therapist might lose ability to empty bladder eye patch given
1183.
Palliative care
improve quality of life meet physical and emotional needs
1184.
mental health pts to
treat based on developmental age, not chronologic age
1185.
amputation
first reaction-many times denial
1186.
Olanzepine/Zyprexa for Anxiety
antipsychotic-causes hyperglycemia and weight gain they can't eat whatever they want for the first two months-risk for agranulocytosis
1187.
Agoraphobia
intervention-desensitation-this is a slow process
1188.
OCD
intervention-allow the ritual-we are not allow to stop it without a physician order-we will send them into a panic attack
1189.
PTSD
intervention- groups
1190.
Hypochondriasis
intervention-limit rumination-will help them not thinking of it
1191.
Social Phobia
Intervention-GAD? intervention-reinforce coping
1192.
Schizophrenia
Paranoid-auditory hallucinations-know what the voices are telling them Disorganized-flat affect, disorganized behavior and speech Catatonic-stupor or extreme agitation, bizarre body posture-they can be in same position for a long timealteration of skin break down can happen
1193.
Prolixin
targets dyskenisia-repetitive involuntary facial and tongue motion
1194.
Aripiprazole
reduce daily delusional thoughts
1195.
Aricept
increase mental cognition
1196.
Haloperidol/Haldol
highest risk of EPS
1197.
Clozapine
agranulocytosis
1198.
Seroquel (for depression)
slipineess
1199.
Congentin
manages EPS
1200.
Risperdal
lowest risks gynecomastia is a major risk in young boys
1201.
Olanzapine/Zyprexa
hyperglicemia
1202.
Autism-alterations in
social skills-interventions-structured routines language-might talk late-interventions-foster independence behaviors-anger, frustration; intervention-safety cognition-depends where they fall-intervention-family health-frequent GI disorders-advised to be on gluten free diet-intervention-offer community resources
1203.
Niacin
flushing-normal
1204.
Rifampin (TB drug)
orange body fluids
1205.
Adenosine
flushing and chest pain, iv push
1206.
Protonix (PPI class)
antiulcer med
1207.
Pitocin
decreases bleeding uterine stimulant
1208.
Fentanyl (narcotic)
reversible agent is Nalaxone
1209.
Metothrexate
...
1210.
Palivizunab
prevents RSV
1211.
Methylprednisolone sodium succinate
given orally or IV IV push
1212.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (Evista)
given for postmenapausal osteoporosis
1213.
Lipitor
no grapefruit
1214.
Prostaglandin-Xalatan-Lantanoprost
...
1215.
Geodon
...
1216.
Indocin
ister with food, milk
1217.
Singulair, montelukast
bronchodilator
1218.
anti inflamatory-Nasonex
dont ister in clients with milk allergy
1219.
Flagyl-no alcohol first 3 days
...
1220.
Viagra-dont give with nitrates
...
1221.
slows osteoporosis-Premarin
...
1222.
avoid foods with tyramine-antibiotic-ZyvoxNeurontin-partial seizure and neuralgia given for these
...
1223.
-Methadone-monitor respiratory
...
1224.
-ster sq with evening meal or HS-Levemir; dont mix with other insulins (long acting insulin); doses must be 12 hrs apart
...
1225.
-antimicrobial-Zocyn-check allergy for penicillin
...
1226.
-for ADHD-available in po form only, taken once daily-Vyvanse-Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
...
1227.
Coumadin
anticoagulant, intake of greens important for vitamin K
1228.
Ariprippazole
avoid grapefruit, alcohol, overheating, dehydration
1229.
Nemanda/Nemantine
avoid diet in fruits and vegetables
1230.
antibiotic
caution in colitis
1231.
Hydrochloride
ister po-moderate to severe dementia such as Alzheimer fresh fruits will cause alkalinity-low excretion of drug
1232.
Actonel
CI with esophageal disorder remain uprights for 30 min take with a full glass of water
1233.
Cardizem
...
1234.
Avodart
BPH drug females of age that might have kids should not handle this
1235.
Chantix-
nicotinic blocker
1236.
Paxil
antidepressant don't take St John Worth take at night time
1237.
Depression
Anhedonia-maintain ADLs sleep alteration-bedtime routine anergia-encourage exercise worthlessness-monitor safety poor concentration-clear directions suicidal ideation-giving away things
1238.
Severe Mania
Anorexia-provide finger foods Accelerated speech-calm demeanor Fragmented thoughts-redirect no impulse control-monitor safety
1239.
SSRI
weight gain therapeutic effect after 1 week
1240.
Lithium
AE with diuretics therapeutic effect after 1 week
1241.
MAOI-
therapeutic effect after 1 week
1242.
TCA
therapeutic effect after 1 week monitor for dysrhythmias
1243.
detoxification of cocaine
s/s several hrs later-poor concentrations
1244.
hypertention crisis
hrs after opiods
1245.
alcohol withdrawal
dont leave them alone Diaphoresis—fluid replacement hallucinations-decrease stimuli Wernicke-Korsakoff-Infuse IV Thiamine
1246.
Oxazepam (Serax)
Delirium Tremens Tachycardia-monitor VS
1247.
stages of Alzeimer
4 only, not 6 stage 2 is moderate-cannot balance checkbook, decline in daily basic hygiene needs,; leave the stove after cooking; stage 1 (mild)-discuss meaning of client's framed photo: integrity vs dispair stage; you want them to have personal things around
1248.
Dementia
decrease in cognition-safety is major problem they need their routine provide education to the whole team taking care of this pt dont rationalize with them
1249.
Anorexia
we don't focus on their weight, they do prepare fluid therapy and enteral feeding for them
1250.
Clozapine
...
1251.
mental health miscellaneous
pt can leave facility if at will involuntary ission occurs if people are deemed a threat to themselves or others clients can communicate with their attorney nurse cannot open postal packages prior to giving to client
1252.
Hcg test-why is important before surgery
a positive pregnancy test may require canceling surgery
1253.
Hcg
rises during pregnancy and maintains the pregnancy raises until about 12 weeks of pregnancy, then body recognizes it and then it drops again
1254.
prenatal examination
report if pt is on a vegetarian diet; usually they are pseudo anemic until 32 weeks, then the iron should become normal again
1255.
first semester
nausea, vomiting, nutrition
1256.
2nd semester
dyspnea, heartburn
1257.
3rd trimester
make sure she know how to recognize false vs true labor signs
1258.
prenatal care
assess at each exam-VS, weight, fundal height...
1259.
Mag Sufate IV
resp 10-priority
1260.
Chronic HTN
mom had HTN prior to pregnancy this pt may develop preeclampsia
1261.
Gestational HTN
mom gets HTN after 20th week of gestation NO protenuria
1262.
STI
higher risk for ectopic pregnancy
1263.
Placenta previa
no vaginal exam painless, bright red bleeding
1264.
abruption placenta
painful dark red bleeding
1265.
hyperemesis
whatch the weight and electrolytes
1266.
hydatidiform mole
avoid pregnancy until hCG returns to normal she can a grape like structure... ideally avoid pregnancy for 4 years ? she is at risk for cancer as well usually this only happens once
1267.
Cerclage
cervical insufficiency
1268.
ectopic pregnancy
unilateral, stabbing, abdominal pain ectopic pregnancy is never a livable pregnancy
1269.
danger signs during pregnancy
fever and chills (infection) decreased or absent fetal movement sudden weight gain (preeclampsia) severe HA ROM prior to 37 weeks gestation vaginal bleeding
1270.
Isotonic IV fluids
...
1271.
If contractions frequency is 90 secs
stop Pitocin check FHR assess pain and fatigue
1272.
severe back pain labor
give back massage place on all fours (legs and nands)
1273.
If baby has a longitudinal lie, with FHR above the umbilicus
prepare for US need to evaluate for breech
1274.
pain
associated with labor
1275.
stage 1 of labor
keep her active after 3-7 cm-help her breath assess FHR and UC comfort
1276.
stage 2 of labor
check FHR q 15 min assist pushing
1277.
stage 3 stage of labor
placenta delivered do newborn care
1278.
stage 4 of labor
priority-prevent bleeding
1279.
fetal monitoring late deceleration
reposition first on L side
1280.
fetal monitoring
VEAL CHOP (what causes it) MINE (what you do about it)-make sure you know where they are in the process
1281.
Late decels
uteroplacental insufficiency
1282.
Lenght of contractions
maximum length of contraction should be 90 secs if 90 secs or longer or FHR is lower than 11-stop Pitocin if a mom is on it
1283.
L&D meds tocolytics-Indomethacin and Terbutaline
stops labor
1284.
Pitocin
used to augment labor/assist labor
1285.
Beamethasone
2 doses 24 hrs apart help to mature fetal lungs
1286.
breastfeeding
don't feed if discomfort is present schedule feeding for breastfeeding q 2-3 hrs meds might transfer to milk if mom is breastfeeding
1287.
Rhogham istration
monitor labs: Indirect Coomb's for baby Direct Coomb's for mom
1288.
PP hemorrhage
priority
1289.
mom breastfeeding on heparin therapy
breast milk will not be affected, after breast feeding is over she can go back to Coumadin
1290.
Initial Newborn Care
at 1 and 5 min check Apgar after drying him off put him skin to skin with mom for thermoregulation evaporation when baby is wet when baby is dry-heat is loss through..
1291.
baby assessment
reflexes check-premie will not demonstrate all the reflexes
1292.
fetal alcohol syndrome
high pitch cry hard to console cognitive disabilities
1293.
tobacco/nicotine
vasoconstricor decreased O2 for baby-increased SIDS risk, asthma
1294.
hypoglycemia in babies
check glucose w/o an order; it takes some time for the baby to get used with the insulin production
1295.
phototerapy
cover eye with mask reposition newborn q 2 hrs cover scrotum take them off light only for feeding
1296.
Kernisterus
yellow baby, we only take the baby out of the light for feeding
1297.
Womens Health
...
1298.
cancers
...
1299.
menopause
hot flashes night sweats palpitations vaginal atrophy osteoporosis
1300.
over 35
increased risk of DVT with oral contraception
1301.
all these matter when choosing oral contraception
history of hypertension severe PMS hist of DVT
1302.
Diflucan
...
1303.
Rocephin
...
1304.
Flagyl
...
1305.
postmenaupausal- 57 yrs old- (on Climara)monitor BP, yearly mammogram, take with food, call provider if bleeding occurs
...
1306.
Methergine
CI in HTN and cardiac disease promotes uterine contractions
1307.
lyrics (Pregabalin)
dont stop abruptly, monitor for edema
1308.
Plavix
Prilosec and Nexium will decrease the effects of this
1309.
Synthroid
give in the morning increases HR
1310.
complicated UTI
give antibiotics CI with sensitivity to cephalosporins-Maxipime
1311.
Gentamicin
antibiotic for bacterial infections monitor UO and renal function
1312.
Antipshychotic-Risperdal
dont mix oral solution with cola or tea
1313.
Aricept
monitor for bradicardia, dont interupt abrutptly
1314.
Lidocaine
not effective against SVT, given IV
1315.
Bystolic
don't stop abrupt, weight daily, can impair thinking and reaction time
1316.
Oxycontin
highly abused-should not be taken within 2 weeks of istration of an MAOI
1317.
Dilaudid
causes spasms of sphincter of odi
1318.
Levaquin
can alter glucose level in diabetic client
1319.
Vancomycin
antibiotic for MRSA risk for Red man syndrome
1320.
Digoxin
assess AP for one min hypokalemia can lead to toxicity
1321.
Inderal
check BP and pulse before istration
1322.
PPI-Nexium (GERD)
don't crush or chew
1323.
Effexor
can increase ptinr, don't discontinue abruptly
1324.
Lithium
mantain Na levels normal
1325.
Lovenox
hold if platelets are less than 100,000 ister sq
1326.
Pradaxa
avoid use with drugs that prolong bleeding keep dry and in a dark bottle
1327.
Varivax vaccine
prevents chicken pox
1328.
Lasix
Diuretic monitor HR, BP monitor weight
1329.
Amiodarone
first line drug for...
1330.
Dilantin
therapeutic level 10-20
1331.
Novolog
...
1332.
Advair (Fluticasone)
long term for asthma
1333.
Concerta
contra with MAOI
1334.
Simvastatin and Zetia-Vytorin
its a combination drug
1335.
Gardasil
prevents HPV istered to both male and female-
1336.
Nitro
onset 1-3 min sublingual
1337.
regular Insulin
the only one istered IV
1338.
Haldol
monitor for EPS causes dry mouth
1339.
Ambien
rapid onset given for short term insomnia
1340.
PEDS-know
infants and children-common causes of death incorrect car seat placement or not being in the seat
1341.
Ritalin
side effects-Tics, nervousness, increased BP; can cause insomnia, don't give in the evening
1342.
pt that is on radiation
no lotion on the side, no scrubbing, just warm water
1343.
know back/spine safety for nurse
upper bod mechanics, position client in the correct way
1344.
1hr oral glucose tolerance test
positive results 145mg/dl, report to provider, adv. pt to avoid caffeine the morning of test because it can increase glucose levels
1345.
Abstract Thinking
Asking questions about similarities between objects or to explain a common proverb or saying
1346.
Acarbose
oral antidiabetic agent that postpones the absorption of glucose
1347.
Acute hemolytic reaction
low back pain due to age of hemolyzed blood cell through kidneys, increased respirations, tachycardia
1348.
ister regular and NPH insulin steps
swab top of both insulin bottles with alcohol wipe, insert air into NPH insulin equal to dose, remove and insert air in regular insulin equal to dose, then withdraw dose from regular insulin and ister then withdraw correct dose from NPH insulin and subcutaneously
1349.
Advance directives
allow client to make decisions and provide written instructions regarding end of life care
1350.
Agoraphobia
behavioral therapy technique pt teaching includes modeling, systematic desensitization, flooding...
1351.
Air travel
2nd trimester, airplane cabin humidity is low (approx.. 8%), which can result in water loss, teach pt to maintain increased hydration with water to compensate for loss
1352.
Akathisia
responds to anti-parkinsonian medication
1353.
Albuterol (Proventil)
activates beta2-adrenergic receptors in the heart, increase in heart rate is a side effect
1354.
Alcohol anonymous (AA)
helps abstinence and sobriety
1355.
Alcoholism
causes CNS depression, drowsiness, slurred speech, and impaired coordination, s/s withdrawal elevated BP/HTN
1356.
Alendronate (Fosamax)
on empty stomach with 8oz water, may cause esophageal ulcerations if lodged in esophagus, remain upright for 30min after
1357.
Altruism
helping meet the needs of others who have experienced similar loss
1358.
Amitriptyline (Elavil)
tricyclic antidepressant must be taken within 3hr of missed dose if not wait til next dose,
1359.
Amniocentesis
evaluate fetal lung maturity
1360.
Amphetamine intoxication
stimulant use, adv. Effect; paranoia
1361.
Amphotericin B
adverse reaction is ototoxicity (vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss)
1362.
Ampicillin (Principen)
signs of allergic reaction hypotension, pruritus, flushing, wheezing
1363.
Anabolic steroids
in adolescence can lead to premature epiphyseal closure thus reducing height potential
1364.
Anaphylaxis Behavioral signs
apprehension, uneasiness, restlessness and anxiety
1365.
Anti-Hypertensives meds
contraindications caffeine
1366.
Antisocial personality disorder
impulse control, reminding client about expectations and providing clear boundaries and consequences of action will help promote client adherence
1367.
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) and fenofibrate (TriCor)
treats hypercholesterolemia, both meds may cause myopathy, pt has increased risk for myopathy than if either taken alone
1368.
Aversion therapy
uses punishment techniques to reduce inappropriate behaviors (alcoholism, aggression)
1369.
Avolition
lack of motivation
1370.
Baclofen (Lioresal)
antispasmodic, decreased muscle spasticity in client w/ MS, can cause urinary retention, drowsiness in early phase of therapy, hypotension
1371.
Benzodiazepine (Lorazepam)
withdrawal causes tremors and dizziness making ADL's difficult to perform
1372.
Bethanechol
muscarinic agonist that increases GI motility leading to abdominal cramps and diarrhea
1373.
Bi-Polar Disorder
increased energy and pressured speech, manic phase is treated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) if a course of medication is ineffective
1374.
Bladder distention
pushes uterus out of pelvis, can palpate fundus above umbilicus and to the right of midline,
1375.
Borderline personality disorder
development of manipulative behaviors that make establishing a meaningful relationship difficult
1376.
Boundary violation
when nurse engage in social relationship with client
1377.
Breastfeeding
baby should have at least 2 stools/day, may eat 8-12 times/ day, milk can be stored in freezer for up to 6mths, should have at least 6wet diapers per day, pt teaching; wake baby Q4hr at night for first 24-48 hr after birth
1378.
Bronchoscopy
post op; check for gag reflex,
1379.
Bulimia Nervosa
s/s tooth erosion, hand calluses, parotid swelling
1380.
Buprenorphrine
prevents withdrawal associated with opiate use, taking during pregnancy can improve maternal and neonatal outcomes
1381.
Bupropion
for nicotine use disorder
1382.
Caffeine (pregnancy)
consuming more than 200mg of caffeine/day increases risk of miscarriage and intrauterine growth restriction
1383.
Calcium carbonate (Tums)
...
1384.
Captopril (Capoten)
treat HTN, greatest risk to pt is infection r/t neutropenia therefore unexplained fever, sore throat, and fatigue can indicate and infection and provider should be notified, avoid ibuprofen or any other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication as it can reduce anti-hypertensive effects of medication
1385.
Carboprost
adv. effect fever
1386.
CD4 T-cell count
indicates the status of the pts immune system, a rise indicates return of immune function for HIV pt
1387.
CD4-T cell count
indicates the status of clients immune system, rise in cd4 counts indicates return of immune function of client w/ HIV
1388.
Cefotetan (Cefotan)
a cephalosporin, group of antibiotics hat are similar to penicillins (PCN), should be avoided in pt who is allergic to PCN
1389.
Celecoxib Celebrex
cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) inhibitors act by suppressing inflammation and relieving pain, will allow pt to move more easily, increases risk of MI because of increased vasoconstriction and unimpeded platelet aggregation
1390.
Cervical laceration
is a slow, oozing trickle of blood, during which fundus can remain firm
1391.
Chest tube drainage device
may ambulate, keep collection device below the level of the pt chest to ensure drainage, only clamp device when checking for air leaks or changing drainage system
1392.
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
for alcohol use disorder, avoid getting pregnant, teratogenic to developing fetus
1393.
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
increases skins sensitivity to UV light pt should apply sunblock to counteract adverse effect
1394.
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
orthostatic hypotension risk for falls, treats schizophrenia
1395.
Chorionic villus sampling
involves removal of small amount of tissure from the fetal section of the placenta to detect genetic conditions
1396.
Cimetidine (Tagamet)
should be taken 1hr before or 2hr after antacid
1397.
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
pt should avoid products with cations such as antacids, iron salts, milk and other dairy products because they reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin, in allergic reaction check for wheezing, diphenhydramine (Benadryl), possibly prep for IV catheter insertion, collect VS to determine pt status
1398.
Clang association
use of rhyming words
1399.
Clozapine (Clozaril)
can cause agranulocytosis, pt should have WBC evaluation
1400.
Cocaine intoxication
tachycardia, elevated BP, dilated pupils, display grandiosity and euphoria
1401.
Cocaine
CNS stimulant, may cause vomiting, dilated pupils and tachycardia
1402.
Coughing
incision with interlocked hands, pillow, towel or blanket to prevent excess stress on the incision when coughing
1403.
C-section
ambulate several times/day to increase circulation in lower extremities and prevent thrombophlebitis
1404.
Cystic Fibrosis
can have constipation should eat diet high in fiber, high calorie diet due to decreased intestinal absorption and increased work of breathing
1405.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
bed rest with affected limb elevated to reduce swelling, fit with elastic stockings, to prevent venous congestion once pt can ambulate
1406.
Delusions
belief that one's thoughts can be heard by someone else, common w/schizophrenia
1407.
Dementia
memory impairment and loss of speech
1408.
Depression
lethargy and slowed speech
1409.
Digoxin and chlorothiazide
increase pt risk of developing digoxin toxicity due to chance of developing hypokalemia
1410.
Digoxin toxicity
nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and fatigue
1411.
Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
an antihistamine, has anticholinergic properties, anticholinergic meds can cause urinary retention thus compounding urinary tract symptoms associated with prostatic hypertrophy, is contraindicated in pt with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
1412.
Displacement
defense mechanism, emotionally transferring anger for one person to innocent victim
1413.
Disulfiram
for alcohol use disorder
1414.
Doxycycline (Vibramycin)
should be taken with a full glass of water to ensure it es into the stomach which will prevent esophageal ulcerations
1415.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
pt awake 15min after ECT, likely to be confused and disoriented, reorient frequently
1416.
Eplerenone
treat HTN, adverse effects; diarrhea, decreased sodium levels, vaginal bleeding, increased potassium levels cause of potassium retention effect
1417.
Erythromycin
apply medication starting from inner canthus to outer canthus, instill 1cm ribbon of medication in lower conjunctiva to ensure proper delivery of medication, medication prophylactically to protect newborn from ophthalmia neonatorum
1418.
Exenatide
treat DM, monitor for abd pain pt at risk for pancreatitis
1419.
Expected anticipatory grieving
statements indicating shock and disbelief, needing to get away from situation, anger against dying person or caregivers,
1420.
Eyedrop instillation
advise pt to look up during to protect cornea and decrease change of blinking, clean eyes starting from inner canthus moving outward,
1421.
Felodipine (Plendil)
grapefruit juice can inhibit metabolism raising level of medication in blood increasing risk of toxicity
1422.
Ferrous sulfate
treat iron deficiency anemia, improvement in hemoglobin levels increases oxygen transport to the tissues and increases activity tolerance
1423.
Fine crackles
continuous, musical sounds which are caused by narrowing of airways
1424.
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
monitor sleeping patterns, insomnia common side effect,
1425.
Fluoxetine
contraindicated with sumatriptan put pt at risk for serotonin syndrome causing tremors, confusion, hallucinations
1426.
Fluphenazine (Prolixin)
avoid sun exposure causes photosensitivity
1427.
Fundal Height
in pregnancy should be approximately the same as the number of weeks gestation plus or minus 2cm
1428.
Furosemide (Lasix)
loop diuretic, can lead to hypokalemia, can cause BP to drop, medication should be withheld if BP 85/60,
1429.
Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
myopathy is an adverse effect, report muscle weakness or tenderness
1430.
Gentamicin (Garamycin)
is nephrotoxic, monitor BUN and serum creatinine levels
1431.
Ginkgo Biloba
herbal supplement to treat a variety of conditions (dementia, vascular disease), may interfere with platelet production and increase the risk of bleeding in clients on anticoagulation therapy (warfarin/antiplatelet medications)
1432.
Glipizide
oral antidiabetic agent that stimulates insulin secretion
1433.
Gonorrhea
STI, can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and tubal scarring which can result in infertility
1434.
Grief
community bereavement group may help cope with feelings of grief
1435.
Haloperidol (Haldol)
typical antipsychotic that decreases symptoms of psychosis and anxiety, adverse reactions tremors, shuffling gait, drooling pseudoparkinsonism
1436.
Heel stick in newborn
1st warm newborns heel
1437.
Heroin
causes CNS depression, drowsiness and slurred speech, pupillary constriction, effective treatment strategy is participation in a methadone maintenance program
1438.
Histrionic personality disorder
impulsive behavior, inappropriate sexual behavior
1439.
Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV2)
3 doses of immunization over 6mths,
1440.
Hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril)
can cause hypokalemia from excessive potassium excretion, other adverse effects are hyperchloremia, hypernatremia, hypercalcemia.
1441.
Hyperemesis gravidarum
S/S persistent vomiting and ketonuria
1442.
Hypoglycemia (newborn)
hypothermia, twitching, tachypnea (respiratory distress)
1443.
Inhalants intoxication
s/s incoordination, nystagmus, blurred vision
1444.
Ipratropium (Atrovent)
an anticholinergic, contraindicated in pt who is allergic to peanuts or soybeans because medication may contain peanut oil and soy lecithin
1445.
Iron (foods)
beef liver, lentils, oysters
1446.
Isoniazid (INH)
can cause liver damage, important for nurse to determing the clients daily alcohol intake because alcohol use increase risk, pt should reduce or avoid all use of alcohol
1447.
Isotretinoin
pt teaching will need to have triglyceride levels monitored, may cause nosebleeds, due to nature of severe birth defects pt will need 2 negative pregnancy test prior to starting medication
1448.
IV Meds
medication that are water soluble can only be istered intravenously
1449.
Jaundice
should be reported within first 24hrs of life, physiologic jaundice can lead to severe cognitive disorders
1450.
Ketorolac (Toradol)
is nephrotoxic and can cause renal impairment, monitor serum creatinine level
1451.
Kosher dietary laws
avoid eating meat and dairy product together
1452.
Lactation suppression
frequent application of cold cabbage leaves to breast can prevent engorgement
1453.
Levodopa/carbidopa (Sinemet)
dopaminergic medication, works by activating dopamine receptors, restoring nerve transmission in the basal ganglia for pt with Parkinsons disease, allows client to move freely and resume ADL's
1454.
Lisinopril (Zestril)
ACE inhibitor, can result in buildup in bradykinin, resulting in nonproductive cough, pt should withhold medication and follup with provider for further evaluation, contraindicated w/ ibuprofen can decrease antihypertensive effect
1455.
Lithium Carbonate (Eskalith)
monitor lithium levels if dosage is changed
1456.
Lower extremity amputee
anchor residual limb dressing at the nearest t proximal to the amputation, cleanse residual limb with mild soap and carefully rinse and dry, maintain compression dressing following amputation in order to promote proper fit of prosthesis and reduce edema, wrap 3x day and prn
1457.
Lumbar laminectomy
pt teaching; involves removing a portion of vertebra to expose spinal cord which produces a sense of instability in spine, avoid twisting and bending, sit in straight back chair, sleep on firm mattress
1458.
Magnesium sulfate
depresses neuromuscular activity, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis
1459.
Magnesium toxicity
bradycardia, hyporeflexia, oliguria (urine output 30ml or less), respirations less than 12/min, increased BUN indicating renal impairment which can decrease excretion and cause magnesium to accumulate to toxic levels
1460.
Major Depression
monitor elevated mood, may be indication the pt plan to commit suicide
1461.
Maladaptive grieving
statements indicating shame and guilt, feelings of being overwhelmed
1462.
Manic behavior
unable to focus on a solitary activity w/o direction from another person, impacts other clients negatively,
1463.
MAOI
contraindications aged cheese
1464.
Marijuana
a hallucinogen, has depressant properties, euphoria, relaxation and paranoia
1465.
Maslow's Hierarchy
Physiological (hunger, thirst, bodily comforts, etc.), Safety/security (out of danger), Belongingness and Love ( with others, be accepted, loved), Esteem (to achieve, be competent, gain approval and recognition), Self-Actualization (morality, creativity, problem solving)
1466.
Mastitis
pump affected breast frequently
1467.
Meconium
develops in utero, first stool ed by newborn w/I first 24 hr, dark green and viscous, contains components of amniotic fluid, cells, intestinal secretions, occult blood
1468.
Medroxyprogesterone
adv effect; loss of bone mineral density advise pt to increase calcium intake while on medication
1469.
Mesalamine (Asacol)
maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease and pt should take daily for at least 3-6 weeks
1470.
Metformin (Glucophage)
oral antidiabetic agent, used to treat DM II by decreasing glucose production in the liver, facilitates decreased glucose production; monitor for adverse effects muscle pain, agitation, GI manifestation such as bitter or metallic taste
1471.
Methamphetamine
expect high fever with overdose of CNS stimulant
1472.
Methotrexates (Rheumatrex)
pt should avoid alcohol due to risk for hepatic fibrosis and liver toxicity
1473.
Metoprolol (Lopressor)
slows the conduction through AV node therefore is contraindicated in pt who have AV block that is greater than first degree, caution in pt with diabetes mellitus because it can mask the manifestations of hypoglycemia
1474.
Milieu therapy
creates therapeutic community in which client has opportunities for learning and healing, inpatient therapy
1475.
Nasogastric tube (NG)
place pt in high fowlers position, determine which naris has greatest airflow, measure appropriate tube length, lubricate 3-4inches of end of tube, instruct client to hyperextend neck
1476.
Negligence
failing to respond to escalating behavior and prevent harm from others
1477.
Neologisms
words made up by the client
1478.
Nephrotic syndrome
with peripheral edema, low sodium diet to assist with diuresis of extracellular fluid
1479.
Nifedipine
causes vasodilation, resulting in decreased BP, can increase orthostatic hypotension and dizziness, change position slowly
1480.
Nitrates
cause relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, resulting in pooling of blood in veins and decreased venous return to heart, decreases cardiac output which causes blood pressure to fall and orthostatic hypotension to occur with change in position
1481.
Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat)
sublingual tablets, treat angina, can take up to 3doses 5min apart if chest pain persist
1482.
Nitroglycerin (TransdermNitro)
advise pt to place patch on different site for each application to prevent skin irritation, medication may cause orthostatic hypotension/dizziness should change position slowly to avoid injury
1483.
NonMaleficence
ethical concept of avoiding harm
1484.
Nonstress test (NST)
orange juice to increase the clients blood sugar and stimulate fetal movement, 2 FHR acceleration of 15/min over 20min period lasting at leatst 15 seconds indicate reactive non-stress test
1485.
Ondansetron (Zofran)
side effects headache and dizziness, pt should avoid driving or using heavy machinery
1486.
Operant conditioning
type of behavior modification that use positive reinforcement to promote a desired behavior
1487.
Oral contraceptives
contraindicated in pt who experience frequent headaches w/vision changes (can indicate cardiovascular condition) because combination can increase risk of CVA, MI, and thromboembolism
1488.
Orientation/preorientation relationship
plan for interactions with the pt
1489.
Oxycodone (OxyContin)
opioid analgesic, pain reliever, can cause CNS depression, contraindicated with diphenhydramine (Benadryl) put pt at risk for sedation, respiratory depression and injury
1490.
Paranoid schizophrenia
dominant symptoms hallucinations and delusions
1491.
Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
may cause tachycardia and other cardiac arrhythmias
1492.
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
stimulates synthesis of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes, can decrease effects of warfarin, providers (titration of medication) base dosage on therapeutic blood levels
1493.
Phytonadione
is ister via IM to newborn,
1494.
Pioglitazone (Actos)
oral antidiabetic agent, works by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, 8-12wks to experience full therapeutic effects of medication
1495.
Pleural rub sounds
loud grating sound caused by pleurisy
1496.
Postpartum diuresis
should begin 12hr after delivery, expected urine output of 3000ml/24hr
1497.
Prednisone (glucocorticoids)
suppress the body's immune response increasing risk of infections, pt should notify provider if they experience the following symptoms sore throat, black tarry stools (indicates GI bleed) due to the increased risk GI ulcers, white patches on tongue (increased risk for candida infections due to immunosuppression), hyperglycemia, weight gain
1498.
Propranolol (Inderal)
beta blocker, bradycardia is a common adverse effect, advice pt to withhold med if pulse rate less than 60bpm, can suppress tachycardia a warning sign of hypoglycemia in pt with DM, advise to rely on other signs
1499.
Propylthiouracil (Propyl-Thyracil)
desired effect HR WNL, reduction in serum T4 level, improved sleep patterns, increased attention span
1500.
PTSD
experience disrupted sleep
1501.
Quetiapine
pt at risk for abnormal glucose metabolism which may result in DM, serum glucose testing regularly
1502.
Reflection
communication technique that lets the client know that their concerns and feeling are heard and understood
1503.
Regular Insulin
clear in appearance, discard if appear cloudy
1504.
Religiosity
obsession with religious ideas and actions
1505.
Repaglinide (Prandin)
HbA1c lab test should be review to obtain information about long term therapeutic, measures blood glucose levels over past 2-3mths; glycosylated HbA1c
1506.
Repression
pt excludes unwanted ideas from conscious awareness
1507.
Respiratory distress (newborn)
S/S; nasal flaring, tachypnea, substernal retractions, grunting
1508.
Retention of placental fragments:
...
1509.
Rho(D) immunoglobin
given to Rh neg. mother who has Rh pos. newborn to prevent mother from developing antigens against the Rh factor
1510.
Risperidone
treat schizophrenia, atypical antipsychotic help to improve/minimize pt w/schizophrenia with difficulty interacting with others/maintaining relationships, put client at risk for developing diabetes due to metabolic effects of medication, obtain fasting glucose baseline prior to istration of first dose, and again, 12wks later, then annually
1511.
Schizophrenia
multiple pos & neg symptoms, flat affect & tangential speech, delusions (delusions of grandeur), appears stuporous, little to no movement at all, pt/family teaching; manage client stress to help control symptoms of illness
1512.
Schizotypal personality disorder
suspicious attitude
1513.
Scopolamine patch
treat motion sickness, should be placed behind the ear
1514.
Signs of Allergic reaction
hypotension, pruritus, flushing, wheezing
1515.
Simvastatin
notify provider if muscle pain or tenderness develops could indicate rhabdomyolysis
1516.
Social worker
help client build a structure to help promote and preserve mental health, including arrangements for employers, day treatments, financial and other community resources
1517.
Spironolactone (aldactone)
potassium sparing diuretic, salt substitutes are high in potassium can place pt at risk for hyperkalemia
1518.
Sumatriptan
contraindicated with use of fluoxetine can lead to excessive stimulation of serotonin receptor putting pt at risk for serotonin syndrome s/s tremor, confusion, hallucinations
1519.
Systematic desensitization
form of behavior modification that employs relaxation techniques in response to specific phobias
1520.
Tardive dyskinesia
lip smacking, tongue rolling, spastic facial expressions
1521.
Tetanus
booster recommended every 10yrs or sooner if injury occurs from a potentially contaminated object
1522.
Tetracycline hydrochloride (Sumycin)
causes photosensitivity and increased severity of sunburn
1523.
Therapeutic lithium level
1.2 meq/L serum lithium level
1524.
Therapeutic relationship:
...
1525.
Timolol eyedrops
treat glaucoma, press the nasolacrimal duct to prevent the medication from absorbing into systemic circulation
1526.
Tolbutamide (Orinase)
treat DM, contraindicated in pt with hypersensitivity to sulfonamide antibiotics that might also be allergic to sulfonylureas
1527.
Tonsillectomy
pt/child can chew gum to prevent throat and ear pain post-op
1528.
Topical decongestants
rebound congestion can occur with prolonged use congestion can become progressively severe
1529.
Tracheostomy child care
allow child to rest for 30-60 seconds after each aspiration to allow oxygen saturation to return to expected levels, suction as needed when there is indication of excessive secretion in airway, suction for no more than 5 sec w/each , hyperventilate w/100% oxygen before and after suctioning
1530.
Triamterene (Dyrenium)
inhibits exchange of (Na) and (K) in the distal nephron retaining (K) and excreting (Na) leading to hyperkalemia
1531.
Triple marker screening
done at 16-18wks gestation, identify chromosomal abnormalities
1532.
Uterine bleeding
relaxed, distended uterus with presence of blood and clots,
1533.
Vancomycin (Vancocin)
adverse reaction ototoxicity
1534.
Varicella (chickenpox vaccine)
hypersensitivity to neomycin is contraindicated for receiving vaccine
1535.
Veracity
duty to tell the truth
1536.
Vesicular sounds
soft, rustling sounds that occur as normal breath sounds
1537.
Vitamin K
needs to be at least 2hr after birth to prevent risk for hemorrhagic disease
1538.
Wheezes
continuous, musical sounds which are caused by narrowing of the airways
bronchdilator
hyperglycemia, hypoK
2.
Nurse should ister lidocaine IV bolus for a client who has ventricular dysrhythmia
R For a patient that is pulseless or not breathing
3.
Nurse should perform synchronized cardio version for a client with supraventricular tacycardia
the nurse should defibrillate for ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation
4.
1 unit of blood
4 hrs, stay first 15 min
5.
carbidopa/levodopa
orthostatic hypotension
6.
Crede's maneuver
technique used to void urine from the bladder , press on pubis symphasis
7.
insulin
NV, hypoglycemia, hangry, shaky, cold, clammy
8.
methotrexate
RA, psoriasis
9.
gabapentin
somnolence, dizziness, edema, most effective 3x day peaks, 2 hrs
10.
nitro and cialis
unsafe drop in BP
11.
no nitro without
IV
12.
tocolytic
relaxed uterus
13.
Protonix- PPI
alters gastric acid secretion, diarrhea, osteoporosis, pneumonia
14.
Risperidone- Risperdal
weight gain, dyslipidemia, EPS rate
15.
Solumedrol
N, headaches, cushings
16.
Lasix and gent together
even more ototoxic
17.
Cycline
skin infection, staph
18.
Antifungal
azole
19.
ARB's use when
ACE doesn't work
20.
BB=
decreased HR
21.
Calcium channel blockers
dipine, Amlodipine norvasc Diltiazem Cardizem, Tiazac Verapamil (Calan, Verelan, Covera-HS)
22.
ED drugs afil
I feel you up, sildenafil
23.
CNS stimulant
phetamine
24.
Antidiuretic - pressin
increase BP
25.
Anemia
PRBC, hgb WDL 12-16
26.
Thrombocytopenia
platelets, 150-400K
27.
Burns-
Plasma protein fraction, albumin, 3.5-5
28.
Hemophilia
cryoprecipitate Factor VIII
29.
hemophilia tests
ptt 30-40 sec, therapeutic 45-80 sec, want increased clotting time 1.5-2
30.
1 unit PRBC
Hgb and Hct both raise 1% per unit
31.
Central venous catheter
aspirate, IV brisk blood return, no resistance when flush with NS, confirm radiology report, should rest superior vena cava, dressing q2 days
32.
PICC
observe antecubital fossa for edema
33.
Triple lumen
1 meds, 1 blood draw etc, complications- pneumothorax, air embolism
34.
triple lumen dwelling complications
occlusion, infection
35.
TPN
change tubing q 24 hrs, dc lipid infusion after 12 hrs, clean iv port before and after
36.
insulin given via IV
regular
37.
DI
ADH deficient, polyuria, can give desmopressin intranasally
38.
Lantus
glargine, lonely lantus doesn't play well with others
39.
another word for A1C
glycosylated hgb
40.
inject 10U reg then 20U NPH
roll nph, clean stoppers, inject 20U air into NPH, inject 10U air into regular, WD 10U reg, then 20U NPH
41.
lanoxin, digoxin
hypoK
42.
Ambien, zolpidem
caution in elderly, opposite effect
43.
MMR hold
allergy to gelatin or neomycin
44.
RH - mom
28 wks, 72h rs after birth rogham, baby should be RH +
45.
methylergonovine (Methergin)
stop contraction, hemorrhage
46.
aqua mephton
vit K
47.
statin take
at night
48.
glucophage / metformin
increase lactic acid levels
49.
glucocorticoid
osteoporitis, cushings, puffy moon face
50.
addison's
high and dry, hypoglycemia, dehydration, bronze skin
51.
budesonide formsterol
prevent asthma, COPD, GI upset, infection
52.
levothyroxine synthroid
take 30 min before breakfast
53.
flagyl and vancomycin
cdiffe
54.
give vanc and gent
over 1 hr
55.
fentanyl
duragesic, change 72 hrs, no heat over site
56.
lithium
0.6-1.2, fine tremors are normal, increase salt, thirst s/s toxicity, lithium and salt compete for binding sites
57.
Clozapine- clozaril
2nd gen antipsychotic, agranulocytosis- dangerously low WBC, constipation, othro Hypotn
58.
typical antispsychotic
SEATANS- sedation, EPS, antocholinergic, tradive dyskinesia, agranulocytosis, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, seizures
59.
atypical like clozaril
decrease risk of eps, weight gain, diabetes, dyslipidemia, agrnaulocytosis, ortho htn
60.
benzo od
romazicon flumazenil
61.
avoid tyramine with MAOI
phenelzine or Nardil
62.
tyramine food
bacon eggs liver, pepperoni, bologna, sausage, pickeld herring, anchovies, shrimp, caviar, yeast, chocolate, alcoholic drinks
63.
tyramine problems
hypertensive crisis, foods are pickled, aged, smoked, fermented, marinated
64.
new trach at bedside
bag valve, 20 set up, suction, two trach tubes
65.
weak legs
hypoK
66.
chron's
corticosteriods, cobblestone
67.
HHNS hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketonic syndrom
> 600 CBG, dehydration, low grade temp, confusion, headaches
68.
normal IOP
10-21
69.
Ulcerative colitis
starts @ rectum, increased risk cancer, more women than meb
70.
PVD
painless ulceration
71.
HyperK
peaked tented T- wave
72.
Cane COAL
cane opposite affected limb, cane stron side
73.
radiation
visitors 6 ft, 30 min day, sign on door, educate r/t isolation, save linens in room
74.
propofol milk of anesthesia
allergy to eggs pharm
75.
vaccines
don't give if egg allergy
76.
brudinskis sign
lay down, tilt neck chich to chest, makes knee/hip flex
77.
Kernigs sign
lay down bend knee AT 90 angle, can't straighten leg, hamstring tight, pain
78.
meningitis
headache, stiff neck, photophobia, seizure precautions, private room, dehydration
79.
test to see if amnio fluid or pee
fern or nitrizine test
80.
smallpox
, face to face, body fluids, aerosol, dever, red spot tongue, rash, most contagious
81.
sepsis
vascular changes, resp compromise, renal, CNS
82.
neonatal sepsis
low ax temp, lethargy, poor suck reflex
83.
nits
lindane no longer used, pretherin creme
84.
ED
can cause MI blood pools in penis
85.
external/internal hemmrhoid
streaks in stool
86.
3rd degree heart block
p & QRS not related
87.
problem after prolonged vomiting
hypoK
88.
parkland formula
4xkgxTBSA, 1st 1/2 in 8 hrs, rest remainint 16 hrs, deduct what previously given and look at time
89.
assess buttocks in traction
never side to side, lift buttocks
90.
AV fistula
use after several weeks, BP in opposite arm, feel thrill no heavy carrying
91.
metabolic imbalance
usually throwing up diarrhea
92.
abrupto placentia
rigid abdomen
93.
mastitis
keep feeding affected side
94.
serotonin antagonist- serotonin tron to the rescue
dolasetron, ondansetron
95.
Continuous bubbling in water seal chamber
means there is a leak
96.
Bubbling in suction chamber
means suction is working
97.
NEURO
...
98.
closed head injury
possible csf leak (yellow ring around a clear moist area seen on pillow)
99.
closed head injury with increaed I
instruct client to exhale when turning and moving in bed
100.
head trauma develops increased I
do this first-hyperventilate the pt(CO2 increased I-this will decrease CO2 and I) -trendelenburg position will increase I-not a good position
101.
subdural hematoma, reduce the I interventions
30 degrees semi fowler, trendelenburg contraindicated
102.
concussion discharge education
call dr if repeated episodes of vomiting occur-sign of I going up no dietary restrictions no activity restrictions unless HA develops for pain, can give acetaminophen, but not sedating drugs
103.
pt taking antipsychotic drugs develops NMS
early sign of this: muscle stiffness, fever, sweating, tremors late signs: dysphagia, unstable BP, respiratory depression -this is an emergency
104.
pt scheduled for CT scan
tell pt that he might experience slight discomfort not exposed to magnetic field
105.
post frontal craniotomy interventions
watch for increased I fluids restricted to 1-2 L per day space out activities, don't cluster provide Oxygen at 2 LPM-will prevent hypoxia which can lead to cerebral edema give Dexamethasone-reduce or prevent cerebral edema raise HOB at 30 degrees don't place in trendelenburg-can cause too much blood flow to the brain
106.
spinal cord injury-bladder management
urinate on a timed schedule, encourage fluids, no need to avoid carbonated drinksthey can have these
107.
suspected spinal cord injury, unconscious
avoid using chin-tilt maneuver during r r-2 breaths for q 30 compressions
108.
complete C7 transection
plan of care might include ventilatory lesions above C6-risk of respiratory paralysis C1-C8 injury-risk of quadriplegia
109.
stroke pt with L side weakness, in order to avoid disuse syndrome
use boots to prevent foot drop, assist pt with ive and active ROM,
110.
stroke major risk factor
hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, nonvalvular Afib
111.
MRI contraindication
pacemaker, cerebral aneurysm clips, metal implants, orthopedic hardware, intrauterine devices, pacemaker, internal surgical clips remove jewelry before give a mild sedative before, if pt is claustrophobic
112.
Myasthenia Gravis
fluctuating muscle weakness that worsens with effort and improves with rest weakness fatigue drooling ptosis oropharyngeal weakness have suction ready ister Pyridostigmine airway clearance-primary attention
113.
Parkinson
give Carbidopa/Levodopa semisolid, thickened food small frequent feedings bath bars recommended ROM and posture exercises
114.
Acute Bacterial Meningitis
complications: hearing impairment, photophobia-put pt in a dim light room no specific diet s/s: HA, fever, nuchal rigidity, altered mental status rapid onset-develops oper hrs to 2 days droplet precautions start to on empiric antimicrobial therapy asap
115.
Meningitis
altered cerebral perfusion from I and inflammation provide care for high I, seizures and hyperthermia fever HA nuchal rigidity Kernig's sign Brudzinski's sign-flexion of the hip and knee in response to forward flexion of the neck opisthotonos -no seizures
116.
infratentorial craniotomy for a brain tumor
keep HOB flat place a small pillow under the nape of the patient's neck to promote venous return and reduce I post any craniotomy monitor q 30 min for neuro check don't flex the neck post procedure-strict I&O maintained, strict fluid intake fluids at 175 ml/hr too much
117.
infratentorial craniotomy
elevate HOB at 30-45 degrees
118.
sustained severe brain injury
interventions are to maintain a low I elevate HOB relaxing atmosphere limit suction don't cluster activities don't discuss pt status at bed side
119.
MS
double vision visual loss impaired sensation mood swings impaired motor function and cerebellar function impaired urination male-sexual impotence weakness numbness of hands fatigue tremors s/s worsening over the past several months nystagmus scanning speech ataxia muscular weakness incontinence common between 20-40 yrs old women
120.
MS discharge instructions
exposure to heat and cold can exacerbate symptoms teach how to avoid fatigue, infections no restrictions in diet, just eat nutritious well balanced meals hard exercise not recommended but physical therapy yes it is recommended failure to store in bladder or failure to empty bladder-common problems constipation-most common bowel complaint
121.
MS manifestations
urinary retention hyperreflexia of the extremities intestinal obstruction ataxia decreased concentration constipation
122.
ALS
muscle weakness atrophy fasciculations dysphagia spasticity of the flexor muscles
123.
Parkinson's
mask like appearance to the face drooling slow speech shuffling gate
124.
GBS
risk for respiratory muscles weakness-paralysis
125.
Bell's palsy
7th cranial nerve priority: assess for pain experience soft diet apply an eye shield over the affected eye-corneal abrasion with Bell's Palsy
126.
trigeminal neuralgia
nerve V
127.
swallowing and speaking
nerve X
128.
facial muscle movement and taste
VII
129.
brain tumor
HA, vomiting, papiledema, seizures, changes in mental status, altered vision
130.
encephalitis
HA, fever, vomiting, menigeal signs
131.
cerebral arteriogram (angiogram of the blood vessels of the brain) (femoral artery access)
pt just came back, interventions: pressure dressing over the site for 4 hrs at least flat for 4 to 24 hrs, bed rest keep the affected extremity straight and immobilized 6 to 8 hrs before-NPO assess for weak pulses after give fluids to excrete dye
132.
lumbar puncture
lie flat after procedure for 4-6 hrs, depends on facility
133.
CN II (optic nerve) assessment
use a Snellen chart
134.
CN III-oculomotor, IV-trochlear and VI-abducens assessment
use penlight,note for nystagmus
135.
CN V (trigeminal nerve) assessment
corneal reflex
136.
CN VIII (acoustic nerve)
Weber test and Rinne test-assess conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
137.
cerebellar and vestibular function
Romberg test
138.
visual acuity
Rosenbaun test
139.
Tonometry
measures intraocular pressure
140.
Glascow Coma Scale
eye opening, motor response, verbal response coma=8 or less lowest score is 3=deep coma 15=perfect score
141.
head injury pt, in order to monitor hypothalamic function
assess urinary output and temperature
142.
brainstem
control of heart rate/ HR, resp rate/ RR
143.
TIA
temporary loss of cognitive function that will probably resolve warning sign of impending CVA brief period of neurologic deficit such as loss of vision, hemiparesis and slurred speech does not have long term neurologic deficits
144.
CVA
may cause long term deficits
145.
Meniere's disease
vertigo tinnitus hearing loss inner ear affected
146.
Acoustic neuroma
unilateral involvement progress without improvement
147.
MATERNITY/OB
...
148.
Carboprost
used in OB bleeding don't give in asthma-contraindicated AE-wheezing
149.
INFECTIOUS
...
150.
airborne
tb, rubeola, chickenpox, varicella door closed negative air pressure room mask-N95
151.
droplet
larger than 5 mcg door can remain open,the droplets are larger so they don't spread face mask for nurse distance between client and family pneumonia, meningococal meningitis
152.
wound infection-like MRSA Cdif RSV-young children secretions are not contained in these infections private room clean gloves when entering room if with surfaces in room-wear gown keep equipment in room
153.
chickenpox children
airborne, direct 2 days before rash appears they are contagious keep nails short no aspirin in kids
154.
rubella
droplet isolate these kids from pregnant women antipyretics and analgesics if its congenital rubella (newborn)--until 12 months old or until negative swabs at 3 months of age
155.
mononucleosis
flu like fever sore throat lymph nodes enlarged avoid with saliva 3 months adolescents risk for rupture spleen-no sports-danger of ruptured spleen
156.
tonsilitis
from strep infection->(risk for glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever) antibiotics
157.
TB
airborne-less than 5 mcg fatigue anorexia nightsweats low grade fever sputum purulent dyspnea x ray man 2 test/ppd-48-72 hrs induration (area hard, you feel the edges around it; greater than 10-pozitive-exposed and infected) immuncompromised patients-greater than 5-pozitive quatiferon tb gold-blood test-fater than sputum cultures-within 24 hrs results available-treatment earlier isolated 2-4 weeks if inpatient-isolated cannot work, isolated health dept notified teaching important dont isolate from family-impossible, already exposed, they should be tested and treated if necessary -teach to cover mouth when coughing and how to dispose tissues full range of meds-don't stop 3 negative sputum tests=go back to work Ethambutol Pyrazinamide-given to shorten treatment to 6 months assess for SE-client might stop meds-assess for nausea (take at night)
158.
Hepatitis
acute inflamatory jaundice RUQ pain tea color urine light color stool elevated ALT and AST A-fecal oral route, contaminated water or food B-parenteral, sexual C-bodily fluids mild or severe symptoms flu like symptoms rest liver to encourage regeneration, rest as much as possible, dont stop activities, but rest or standard precautions high carbs diet moderate fats and protein no alcohol careful with meds-break down in liver A-no treatment, just hand washing, their own towels no meds given, but in B,C-antivirals given
159.
Lyme
erythematous lesion-bulls eye flu like symtoms stage 2-cardiac and neuro problems stage 3-large t problems 3-4 weeks antibiotics
160.
syphillis
cupper color rash spread, mucus membranes congenital in baby Penicillin
161.
gonorrhea
thick disharge many times no symptoms in females-PID-sterility doxycycline, rocemphin
162.
genital herpes
painful vesicular genital lesions after outbreak, virus still there in skin, can reoccur with stress, menses spread to infants no vaginal birth sitz bath acyclovir-dont treat the virus, just decreases course pap spears oral antibiotics no sex-while lesions present use condoms in between
163.
chalamydia
urethritis-men thich discarge, odor-women mucus membrane Doxycycline
164.
Hiv
aids-from deffective immune system from opportunistic infection: sarcoma contaminated blood or needles sexual placental transmission breast milk transmission prevention: no share of needles while drug use standard precautions in hospital high protein calorie diet of family and client important
165.
poison control
prevention toddlers-common victims meds in locked cabinets check with the eyes of a children don't take meds in front of them dont keep meds in purses accidental poison s/s-sudden change of child behaviour, empty container around the child have number available for poison control save vomitus and urine contrai to vomiting-unconscious child, petroleum base substances, corrosive substances poison control will decide what to do dont give a large amount of fluids-will increase absorption
166.
led
neuro affection irritability, increased i identify the source-nurse role homes built before 70's, oil based, pottery with oil based
167.
hazardous waste contamination
decontaminate-first thing prevent spread clean up contamination monitor personnel that has been exposed if you have a contaminated patient-dont know what they are contaminated with-first thing find out what they are contaminated with,
168.
hemophyllia
mom transmits gene to her son sex linked disorder 50% chance that mom will it to each children affected male gets the gene from mother and can transmit it only to the doughter
169.
laryngotracheobronchitis
inspiratory stridor and restlessness edema and inflammation of upper airways elevated RR
170.
night terrors
normal between 4-7
171.
otitis meds common meds
antihistamines steroids
172.
crushing meds for children
what do you crush or not crush
173.
infant
safe crib car seat-rear face, until 20 lbs, after front faced seat, back seat not front seat bath temperature small pieces toys-chicking child proof home plugs covered plants that are poisonous-don't keep these
174.
preschoolers and school age
safety helmet for bicycles-important bikes and scooters- ride on sidewalk sports safety-stay active cause of obesity, but have appropriate equipment, appropriate age group activities
175.
teenager
males-teach them how to deal with anger safety while driving-ask if they wear seatbelt 100% of the time, no cell phone drugs-teach about it
176.
adults safety
talk about guns exercise old adults-are they safe while ambulating? shoes-are they appropriate, walker-do they need one?, stairs-up and down correct, hand rails, don't carry things upstairs, do they have a way to someone in case they fall
177.
disaster planning
red-unstable, immediate attention yellow-stable, ca wait green-stable, can wait longer, the walking wounded black-fatal injuries, unstable ---use these colors only if system is overwhelemed-question will say it
178.
bioterrorismanthrax
cutaneous/skin-skin , no person to person, animal workers; standard precautions inhalation-spores; no person to person ; resp failure, shock, hemorrhagic shock-doxycycline
179.
Tetralogy of Fallow
Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis Ventricular septal defect
180.
...
Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis Ventricular septal defect
181.
infants
exploratory play
182.
todlers
imitation
183.
school age
working with otherrs groups, collaborative play hobbies
184.
erikson stages
infant-trust vs mistrust-stable caregiver toddlers-18m-3 yrs-autonomy vs shame and doubt-toilet training, walking, muscular coordination, they want to do things by themselves-autonomy preschool-3-6 yrs-initiative vs guilt-constant discovery school age-industry vs inferiority-tasks are imp-teams and groups are present-inferiority possible if role not met adolescence-12-20 yrs-peers more important than parents-think of careers start; disease-cannot fit in with the group; eg diabetic teenager cannot meet with friends and eat what they want young adulthood-20-25-commitment, family start 45-64 yrs-middle adulthood-generativity vs stagnation 65 and over-integrity vs despair-progressing towards the end of life-feeling that their life was meaningful
185.
screening tests
Denver test-birth to 6 years
186.
growth and development
...
187.
muscular developmet
screen routine infant for muscular development teach parents about milestones progression
188.
1-2 months
poor head control frequent feeding needed gain 5-7 oz weekly first few months
189.
3-4 monts
head control get up with head smile 4 m-loose reflexes become more social, eye
190.
5-6 m
double weight grasping objects weight slows down-4 oz a week turn from back to stomach-dont leave alone on changing table-teach parents
191.
7-8 m
stranger anxiety fear of stranger, wants mom 8 m-separation-stages -protest -dispair-they dont want to eat, play -denial-when parent comes back-ignore
192.
9-10 m
more mobile sitting position lift can say gaga.. respond with anger crawling starts possible 10m-pull to standing house baby proof cause now they are more mobile
193.
11-12 m
weight triple can sit from standing position wat with fingers babinski reflex changes from baby fanning injury, failure to thrive, development problems injury-most at risk small pieces things-choking dont give candy, nuts, hot dogs-small falls-risk for injury car seats-teach-completely restraint burns-outlets, cords failure to thrive-not enough growth, physical defects, not good parenting nutritional feeding has to be met age appropriate toys-nclex loves these toys should stimulate, also think safety, no sharp edges introduction of solid foods-variety but not too many at once, one q 2 weeks, starting with 6 m rice cereal-first, can mix with formula or breast milk no fruit juices in bottles-teeth problems finger foods-watch for choking
194.
15-18 m-todler
lots of vocabulary walking alone anterior fontanelle closes at 18 m tumb sucking 4 blocks together-15 m old tantrums-18 start-normal-until 2
195.
24-30 m
increase vocabulary tippytoe walk sphincter control-2 1/2 around that time 30 m-4 times birth weight they like push pull toys, stuffed animals, dolls negativism-they say no, dont ask yes/no questions -routine important safety-active so risk for injuries; mva's-most at risk, car seat safety, restraint seat drowning abuse
196.
3-5 yrspreschooler
3-vocabulary exploring-1500 words; brushing teeth; discipline, limits important 5 yrs-2500 words-identity play, play like mom and dad; love to play; housekeeping toys-stoves, cars; trycicles; tolerate separation from parents fear of death at this age; give a shot showing on a doll; help with increasing separation from parents
197.
7 yrs
boys play with boys girls play with boys
198.
9
seeking friends starting conflict with parents on the go
199.
10-12
love conversation choosing friends more selectively interested in other sex reading sowing construction sports bicycle industry vs inferiority-accomplishment important should be dry at night-no bed wetting at 12 void before bedtime, there are meds available for bed wetting
200.
Verapamil
SVT
201.
CVA
corneal abrasion
202.
permethrin
for head lice repeat the application of cream-rinse in 7 days if nits still present, repeated only at 7 days after first application comb hair daily with a nit comb clean clothing with very hot water and RID special detergent
203.
ceftriaxone
its a cephalosporin in pt for postop infection monitor tongue and oral cavity for growth of microorganisms
204.
hiatal hernia and reflux
less likely to wake up at night from heartburn if stomach is emty
205.
hypothyroidism
client very sensitive to narcotics, barbiturates, anesthetics-avoid narcotic sedatives
206.
type 2 diabetic pt going for surgery is subscribed insulin postop instead of his usually oral meds-why
being npo inhibits blood sugar control
207.
pneumothorax, chest tube
lung has re-expanded=the fluid in the water seal chamber does not fluctuate with respirations air leak=continuous bubbling in the water chamber, gentle bubbling is normal
208.
elderly type 1 diabetic
blood glucose tests are better than urine because the renal glucose threshold in elevated in elderly
209.
US at 32 weeks
getting gestational age
210.
amniocentesis
LS ratio to assess baby's lungs determines if there are any problems with spinal cord determines early problems with baby's blood
211.
tracheostomy
...
212.
allnurses random facts
1. barium swallow for 3 month old infant - npo for three hours 2. temporary pacemaker for mi client - increase cardiac output is the primary purpose 3. plasma cholesterol screening - only sips of water for 12 hours 4. reminiscing group - primary goal is to review and share their life experience with the group member 5. miller-abbott tube - removes fluid and gas in the small intestine; provides intestinal decompression 6. levin or salem stump - decompresses the stomach; prevent fluid and gas accumulation in the stomach 7. promethazine hcl (phenergan) - check patency of the patient's vein before of drug, extravasation will cause necrosis 8. insulin dependent diabetic, unable to urinate -- autonomic neuropathy 9. overdose of aspirin will produce parkinsons dse type sx 10. do not erythromycin to multiple sclerosis pt
213.
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
-antianxiety used to tx symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal
214.
terbutaline Brethine mag sulfate
tx for preterm labor
215.
Benzatropine (Cogentin)
-used to tx parkinsonian side effects of Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) (antipsychotic med)
216.
Methadone
hydrochloride-opiod analgesic; tx for narcotic withdrawal
217.
Nifedipine (Procardia)
antianginal med (CCB) decreases myocardial O2 demand.
218.
Digoxin
strengthens myocardial contractio0n & slows conduction thru AV node
219.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
inhibits prothrombin synthesis
220.
Aminocaproic acid (Amicar)
antifibrinolytic prevents recurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
221.
Lithium
tx manic phase of bipolar
222.
Nimodipine
CCB decreases spasm in cerebral blood vessels
223.
diltiazem
CCB inhibits Ca+ influx vascular smooth muscle reduces myocardial O2 demand &decreases force of ventricular contraction
224.
clotrimazole
antifungal; treats rashes.
225.
sphincter control
18 months
226.
Buerger's disease
digital sensitivity to cold intermittent claudication (pain with exercise)
227.
aging
nocturia increase need to frequent urination
228.
gastric ulcer
pain half and hr or 1 hr after a meal pain rarely at night, not helped by ingestion of food
229.
duodenal ulcer
pain at night, 2-3 hrs after a meal, prior to ingestion of a meal
230.
lumbra laminectomy
Educate about exercise to strengthen the abdominal muscle
231.
promethazine
extravasation of vein, iv
232.
tetrahydrozoline
contrai in angle closure glaucoma
233.
recurrent uti
limit milk ordered Mandelamine
234.
miller abot tube
used for decompression of onstruction
235.
aids pts
get dementia, many of them
236.
hypoparathyroidism
low calcium be ready to deal with dysrhythmiaa
237.
iv placement
not close to t
238.
rsv
...
239.
Bun
7-18 (older)
240.
Creatinine
0.7-1.4
241.
PT
9.5-12
242.
autonomic dysreflexia
...
243.
graves disease
heat intolerance metabolic rate increased
244.
tetracycline
use sunscreen outdoors
245.
propanolol
s/e bronchospasm
246.
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
npo-for several hrs lidocaine-numb the esophagus-risk for for aspiration possibly iv sedation
247.
Ankle brachial index
...
248.
Alteplase
...
249.
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
...
250.
Labs for Mi
...
251.
stress test
stop if pain
252.
Pepcid
report to dr if pt is about to be put on antiplatelets meds-it might not work
253.
Docusate
stool softner
254.
Omeprazole
makes the Clopidogrel not work
255.
30 months
able to jump
256.
18 months
walk up and down the stairs while holding self
257.
low K
risk for Dig toxicity call doc
258.
PSA
draw before digital rectal exam
259.
tube feeding
rinse the bag and change formula q 4 hrs
260.
ng tube, before feeding
check ph-3 is good-for the aspirated contents
261.
Ciprofloxacin
rash-stop drug and call dr
262.
iv K
if burning-decrease rate
263.
aPTT
1.5-2 x the therapeutic value is ok
264.
cerebellar tumor
losing balance easily
265.
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
can tell difference in taste
266.
CN VIII (acoustic)
loss of hearing temporal lobe (auditory center)
267.
gravity drip IV
piggy bag has to be higher than primary bag
268.
before giving dopamine iv
check iv patency risk for extravasation
269.
GEMFIBROZIL
...
270.
PERPHENAZINE
...
271.
TERBUTALINE
...
272.
ZIDOVUDINE
...
273.
PROCAINAMIDE
...
274.
PROCHLOPERAZINE
...
275.
BROMPHENIRAMINE
...
276.
PHENYLPROPANOLAMINE
...
277.
Random meds
Carbamazepine therapeutic serum level is 4 - 12 mcg/dL Cycloserine is an antituburculan and needs weekly drug levels foscarnet (Foscavir) can be toxic to kidneys so creatinine is monitored. Therapeutic serum digoxin is 0.5 - 2 mg/dL morphine is contraindicated in acute pancreatitis because is causes the spasms but the demerol is the drug of choice. Dantrium (dantroline) common drug kept in the OR for Malignant Hyperthermia No birth control pills with antiseizure meds....lowers the B's effects Metylergonovine-to contract uterus. before giving check BP. dont give if vascular diseases are present. MgSo4-CNS Deppressant and Anticonvulsant = normal range 4-7.5, effective if no seizures. Adverse reactions: Flushing, decrease in RR, Muscle weakness filgrastim (neupogen) - increase neutrophil count epoietin alfa (epogen) - increase rbc/erythrocytes 1. prozac, zoloft, paxil- tx of depression. 2. sodium nitroprusside- sheild from light. wrap in foil 3. cephalosporins- check for allergies to penicillins. pt could be hypersensitive. 4. pts recieving lasix should be assessed for tinnitus and hearing loss 5. anticoagulants cant dissolve a formed thrombus but tpas can. PVC's -Lidocaine Verapamil - treatment of supraventricular tachycardias, check heart rate Clomiphene- induces ovulation by changing hormonal effect on the ovary DO NOT give a pregnant laboring patient on methadone STADOL (precipitates withdrawal) contractions > 90 seconds, FHR < after contraction peak. . .turn off the pitocin [oxytocin] (if running) give O2 by tight face mask, reposition on left side, increase IV fluid rate, notify caregiver, document Aminoglycosides (gentamycin, etc.) affect 8th cranial nerve function (hearing) and are nephrotoxic he adverse effects of Anti psychotics can be ed using this: SHANCE S-SUNLIGHT SENSITIVITY( Use hats and sunscreen) H-HEPATOTOXICITY( Monitor LFT) A-AGRANULOCYTOSIS( Characterised by fever and sore throat) N-NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME( Characterised by fever and muscular rigidity) C-CIRCULATORY PROBLEMS( Leukopenia and orthostatic hypotension) E-EXTRA PYRAMIDAL SYMPTOMS( ister anticholinergics and anti parkinsonian agents) SVT - Adenosine Atrial Flutter - Anticoagulants Atrial Fibrillation - Beta Blockers, Digoxin PVC - Amiodarone Ventricular Tachycardia - Amiodarone
Ventricular Fibrillation - Defibrillation Torsades de Pointes - Magnesium Sulfate 1st Degree AV Block - No treatment usually 2nd Degree AV Block Type I - Atropine 2nd Degree AV Block Type II - Pacemaker 3rd Degree AV Block Complete - Emergent Pacemaker, Atropine, Epinephrine, Dopamine Sinus Bradycardia - Atropine or Epinephrine Sinus Tachycardia - Beta Adrenergic or Calcium Channel Blocker digoxin 05-2.0 ng/ml lithium 0.6-1.5 meq/l dilantin 10-20 mcg/dl theophylline 10-20 mcg/dl lithium 0.5-1.5 meq/l coumadin pt: 12-20 sec....therapeutic range 1.5-2 times the control inr: 2-3 heparin ptt: 30-60 sec...therapeutic range 1.5-2 times the control 278.
Electrolytes
Hyperkalemia = narrow, peaked T waves on cardiac monitor Hypokalemia = Peaked P, Flat T, Depressed ST and Prominent U HYPOCALCEMIA (not enough sedatives) + trouseau and + chovstek's sign incr DTR stridor, laryngospasm swallowing problem=aspiration ALDOSTERONE insufficiency -Hypo-Na-emia, Hyper-K-emia, hypo-Volemia. WHEN Na decrease, K increase addisons= hyponatremia, hypotension, decreased blood vol, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia cushings= hypernatremia, hypertension, incrased blood vol, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia 4. SIADH Na <120 Hx of lung cancer Specific gravity > 1.035 Diabetes Insipidus Na> 160 head injury Specific gravity <1.005
279.
Defense mechanisms
phobias include projection and displacement
280.
Delegation Rule of Thumb?
DO NOT delegate what you can EAT! E - evaluate A - assess T - teach
281.
VV and AA?
EleVate Veins; dAngle Arteries for better perfusion
282.
Apgar Scoring?
A= appearance (color all pink, pink and blue, blue [pale]) P= pulse (>100, < 100, absent) G= grimace (cough, grimace, no response) A= activity (flexed, flaccid, limp) R= respirations (strong cry, weak cry, absent)
283.
Airborne Transmission?
My - Measles Chicken - Chicken Pox/Varicella Hez - Herpez Zoster/Shingles TB
284.
Protocol for Airborne Transmission?
Private Room - negative pressure with 6-12 air exchanges/hr Mask, N95 for TB
285.
Droplet Precautions Transmission?
DROPLET think of SPIDERMAN! S - sepsis S - scarlet fever S - streptococcal pharyngitis P - parvovirus B19 P - pneumonia P - pertussis I - influenza D - diptheria (pharyngeal) E - epiglottitis R - rubella M - mumps M - meningitis M - mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia An - Adenovirus
286.
Protocol for Droplet Precautions?
Private Room or cohort mask
287.
transmission precautions
PRECAUTION MRS.WEE M - multidrug resistant organism R - respiratory infection S - skin infections * W - wound infxn E - enteric infxn - clostridium difficile E - eye infxn - conjunctivitis
288.
What to do in the case of- an Air/Pulmonary Embolism?
S&S: chest pain, difficulty breathing, tachycardia, pale/cyanotic, sense of impending doom --> turn pt to left side and lower the head of the bed.
289.
What to do in the case of- A woman in labor with UnReassuring FHR?
(late decels, decreased variability, fetal bradycardia, etc) --> turn on left side (and give O2, stop Pitocin, increase IV fluids)
290.
What to do in the case of tube feeding with decreased LOC?
position pt on right side promotes emptying of the stomach with the HOB elevated to prevent aspiration
291.
During epidural puncture?
Side lying
292.
After lumbar puncture?
e (and also oil-based Myelogram)--> pt lies in flat supine (to prevent headache and leaking of CSF)
293.
What to in the case of- Pt with heat stroke?
Lie flat with legs elevated
294.
During CBI (continuous bladder irrigation)
(CBI) --> catheter is taped to thigh so leg should be kept straight. No other positioning restrictions.
295.
After Myringotomy?
Position on the side of the AFFECTED EAR after surgery to allow drainage of secretions
296.
After Cataract surgery?
pt will sleep on unaffected side with a night shield for 1-4 weeks.
297.
After Thyroidectomy?
low or semi-Fowler's, head, neck and shoulders.
298.
Infant with Spina Bifida?
position prone (on abdomen) so that sac does not rupture
299.
Buck's Traction?
(skin traction) --> elevate foot of bed for counter-traction
300.
After Total Hip Replacement?
don't sleep on operated side, don't flex hip more than 4560 degrees, don't elevate HOB more than 45 degrees. Maintain hip abduction by separating thighs with pillows.
301.
Prolapsed Cord?
knee-chest position or Trendelenburg
302.
Infant with Cleft lip?
position on back or in infant seat to prevent trauma to suture line. While feeding, hold in upright position.
303.
To prevent dumping syndrome?
(post-operative ulcer/stomach surgeries) --> eat in reclining position, lie down after meals for 20-30 minutes (also restrict fluids during meals, low CHO and fiber diet, small frequent meals)
304.
Above the knee amputation?
elevate for first 24 hours on pillow, position prone daily to provide for hip extension.
305.
Below the knee amputation?
foot of bed elevated for first 24 hours, position prone daily to provide for hip extension.
306.
Detached Retina?
area of detachment should be in the dependent position-- dependent meaning ed by something
307.
Enema positioning?
position pt in left side-lying (Sim's) with knee flexed
308.
After Supratentorial Surgery?
(incision behind hairline) --> elevate HOB 30-45 degrees
309.
After Infratentorial Surgery?
(incision at nape of neck)--> position pt flat and lateral on either side.
310.
During internal radiation?
on bedrest while implant in place
311.
Autonomic Dysreflexia/ Hyperreflexia?
S&S: pounding headache, profuse sweating, nasal congestion, goose flesh, bradycardia, hypertension place client in sitting position elevate HOB first before any other implementation.
312.
Shock?
bedrest with extremities elevated 20 degrees, knees straight, head slightly elevated (modified Trendelenburg)
313.
Head Injury?
elevate HOB 30 degrees to decrease intracranial pressure
314.
Peritoneal Dialysis when outflow is inadequate?
turn pt from side to side BEFORE checking for kinks in tubing (according to Kaplan)
315.
Lumbar Puncture?
AFTER the procedure, the client should be placed in the supine position for 4 to 12 hrs as prescribed. (Saunders 3rd ed p. 229)
316.
The difference between Myasthenia Gravis, Myastenia Crisis, and Cholinergic Crisis?
Myasthenia Gravis: worsens with exercise and improves with rest. Myasthenia Crisis: a positive reaction to Tensilon--will improve symptoms Cholinergic Crisis: caused by excessive medication-stop med-giving Tensilon will make it worse
317.
Prior to liver biopsy?
Its important to be aware of the lab result for prothrombin time
318.
From the ass? From the Mouth?
From the a** (diarrhea)= metabolic acidosis From the mouth (vomitus)=metabolic alkalosis
319.
Myxedema/ hypothroidism?
slowed physical and mental function, sensitivity to cold, dry skin and hair
320.
Graves disease/ Hyperthyroidism?
accelerated physical and mental function; sensitivity to heat, fine/soft hair
321.
Thyroid storm?
increased temp, pulse and HTN
322.
Post Thyroidectomy?
semi-Fowler's, prevent ncek flexion/hyperextension, trach at bedside
323.
Hypo-parathyroid?
CATS - convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasms, stridor (decreased calcium), high Ca, low phosphorus diet
324.
Hyperparathyroid?
fatigue, muscle weakness, renal calculi, back and t pain (increased calcium), low Ca, high phosphorus diet
325.
Hypovolemia?
incrased temp, rapid/weak pulse, increase respiration, hypotension, anxiety, urine specific gravity >1.030
326.
Hypervolemia?
bounding pulse, SOB, dyspnea, rares/crackles, peripheral edema, HTN, urine specific gravity <1.010; Semi-Fowler's
327.
Diabetes Insipidus?
(decreased ADH): excessive urine output and thirst, dehydration, weakness, ister Pitressin
328.
SIADH?
(increased ADH): change in LOC, decreased deep tendon reflexes, tachycardia, n/v/a, HA; ister Declomycin, diuretics
329.
HypoKalemia?
muscle ewakness, dysrhythmias, increase K (raisins, bananas, apricots, oranges, beans, potatoes, carrots, celery)
330.
HyperKalemia?
MURDER - muscle weakness, urine (oliguria/anuria), respiratory depression, decreased cardiac contractility, ECG changes, reflexes
331.
Hyponatremia?
nausea, muscle cramps, increased I, muscular twitching, convulsion; osmotic diuretics, fluids
332.
Hypernatremia?
increased temp, weakness, disorientation/delusions, hypotension, tachycardia; hypotonic solution
333.
Hypocalemia?
CATS - convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasms and stridor
334.
Hypercalemia?
muscle weakness, lack of coordination, abdominal pain, confusion, absent tendon reflexes, sedative effect on CNS
335.
HypoMg?
tremors, tetany, seizures, dyrshythmias, depression, confusion, dysphagia; dig toxicity
336.
HyperMg?
depresses the CNS, hypotension, facial flushing, muscle ewakness, absent deep tendon reflexes, shallow respirations, emergency
337.
Addisons?
hypoNa, hyperK, hypoglycemia, dark pigmentation, decreased resistance to stress, fractures, alopecia, weight loss, GI distress
338.
Cushings?
hyperNa, hypoK, hyperglycemia, prone to infection, muscle wasting, weakness, edema, HTN, hirsutism, moonface/buffalo hump
339.
Addisonian Crisis?
n/v, confusion, abdominal pain, extreme weakness, hypoglycemia, dehydration, decreased BP
340.
Pheochromocytoma?
hypersecretion of epi/norepi, persistent HTN, increased HR, hyperglycemia, diaphoresis, tremor, pounding HA; avoid stress, frequent bating and rest breaks, avoid cold and stimulating foods, surgery to remove tumor
341.
NMS?
-NMS is like S&M; -you get hot (hyperpyrexia) -stiff (increased muscle tone) -sweaty (diaphoresis) -BP, pulse, and respirations go up & -you start to drool
342.
Dangerous thing to get during pregnancy?
I kept forgetting which was dangerous when you're pregnant; regular measles (rubeola), or German measles (rubella), so : -never get pregnant with a German (rubella)
343.
Tetraology of Fallot?
Tetralogy of fallot; HOPS Think DROP(child drops to floor or squats) or POSH Defect, septal Right Ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorts Pulmonary stenosis
344.
Autonomic Dysreflexia?
Autonomic dysreflexia: potentially life threatening emergency - elevate head of bed to 90 degree - loosen constrictive clothing - assess for bladder distention and bowel impaction (triger) - ister antihypertensive meds (may cause stroke, MI, seisure )
345.
FHR patterns in ob?
Have trouble ing fhr patterns in OB? Think VEAL CHOP VC EH AO LP V = variable decels; C = cord compression caused E = early decels; H = head compression caused A = accels; O = okay, not a problem! L = late decels = placental insufficiency, can't fill
346.
For cord compression in OB?
For cord compression, place the mother in the TRENDELENBERG position because this removes pressure of the presenting part off the cord. (If her head is down, the baby is no longer being pulled out of hte body by gravity) If the cord is prolapsed, cover it with sterile saline gauze to prevent drying of the cord and to minimize infection.
347.
Late Decels?
For late decels, turn the mother to her left side, to allow more blood flow to the placenta.
348.
Before Epidural?
Hydration is a big priority!
349.
Major risks of epidural?
Hypotension and bradypnea / bradycardia are major risks and emergencies.
350.
OB secret?
NEVER check the monitor or a machine as a first action. Always assess the patient first; for exmaple listen to the fetal heart tones with a stethoscope in NCLEX land. Sometimes it's hard to tell who to check on first, the mother or the baby; it's usually easy to tell the right answer if the mother or baby involves a machine. If you're not sure who to check first, and one of the choices involves the machine, that's the wrong answer.
351.
Hearing the baby in OB?
If the baby is a posterior presentation, the sounds are heard at the sides. If the baby is anterior, the sounds are heard closer to midline, between teh umbilicus and where you would listen to a posterior presentation. If the baby is breech, the sounds are high up in the fundus near the umbilicus. If the baby is vertex, they are a little bit above the symphysis pubis.
352.
Ventilator Alarms?
HOLD High alarm- Obstruction due to incr. secretions, kink, pt. coughs, gag or bites Low press alarm- Disconnection or leak in ventilatior or in pt. airway cuff, pt. stops spontaneous breathing
353.
To blood sugar?
hot and dry-sugar high (hyperglycemia) cold and clammy-need some candy (hypoglycemia)
354.
I and Shock have?
I AND SHOCK HAVE OPPOSITE V/S I-increased BP, decreased pulse, decreased resp. shock- decreased BP, increased pulse, increased resp.
355.
Cor Pulmonae?
right sided heart failure caused by left ventricular failure (so pick edema, jvd, if it is a choice.)
356.
Heroin withdrawl in a neonate?
Irritable, and poor sucking
357.
Jews?
No meat and milk together
358.
Brachial Pulse?
Pulse area r on infant
359.
What to check children for at age 12 months?
always check lead posioning levels
360.
Sources of potassium?
Bananas, potatoes, citrus fruits
361.
What is obtained before starting any iv antibiotic?
Cultures
362.
Why would a pt with leukemia have epistaxis?
b/c of low platelets
363.
Best way to warm a newborn?
skin to skin on mom with a blanket
364.
When a pt comes in and she is in active labor?
nurses FIRST action is to listen to fetal rate/tone
365.
How to treat phobic disorders?
systematic desensitization
366.
Best way to tube feed or feed kids?
small frequent is better than large
367.
With lower amputations?
place in prone position
368.
LVN/LPN cant?
Handle any blood
369.
Cardinal signs of ARDS?
Cardinal sign of ARDS is hypoxemia (low oxygen level in tissues).
370.
Best indicator of dehydration?
weight
371.
Besides sodium, water also follows?
Glucose
372.
Use of cold and hot?
Use cold for acute pain (sprained ankle) and heat for chronic pain (arthritis)
373.
Guided imagery is great for?
CHRONIC pain
374.
When patient is in distress?
Med istration is rarely a good choice
375.
Pneumonia?
pneumonia, fever and chills are usually present. For the elderly confusion is often present.
376.
COPD and Pneumonia?
COPD is chronic, pneumonia is acute. Emphysema and bronchitis are both COPD. in COPD patients the baroreceptors that detect the CO2 level are destroyed. Therefore, O2 level must be low because high O2 concentration blows the patient's stimulus for breathing.
377.
4 options for cancer?
chemo, radiation, surgery, allow to die with dignity.
378.
Nuetropenic patients?
no live vaccines, no fresh fruits, no flowers should be used for neutropenic patients.
379.
Where are chest tubes placed?
chest tubes are placed in the pleural space.
380.
Diff between angina and MI?
angina (low oxygen to heart tissues) = no dead heart tissues. MI= dead heart tissue present.
381.
Preload and Afterload?
Preload affects amount of blood that goes to the R ventricle. Afterload is the resistance the blood has to overcome when leaving the heart.
382.
CABG?
for a CABG operation when the great saphenous vein is taken it is turned inside out due to the valves that are inside.
383.
1 tsp= how many ml ?
1 t (teaspoon)= 5 ml
384.
1 tablespoon = how many ml?
1 T(tablespoon)= 3 t = 15 ml
385.
How many oz in a ml?
30 ml = 1 oz
386.
1 cup= how many oz?
1 cup= 8 oz
387.
1 quart = how many pints?
1 quart = 2 pints
388.
1 pint = how many cups?
1 pint= 2 cups
389.
1 gr= how many mg?
1 gr (grain)= 60 mg
390.
1 g = how many mg?
1 gram = 1000 mg
391.
1 kg= how many pounds?
2.2
392.
1 lb = how many ozs?
one pound equals 16 0z
393.
Temp conversion?
* To convert Centigrade to F. F= C+40, multiply 9/5 and substract 40 * To convert Fahrenheit to C. C= F+40, multiply 5/9 and substract 40.
394.
After Endoscopy?
after endoscopy check gag reflex.
395.
TPN is given in ?
TPN(total parenteral nutrition) given in subclavian line.
396.
Low Residue diet?
low residue diet means low fiver
397.
Diverticulitis?
diverticulitis (inflammation of the diverticulum in the colon) pain is around LL quadrant.
398.
Appendicitis
Appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix) pain is in RL quadrant with rebound tenderness.
399.
Cause of Ascites?
portal hypotension + albuminemia= Ascites.
400.
Who produces insulin?
beta cells of pancreas produce insulin
401.
s3 heart sound is normal? not?
Normal in CHF from the squishin'.. NOT normal in an MI patient
402.
Signs observed in hypocalemia?
Trousseau and Tchovoski signs observed in hypocalcemia
403.
DKA?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)= when body is breaking down fat instead of sugar for energy. Fats leave ketones (acids) that cause pH to decrease. 71. DKA is rare in diabetes mellitus type II because there is enough insulin to prevent breakdown of fats.
404.
s/s of a fat embolism?
petechiae. Treated with heparin.
405.
Knee replacement?
for knee replacement use continuous ive motion machine.
406.
Glaucoma patients loose?
glaucoma patients lose peripheral vision. Treated with meds
407.
c02 builds up and causes?
Co2 causes vasoconstriction.
408.
Where are most spinal cord injuries?
most spinal cord injuries are at the cervical or lumbar regions
409.
autonomic dysreflexia
autonomic dysreflexia ( life threatening inhibited sympathetic response of nervous system to a noxious stimulus- patients with spinal cord injuries at T-7 or above is usually caused by a full bladder.
410.
Myasthenia gravis?
myasthenia gravis= decrease in receptor sites for acetylcholine. Since smallest concentration of ACTH receptors are in cranial nerves, expect fatigue and weakness in eye, mastication, pharyngeal muscles.
411.
Guillian Barre?
Guillain-Barre syndrome= ascending paralysis. Keep eye on respiratory system.
412.
Parkisons?
parkinson's = RAT: rigidity, akinesia (loss of muscle mvt), tremors. Treat with levodopa.
413.
TIA?
TIA (transient ischemic attack) mini stroke with no dead brain tissue
414.
CVA?
CVA (cerebrovascular accident) is with dead brain tissue.
415.
Hodgkins disease?
Hodgkin's disease= cancer of lymph is very curable in early stage.
416.
Rule of nines?
Rule of NINES for burns Head and Neck= 9% Each upper ext= 9% Each lower ext= 18% Front trunk= 18% Back trunk= 18% Genitalia= 1%
417.
Peds weight ?
Birth weight doubles by 6 month and triple by 1 year of age.
418.
Dig rule for kids?
if HR is <100 do not give dig to children.
419.
First sign of cystic fibrosis?
first sign of cystic fibrosis may be meconium ileus at birth. Baby is inconsolable, do not eat, not ing meconium.
420.
Heart Defects?
heart defects. for cyanotic -3T's( Tof, Truncys arteriosus, Transposition of the great vessels). Prevent blood from going to heart. If problem does not fix or cannot be corrected surgically, CHF will occur following by death. 94. with R side cardiac
421.
Heart problems?
with R side cardiac cath=look for valve problems with L side in adults look for coronary complications
422.
What disease leads to cardiac valve malfunctions?
Rhematic fever
423.
Cerebral palsy?
poor muscle control due to birth injuries and/or decrease oxygen to brain tissues
424.
I?
I (intracranial pressure) should be <2. measure head circonference.
425.
Signs to look for in meningitis?
for Meningitis check for Kernig's/ Brudzinski's signs.
426.
Wilms tumor?
Wilm's tumor is usually encapsulated above the kidneys causing flank pain.
427.
Facts about hemophilia?
It is X-linked. Mother es the disease to her son
428.
What happens when phenylalanine increases?
brain problems occur
429.
Bucks traction =
knee immobility
430.
Russel Traction =
femur or lower leg instability
431.
Dunlap traction=
Skeletal or skin
432.
Bryant's traction=
Children <3yoa, <35 lbs with femur fx
433.
How to put on traction?
Place the apparatus first then place the weight (der)
434.
Where should placenta be?
Upper part of the uterus
435.
Eclampsia is a ?
seizure>
436.
A patient with vertical c- section will likely have?
another c section with any more kids
437.
Amniocentesis is performed? and why?
perform amniocentesis before 20 weeks gestation to check for cardiac and pulmonary abnormalities.
438.
Rh?
mothers receive rhogam to protect next baby.
439.
Fontanelles?
anterior fontanelle closes by 18 months. Posterior 6 to 8 weeks.
440.
caput succedaneum=
caput succedaneum= diffuse edema of the fetal scalp that crosses the suture lines. Swelling reabsorbs within 1 to 3 days.
441.
Pathological jaundice?
pathological jaundice= occurs before 24hrs and last7 days. Physiological jaundice occurs after 24 hours.
442.
Diff between placenta previa and placenta abrupto?
placenta previa = there is no pain, there is bleeding. Placenta abruption = pain, but no bleeding.
443.
Bethamethasone?
bethamethasone (celestone)=surfactant. Med for lung expansion.
444.
Dystocia?
dystocia= baby cannot make it down to canal
445.
Therapies?
milieu therapy= taking care of patient/environment cognitive therapy= counseling crisis intervention=short term.
446.
Rule of thumb for obsessions/distractions?
Osession is to thought. Compulsion is to action
447.
Rule of thumb for assisting pysch patients?
if patients have hallucinations redirect them. In delusions distract them.
448.
Alzheimers?
Alzheimer's disease is a chronic, progressive, degenerative cognitive disorder that s for more than 60% of all dementias
449.
Hyperthyroidism?
HYPERthyroidism think of MICHAEL JACKSON in THRILLER! SKINNY, NERVOUS, BULDGING EYES, Up all night, heart beating fast
450.
Awesome ing for cranial nerves?
Cranial Nerves: *I am sorry if this vulgar for some, but hey, it sticks Sensory=S Motor=M Both=B Oh (Olfactory I) Some Oh (Optic II) Say Oh (Oculomotor III) Marry To (Trochlear IV) Money Touch (Trigeminal V) But And (Abducens VI) My Feel (Facial VII) Brother A (Auditory VIII) Says Girls (Glossopharyngeal IX) Big Vagina (Vagus X) Bras And (Accessory XI) Matter Hymen (Hypoglassal XII) More
451.
Hypernatremia? SALT?
Hyper natremia (greater than 145) SALT! Skin flushed Agitation Low grade fever Thirst
452.
Developmental milestones?
Developmental 2-3 months: turns head side to side 4-5 months: grasps, switch & roll 6-7 months: sit at 6 and waves bye-bye 8-9 months: stands straight at eight 10-11 months: belly to butt (phrase has 10 letters) 12-13 months: twelve and up, drink from a cup
453.
Hepatitis?
Hepatitis Hepatitis: -ends in a VOWEL, comes from the BOWEL (Hep A) Hepatitis B=Blood and Bodily fluids Hepatitis C is just like B
454.
Apgar scores/scoring?
Apgar measures HR,RR,Muscle tone, Reflexes,Skin color each 0-2 point. 8-10 OK. 0-3 RESUSCITATE.
455.
Cute way to glascow coma?
GLASGOW COMA SCALE. EYES, VERBAL,MOTOR! It is similar to measuring dating skills...max 15 points -one can do it if below 8 you are in Coma. So, to start dating you gotta open your EYES first, if you albe to do that spontaneously and use them correctly to SEE whom you dating you earn 4. But if she has to scream on you to make you open them it is only 3....and 1 you dont care to open even if she tries to hurt you. if you get good EYE (4 points) then move to VERBAL. talk to her/ him! if you can do that You are really ORIENTED in situation she/he uncontiously gives you 4 points! if you like her try not to be CONFUSED (3), and of cause do not use INAPPROPRIATE WORDS (3), she will not like it)), try not to RESPOND WITH INCOMPREHENSIBLE SOUNDS (2), if you do not like herjust show no VERBAL RESPONSE(1) Since you've got EYE and VERBAL you can MOVE now using your Motor Response Points. THis is VERY important since Good moves give you 6!
456.
What to do for addisons/cushings?
Addison's disease (need to "add" hormone) Cushing's syndrome (have extra "cushion" of hormones)
457.
Dumping syndrome?
Dumping syndrome: increase fat and protein, small frequent meals, lie down after meal to decrease peristalsis, wait 1 hr after meals to drink.
458.
Blood typing?
For blood types: "O" is the universal donor ( "o" in donor) "AB" is the universal receipient
459.
Gross things to about nurses with herpes!!!!
Disseminated Herpes Zoster is AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS, as to Localized Herpes Zoster is PRECAUTIONS. A nurse with a localized herpes zoster CAN care for patients as long as the patients are NOT immunosuppressed and the lesions must be covered!
460.
Birth control- Diaphram?
Diaphragm must stay in place 6 hours after intercourse. They are also fitted so must be refitted if you lose or gain a significant amount of weight.
461.
Cushing ulcers and cushings triad?
Cushings ulcers r/t BRAIN injury *Cushings triad r/t I in BRAIN (htn, bradycard, irr. resp)
462.
Thyroid storm and myxedema?
Thyroid storm is HOT (hyperthermia) *Myxedema coma is COLD (hypothermia)
463.
Nondairy sources of calcium?
Non dairy sources of calcium include RHUBARB, SARDINES, COLLARD GREENS
464.
Whats petaling?
You can petal the rough edges of a plaster cast with tape to avoid skin irritation.
465.
How do you teach someone to reduce back aches?
With low back aches, bend knees to relieve
466.
Koplick's spots?
* Koplick's spots are red spots with blue center characteristic of PRODROMAL stage of Measles. Usually in mouth.
467.
Pancreatitis pts>?
* Pancreatitis patients but them in fetal position, NPO, gut rest, prepare antecubital site for PICC cuz they'll probably be getting TPN/Lipids
468.
Trendelenberg's test?
Trendelenburg test - for varicose veins. If they fill proximally = varicosity.
469.
What can't you give to immunosupressed pts?
Yogurt has live cultures- dont give to immunosuppressed pt
470.
How to itch under a cast?
Itching under cast area- cool air via blow dryer, ice pack for 10- 15 minutes. NEVER use qtip or anything to scratch area
471.
Murphy's sign?
Murphy's sign - pain with palpation of gall bladder area seen with cholecystitis
472.
Cullens sign?
Cullen's sign - ecchymosis in umbilical area, seen with pancreatitis
473.
Turner's sign?
Turner's sign - flank grayish blue (turn around to see your flanks) pancreatitis
474.
Mcburney's point?
McBurney's Point - pain in RLQ indicative of appendicitis--RLQ - appendicitis, watch for peritonitis
475.
Pain in the LLQ indicative of?
LLQ - diverticulitis , low residue, no seeds, nuts, peas
476.
Guthrie test?
Guthrie Test - Tests for PKU, baby should have eaten source of protein first
477.
Shilling test?
Shilling Test - test for pernicious anemia/ how well one absorbs Vit b12
478.
Allen's test?
Allen's test - occlude both ulnar and radial artery until hand blanches then release ulnar. If the hand pinks up, ulnar artery is good and you can carry on with ABG/radial stick as planned. ABGS must be put on ice and whisked to the lab.
479.
Tenkhoff cath?
oIt's ok to have abdominal craps, blood tinged outflow and leaking around site if the Peritoneal Dialysis cath (tenkhoff) was placed in the last 1-2 wks. Cloudy outflow NEVER NORMAL.
480.
Meconium stained protocol?
oAmniotic fluid yellow with particles = meconium stained`
481.
Hyper reflexive? Absent reflexsive?
oHyper reflexes (upper motor neuron issue "your reflexes are over the top") oAbsent reflexes (lower motor neuron issue)
482.
When is Rhogam given and how?
oRhogam : given at 28 weeks, 72 hours post partum, IM. Only given to Rh NEGATIVE mother.
483.
Coomb's test?
Also if indirect Coomb's test is positive, don't need to give Rhogam cuz she has antibody only give if negative coombs
484.
Order of assessment?
Order of assessment: Inspection, Palpation, Percussion and Ausculation. EXCEPT with abdomen cuz you don't wanna mess with the bowels and their sounds so you Inspect, Auscultate, Percuss then Palpate (same with kids, I suppose since you wanna go from least invasive to most invasive sine they will cry BLOOD MURDER ! Gotta love them kids !)
485.
Latex allergies?
Latex allergies => Assess for allergies to bananas, apricots, cherries, grapes, kiwis, ion fruit, avocados, chestnuts, tomatoes, peaches
486.
ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ( ALS ) is a condition in which there is a degeneration of motor neurons in both the upper & lower motor neuron systems.
487.
TEF?
Transesophageal Fistula (TEF) - esophagus doesn't fully develop (this is a surgical emergency) The 3 C's of TEF in the newborn: 1) Choking 2) Coughing 3) Cyanosis
488.
MMR SHot?
The MMR vaccine is given SQ not IM.
489.
Color codes?
Red--unstable, ie, occluded airway, actively bleeding, see first Yellow---stable, can wait up to an hour for treatment, ie burns, see second Green---stable, can wait even longer to be seen, "walking wounded" Black--unstable clients that will probably not make it, need comfort measures
490.
Greeks?
Greek heritage - they put an amulet or any other use of protective charms around their baby's neck to avoid "evil eye" or envy of others
491.
4 year olds?
4 year old kids cannot interpret TIME. Need to explain time in relationship to a known COMMON EVENT (eg: "Mom will be back after supper").
492.
Hep B vaccine always ask?
Anaphylactic reaction to baker's yeast is contraindication for Hep B vaccine.
493.
Flu shot always ask?
allergic to eggs??? (Tristan D. ) !
494.
Before giving MMR>?
** Ask for anaphylactic rxn to eggs or neomycin before MMR
495.
If kid has a cold?
**If kid has cold, can still give immunizations
496.
SARS?
**SARS (severe acute resp syndrome) airborne + (just like varicella)
497.
Disease precautions?
** Hepatitis A is precautions ** Tetanus, Hepatitis B, HIV are STANDARD precautions
498.
Willam's position?
** William's position - Semi Fowlers with knees flexed (inc. knee gatch) to relieve lower back pain.
499.
Signs of a hip fracture?
SIGNS of a Fractured hip: EXTERNAL ROTATION, SHORTENING, ADDUCTION
500.
S/S of a fat embolism?
Fat Embolism: Blood tinged sputum (r/t inflammation), inc ESR, respiratory alkalosis (not acidosis r/t tachypnea), hypocalcemia,increased serum lipids, "snow storm" effect on CXR.
501.
Complications of mechanical ventilation?
Complications of Mechanical Ventilation: Pneumothorax, Ulcers
502.
Paget's disease?
Paget's Disease - tinnitus, bone pain, enlargement of bone, thick bones.
503.
Intravenous Pylogram requires?
** IVP requires bowel prep so they can visualize the bladder better
504.
ACID ash diet?
Acid Ash diet - cheese, corn, cranberries, plums, prunes, meat, poultry, pastry, bread
505.
Alkaline Ash diet?
Alk Ash diet- milk, veggies, rhubarb, salmon
506.
Orange tag in pysch
Orange tag in triage is non emergent Psych
507.
Greenstick fracture?
Greenstick fractures, usually seen in kids bone breaks on one side and bends on the other
508.
Side effects of thyroid hormones?
Insomnia is a side effect of thyroid hormones. Saunders confirms it. Makes sense though!Increased met. rate, your body is "too busy to sleep" as opposed to the folks with hypothyroidism who may report somnolence (dec. met rate, body is slow and sleepy).
509.
Botox?
** BOTOX for strabismus. Patch the GOOD eye so that the weaker eye can get stronger. Found a cool link about its use in peds pt with strabismus. I had to look it up cuz I heard it was important ah hem ah hem
510.
Tidal volume?
** TIDAL VOLUME is 7 - 10ml / kg
511.
COPD patients?
** COPD patients : 2LNC or less (hypoxic NOT hypercapnic drive), Pa02 of 60ish and Sa02 90% is normal for them b/c they are chronic CO2 retainers. ...
512.
Stranger Danger>?!?
Stranger anxiety is greatest 7 - 9 months, Separation anxiety peaks in toddlerhood
513.
Lymes mostly found in
Lymes is found mostly in Conneticuts
514.
Asthma and arthritis best excercise?
swimming
515.
What is a bad sign in asthma?
intercostal retractions=bad!
516.
ABG drawin?
When drawing an ABG, you need to put the blood in a heparinized tube, make sure there are no bubbles, put on ice immediately after drawing, with a lable indicating if the pt was on room air or how many liters of O2. to preform the Allen's Test prior to doing an ABG to check for sufficient blood flow
517.
Before a pft?
Before going for Pulmonary Fuction Tests (PFT's), a pt's bronchodilators will be with-held and they are not allowed to smoke for 4 hrs prior
518.
For a lung biopsy?
For a lung biopsy, position pt lying on side of bed or with arms raised up on pillows over bedside table, have pt hold breath in midexpiration, chest x-ray done immediately afterwards to check for complication of pneumothorax, sterile dressing applied
519.
For a lumbar puncture?
For a lumbar puncture, pt is positioned in lateral recumbent fetal position, keep pt flat for 2-3 hrs afterwards, sterile dressing, frequent neuro assessments
520.
For an EEG test?
EEG, hold meds for 24-48 hrs prior, no caffine or cigarettes for 24 hrs prior, pt can eat, pt must stay awake night before exam, pt may be asked to hyperventilate and watch a bright flashing light, after EEG, assess pt for seizures, pt's will be at increased risk
521.
Munchhausen Syndrome?
-Munchausen Syndrome is a psychiatric disorder that causes an individual to self-inflict injury or illness or to fabricate symptoms of physical or mental illness, in order to receive medical care or hospitalization. In a variation of the disorder, Munchausen by proxy (MSBP), an individual, typically a mother, intentionally causes or fabricates illness in a child or other person under her care.
522.
MS?
-Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic, progressive disease with demyelinating lesions in the CNS which affect the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. Motor S/S: limb weakness, paralysis, slow speech Sensory S/S: numbness, tingling, tinnitus Cerebral S/S: nystagmus, ataxia, dysphagia, dysarthria
523.
Huntington's Chorea?
Huntington's Chorea: 50% genetic, autosomal dominant disorder S/S: chorea --> writhing, twisting, movements of face, limbs and body -gait deteriorates to no ambulation -no cure, just palliative care
524.
Shift to the left means?
WBC shift to the left in a patient with pyelonephritis neutrophils kick in to fight infection
525.
How to Dx a AAA?
Definitive diagnosis for abd. aortic aneurysm (AAA) --> CT scan
526.
Uremic Fetor?
Uremic fetor --> smell urine on the breath
527.
Hirschsprungs?
-Hirschsprung's --> bile is lower obstruction, no bile is upper obstruction; ribbon like stools.
528.
No Cantalope?
Thank you, I finally realize why a person shouldn't have cantaloupe before a occult stool test, because cantaloupe is high in vit c and vit c causes a false + for occult blood. Now I just need to figure out why they can't have fish.
529.
Penis Problems?
Hypospadias: abnormality in which urethral meatus is located on the ventral (back) surface of the penis anywhere from the corona to the perineum ( hypo, low (for lower side or under side) Epispadias: opening of the urethra on the dorsal (front) surface of the penis Priapism: painful erection lasting longer than 6 hrs.
530.
When you see coffee brown emesis think?>
Peptic ulcer
531.
For PVD ?
For PVD DAVE (Legs are Dependent forArterial & for Venous Elevated)
532.
Traction rule?
Never release traction unless you have an order from an MD to do so
533.
Halo?
Questions about a halo? safety first, have a screwdriver nearby.
534.
Compartment syndrome?
compartment syndrome is an emergency situation. Paresthesias and increased pain are classic symptoms. Neuromuscular damage is irreversible 4-6 hours after onset.
535.
Behavior/Developmental-Peds
Behavior motivated by need to avoid anxiety and satisfy needs 1. Infancy 0-18 months others will satisy needs 2. childhood >6yrs learn to delay need gratification 3. juvenile 6-9 years learn to relate to peers 4. preadolescence 9-12 yrs learns to relate to friends of of opposite sex 5. early adolescence12-14yrs:learn independence and how to relate to opposite sex 6. late adolecence 14-21yrs: develop intimate relationship with person of opposite sex is this not about communication?....
536.
Fetal alcohol sydrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome -upturned nose -flat nasal bridge -thin upper lip -SGA
537.
Immunizations rules?
vastus lateralis is IM istration site for 6month infants For toddlers above 18 months ventrogluteal The deltoid and gluteus maximus are appropriate sites for children`
538.
Eyes?
OU- both eyes OS- left eye OD- right eye ( dominent Right eye- just a tip to )
539.
Cane walking?
1. COAL (cane walking): C - cane O - opposite A - affected L - leg
540.
In depth- Color codes??
Red- Immediate: Injuries are life threatening but survivable with minimal intervention. Ex: hemothrax, tension pneumothorax, unstable chest and abdominal wounds, INCOMPLETE amputations, OPEN fx's of long bones, and 2nd/3rd degree burn with 15%-40% of total body surface, etc. Yellow- Delayed: Injuries are significant and require medical care, but can wait hrs without threat to life or limb. Ex: Stable abd wounds without evidence of hemorrhage, fx requiring open reduction, debridement, external fixation, most eye and CNS injuries, etc. Green- Minimal: Injuries are minor and tx can be delayed to hrs or days . Individuals in this group should be moved away from the main triage area. Ex: upper extremity fx, minor burns, sprains, sm. lacerations, behavior disorders. Black- Expectant: Injuries are extensive and chances of survival are unlikely. Seperate but dont abandoned, comfort measures if possible. Ex: Unresponsive, spinal cord injuries, woulds with anatomical organs, 2nd/3rd degree burn with 60% of body surface area , seizures, profound shock with multipe injuries, no pulse, b.p, pupils fixed or dilated.
541.
Thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis prep- Take v.s., shave area around needle insertion, position patient with arms on pillow on over bed table or lying on side, no more than 1000cc at a one time. Post- listen for bilateral breath sounds, v.s., check leakage, sterile dressing.
542.
Cath lab?
Cardiac cath- npo 8-12hr, empty bladder, pulses, tell pt may feel heat palpitations or desire to cough with dye injection. Post- Vital signs keep leg straight bedrest 6-8hr.
543.
MRI?
MRI- claustrophobia, no metal, assess pacemaker
544.
Cerebral angio prep?
cerebral angio prep- well hydrated, lie flat, sire shaved, pulses marked post- keep flat 12-14hr, check site, pulses,force fluids.
545.
More info on lumbar puncture?
Lumbar puncture- fetal postion. post- nuero assess q15-30 until stable, flat2-3hr, encourage fluids, oral anlgesics for headache, observe dressing
546.
More info on EEG?
EEG- no sleep the night before, meals not withheld, no stimulants for 24hr before, tranquilizer/stimulant meds held 24-48hr before, may be asked to hyperventilate 3-4min and watch a bright flashing light.
547.
Myelogram?
Myelogram- Npo 4-6hr, allergy hx, phenothiazines, cns depressants, and stimulants withheld 48hr prior, table will be moved to various postions during test. Post- neuro q2-4, water soluble HOB up, oil soluble HOB down, oral analgesics for h/a, encourage po fluids, assess for distended bladder, inspect site.
548.
Liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy- vit k , npo morning of exam 6hr, give sedative, Teach pt that he will be asked to hold breath for 5-10sec, supine postion, lateral with upper arms elevated. Post- postion on right side, frequent v.s., report severe ab pain stat, no heavy lifting 1wk.
549.
Paracentesis?
Paracentesis- semi fowlers or upright on edge of bed, empty bladder. Post- v.s., report elevated temp, observe for signs of hypovolemia.
550.
Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy- CO2 used to enhances visual, general anesthesia, foley. Post- walk patient to decrease CO2 build up used for procedure.
551.
Sengstaken blakemore tube ?
Sengstaken blakemore tube used for tx of esophageal varices, keep scissors at bedside.
552.
Hemovac?
Hemovac- used after mastectomy, empty when full or q8hr, remove plug, empty contents, place on flat surface, cleanse opening and plug with alcohol sponge, compress evacuator completely to remove air, release plug, check system for operation.
553.
Common S/S of PTB?
Common Signs and Symptoms 01. PTB - low-grade afternoon fever.
554.
Common S/S of pneumonia?
Rusty sputum
555.
Common S/S of asthma
Wheezing on EXPIRATION
556.
Common S/S of emphysema?
Barrel chest
557.
Common S/S of Kawasaki syndrome?
Strawberry tongue
558.
Common S/S of pernicious anemia
red beefy tongue
559.
Common S/S of down syndrome
protruding tongue
560.
Common S/S of Cholera?
Rice watery stool
561.
Common S/S of Malaria?
Stepladder like fever with chills
562.
Common S/S of Thypohiod
Rose spots on abdomen
563.
Common S/S of Diptheria?
Psuedo membrane formation
564.
Common S/S of measles?
Kopliks spots
565.
Common S/S of SLE?
Butterfly rashes
566.
Common S/S of Liver cirrhoisis?
Spider like varices- Varices can be in stomach, esophagus or the skin! They are just spider/varicose veins! Ithcy on the skin
567.
Common S/S of leprosy?
Lioning face
568.
Common S/S of Bulimia?
chipmunk face
569.
Common S/S of appendicitis
rebound tenderness
570.
Common S/S of Dengue
petechiae or + Herman's sign
571.
Common S/S of Meningitis?
Kernigs Sign (leg flex then leg pain on extension) Brudinzski sign (neck flex= lower leg flex)
572.
Common S/S of Tetany?
Risus Sardonicus
573.
Common S/S of pancreatitis?
Cullens sign ( ecchymosis of umbilicus) (+) Grey Turner spots
574.
Common S/S of pyloric stenosis?
olive like mass
575.
Common s/s of PDA
Machine like murmur
576.
Common S/S of addisions?
bronze like skin pigmentation
577.
Common S/S of Cushings syndrome?
Moon face appearance and buffalo hump
578.
Common S/S of Intusseption?
Sausage shaped mass , Dance sign (empty portion of RLQ)
579.
Common S/S of MS>?
Charcot's Triad (IAN)
580.
Common S/S of MG?
Descending muscle weakness
581.
Common S/S of guillian Barre Syndrome
Ascending muscle paralysis.. dont confuse with MG
582.
Common S/S of chicken pox?
Vesicular rash (central to distal) dew drop on rose petal
583.
Common S/S of LTB?
inspiratory stridor.. LTB = croup!!!!
584.
Common S/S of TEF?
4 C'S- Coughing, Choking, Cyanosis and continuous droolings
585.
Common S/S of epiglottitis?
3 D'S --Drooling, Dysphonia, Dysphagia
586.
Common S/S of Hodgkins Disease/Lymphoma?
Painless, progressive englargement of spleen and lymph tissues, and Reedstenberg cells!
587.
Common S/S of Infectious Mononucleosis?
Hallmark= Sore throat, cervical lymph adenopathy, fever
588.
Common S/S of parkinsons?
Pilling rolling tremors
589.
Cmmon S/S Fibrin Hyalin?
Expiratory grunt-- Causes Infant respiratory distress!
590.
Common S/S of cystic fibrosis?
Salty skin
591.
Common S/S of DKA
Kussmauls breathing (deep rapid RR)
592.
Common S/S of Bladder Cancer?
painless hematuria... CA=Cancer ! Duhh
593.
Common S/S of BPH?
reduced size and force of urine
594.
Common S/S of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Nilosky's sign (seperation of epidermis caused by rubbibng of the skin)
595.
Common S/S of retinal detachment?
Visual floaters, flashes of light, curtain vision
596.
Common S/S of glaucoma?
Painful vision loss, tunnel/gun barrel/ halo vision (peripheral vision loss)
597.
Common S/S of Cataract?
PainLESS vision loss, opacity of lens, blurring of the vision
598.
Common S.S of Retino Blastoma?
Cat's eye reflex (grayish discoloration of the pupil)
599.
Common S/S Acromegaly?
Coarse facial features
600.
Common S/S Duchennes Muscular Dystrophy?
Gower's sign (use of the hands to push ones self from the floor_) Looks EXACTLY like the Pilates Downward dog!!!!!!!
601.
Common S/S of GERD?
Barrets Esophagus (erosion of the lower portion of the esophageal mucosa)
602.
Common S/S Hepatic Encephalopathy ?
Flapping tremors
603.
Common S/S of Hydrocephalosis?
Bossing Sign (prominent forehead)
604.
Common S/S of Increased I?
HYPERTENSION, BRADYpnea, BRADYcardia (cushings triad)!
605.
Common S/S of Shock?
HYPERtension TACHYpnea and TACHYcardia
606.
Common S/S Meniere's Disease?
Vertigo, Tinnitus
607.
Common S/S of Cystitis?
Burning on urination
608.
Common S/S of hypocalcemia?
Chvostek and Trosseaus sign! Also hypomag!
609.
Common S/S of Ulcerative Colitis?
Recurrent bloody diarrhea
610.
Common S/S of Lyme's disease
Bull's eye rash
611.
Common S/S of Basilar Fracture?
Ottorhea
612.
Common S/S of orbital fracture?
Battles Sign and Racoon's eyes
613.
Osteomyeltitis?
Osteomyletitis is an infectious bone dz. Give blood cultures and antibiotics, then if necessary surgery to drain abscess.
614.
Nephrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome s/s edema + hypotension. Turn and reposition (risk for impaired skin integrity)
615.
Renal impairment labs?
Renal impairment: serum creatinine elevated and urine clearance decreased
616.
Normal Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin Neonates 18-27 3 mos 10.6-16.5 3 yrs 9.4-15.5 10 yrs 10.7-15.5
617.
Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis: take vs q 4 hrs + daily weights
618.
Age 4=5 year shots?
Age 4 to 5 yrs child needs DPT/MMR/OPV
619.
Cystic fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis give diet low fat, high sodium, fat soluble vitamins ADEK. Aerosal bronchodilators, mucolytics and pancreatic enzymes.
620.
More info on droplet precautions?
Droplet Precautions:sepsis, scarlet fever, streptococcal pharyngitis, parovirus B19, pnuemonia, pertusis, influenza, diptheria, epiglottis, rubella, mumps, meningitis, mycoplasma and adenovirus. Door open, 3 ft distance, private room or cohort, mask
621.
Meningeal irriatation>?
Meningeal irritation S/s nuchal rigidity, positive Brudzinski + Kernig signs and PHOTOPHOBIA too!
622.
Babinski sign?
toes curl= GREAT Toes fan = BAD
623.
GTT for preggos?
Glucose Tolerance Test for preggies result of 140 or highter needs further evaluation.
624.
Cranial nerves for Assessing extraocular eye movements?
3,4,6
625.
Stomas?
Stomas dusky stoma means poor blood supply, protruding means prolapsed, sharp pain + rigidity means peritonitis, mucus in ileal conduit is expected.
626.
Tension Pneumothorax?
Trachea shifts to the opposite side
627.
Change in color is ?
a LATE sign! Always~!
628.
Incentive Spirometry steps?
Incentive Spirometry steps:1) Sit upright 2) Exhale 3) Insert mouthpiece 4) Inhale for 3 seconds, and then HOLD for 10 seconds
629.
MRSA and VRSA precautions?
*MRSA - precaution ONLY *VRSA - AND airborne precaution (Private room, door closed, negative pressure)
630.
Thrombocyopenia- bleeding precautions
*Thrombocytopenia -Bleeding precautions! 1)Soft bristled toothbrush 2)No insertion of anything! (c/i suppositories, douche)
631.
Burn Degrees?
1st Degree - Red and Painful 2nd Degree - Blisters 3rd Degree - No Pain because of blocked and burned nerves
632.
Menieres's disease?
*Meniere's Disease - diuretics to decrease endolymph in the cochlea, restrict Na, lay on affected ear when in bed. Triad: 1)Vertigo 2)Tinnitus 3)N/V
633.
Gastric ulcer pain
*Gastric Ulcer pain occurs 30 minutes to 90 minutes after eating, not at night, and doesn't go away with food
634.
Med that can't be infused Intra osseously?
One medication that cannot be istered by intraosseous infusion is isoproterenol, a beta agonist.
635.
Sickle cell crisis?
During sickle cell crisis there are two interventions to prioritize: fluids and pain relief.
636.
Glomerulonephritis considerations
With glomerulonephritis you should consider blood pressure to be your most important assessment parameter. Dietary restrictions you can expect include fluids, protein, sodium, and potassium.
637.
Labs for congenital heart disease?
yesterday when I mentioned how congenital cardiac defects result in hypoxia which the body attempts to compensate for (influx of immature rbc's)? Labs ing this would show increased hematocrit, hemoglobin, and rbc count.
638.
Kidneys and ears?
Did you know there is an association between low-set ears and renal anomalies? Now you know what to look for if down's isn't there to choose. (just to expand on it a little, the kidneys and ears develop around the same time in utero. Hence, they're shaped similarly. Which is why when doing an assessment of a neonate, if the nurse notices low set or asymmetrical ears, there is good reason to investigate renal functioning. Knowing that the kidneys and ears are similar shapes helped me this).
639.
School aged kids and five year olds?
School-age kids (5 and up) are old enough, and should have an explanation of what will happen a week before surgery such as tonsillectomy.
640.
What if a toddler says no to medication?
If you gave a toddler a choice about taking medicine and he says no, you should leave the room and come back in five minutes, because to a toddler it is another episode. Next time, don't ask.
641.
First sign of pyloric stenosis in a baby?
The first sign of pyloric stenosis in a baby is mild vomiting that progresses to projectile vomiting. Later you may be able to palpate a mass, the baby will seem hungry often, and may spit up after feedings.
642.
Kawasaki disease causes?
We know Kawasaki disease causes a heart problem, but what specifically? Coronary artery aneurysms d/t the inflammation of blood vessels.
643.
A child with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt
A child with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt will have a small upper-abdominal incision. This is where the shunt is guided into the abdominal cavity, and tunneled under the skin up to the ventricles. You should watch for abdominal distention, since fluid from the ventricles will be redirected to the peritoneum. You should also watch for signs of increasing intracranial pressure, such as irritability, bulging fontanels, and high-pitched cry in an infant. In a toddler watch lack of appetite and headache. Careful on a bed position question! Bed-position after shunt placement is flat, so fluid doesn't reduce too rapidly. If you see s/s of increasing i, then raise the hob to 15-30 degrees.
644.
What could cause bronchopulmonary dysplasia?
What could cause bronchopulmonary dysplasia? Dysplasia means abnormality or alteration. Mechanical ventilation can cause it. Premature newborns with immature lungs are ventilated and over time it damages the lungs. Other causes could be infection, pneumonia, or other conditions that cause inflammation or scarring.
645.
How do children less than one breathe?
It is essential to maintain nasal patency with children < 1 yr. because they are obligatory nasal breathers.
646.
Milk for kids?
Watch out for questions suggesting a child drinks more than 3-4 cups of milk each day. (Milks good, right?) Too much milk reduces intake of other essential nutrients, especially iron. Watch for anemia with milk-aholics. And don't let that mother put anything but water in that kid's bottle during naps/over-night. Juice or milk will rott that kids teeth right out of his head.
647.
Traction in kids?
What traction is used in a school-age kid with a femur or tibial fracture with extensive skin damage? Ninety, ninety. Huh? I never heard of it either. The name refers to the angles of the ts. A pin is placed in the distal part of the broken bone, and the lower extremity is in a boot cast. The rest is the normal pulleys and ropes you're used to visualizing with balanced suspension. While we're talking about traction, a kid's hinder should clear the bed when in Bryant's traction (also used for femurs and congenial hip for young kids).
648.
Yeast infection in a babys mouth?
If you can remove the white patches from the mouth of a baby it is just formula. If you can't, its candidiasis.
649.
MMR and Varicella?
Just know the MMR and Varicella immunizations come later (15 months).
650.
Cryptoorchidism?
Undescended testis or cryptorchidism is a known risk factor for testicular cancer later in life. Start teaching boys testicular self exam around 12, because most cases occur during adolescence.
651.
Maslow for a guy who lost his house in a fire?
- A guy loses his house in a fire. Priority is using community resources to find shelter, before assisting with feelings about the tremendous loss. (Maslow).
652.
Kids pain relief in NCLEX land?
No aspirin with kids b/c it is associated with Reye's Syndrome, and also no nsaids such as ibuprofen. Give Tylenol.
653.
How will CSF look in meningitis?
CSF in meningitis will have high protein, and low glucose.
654.
Suctioning is good--except
No nasotracheal suctioning with head injury or skull fracture.
655.
Peds positioning for GERD?
Position prone w hob elevated with gerd. In almost every other case, though, you better lay that kid on his back (Back To Sleep - SIDS).
656.
When instilling eardrops?
Pull pinna down and back for kids < 3 yrs. when instilling eardrops.
657.
Kids with RSV?>
Kids with RSV; no lenses or pregnant nurses in rooms where ribavirin is being istered by hoot, tent, etc.
658.
Positioning with pneaumonia?
Positioning with pneumonia - lay on the affected side to splint and reduce pain. But if you are trying to reduce congestion the sick lung goes up. (Ever had a stuffy nose, and you lay with the stuff side up and it clears?)
659.
TB test confirmation?
A positive ppd confirms infection, not just exposure. A sputum test will confirm active disease.
660.
Asthmas and wheezers?
Coughing w/o other s/s is suggestive of asthma. Speaking of asthma, watch out if your wheezer stops wheezing. It could mean he is worsening.
661.
What treats tet spells?
Tet spells treated with morphine.
662.
Group-A strep?
Group-a strep precedes rheumatic fever. Chorea is part of this sickness (grimacing, sudden body movements, etc.) and it embarrasses kids. They have t pain. Watch for elevated antistreptolysin O to be elevated. Penicillin!
663.
Tylenol poisioining ?
Tylenol poisoning - liver failure possible for about 4 days. Close observation required during this time-frame, as well as tx with Mucomyst.
664.
Radioactive iodine?
Radioactive iodine - The key word here is flush. Flush substance out of body w/3-4 liters/day for 2 days, and flush the toilet twice after using for 2 days. Limit w/patient to 30 minutes/day. No pregnant visitors/nurses, and no kids.
665.
Main hypersensitivity for antiplatelet drugs?
broncospasm (anaphylaxis)
666.
Common sites for metastatsis?
liver, brain, lung, bone, and lymph
667.
Orthostatis is verfied by?
a drop in presssure with increasing heart rate... Orthostatis= orthostatic hypotension
668.
Bence Jones protein in urine?
confirms multiple myeloma
669.
How do you treat a small bowel obstruction?
Don't fall for 'reestablishing a normal bowel pattern' as a priority with small bowel obstruction. Because the patient can't take in oral fluids 'maintaining fluid balance' comes first.
670.
G tube and J tubes are usually?
Other than initially to test tolerance, G-tube and J-tube feedings are usually given as continuous feedings.
671.
Side rail rules?
Four side-rails up can be considered a form of restraint. Even in LTC facility when a client is a fall risk, keep lower rails down, and one side of bed against the wall, lowest position, wheels locked.
672.
Post spleenectomy?
Pneumovax 23 gets istered post splenectomy to prevent pneumococcal sepsis.
673.
Potassium lab importance?
Let's say every answer in front of you is an abnormal value. If potassium is there you can bet it is a problem they want you to identify, because values outside of normal can be life threatening. Normal potassium is 3.5-5.0. Even a bun of 50 doesn't override a potassium of 3.0 in a renal patient in priority.
674.
Every new ission needs?
You will ask every new ission if he has an advance directive, and if not you will explain it, and he will have the option to sign or not.
675.
Potassium and acid base balance?
A little trick regarding potassium: ALKALOSIS: K is LOW Acidosis is just the opposite: K is High The vital sign you should check first with high potassium is pulse (due to dysrhythmias).
676.
What is bleeding considered in ADPIE?
Bleeding is part of the 'circulation' assessment of the ABCD's in an emergent situation. Therefore, if airway and breathing are ed for, a compound fracture requires assessment before Glasgow coma scale and a neuro check (D=disability, or neuro check)
677.
What to do in a sucking stab wound?
The immediate intervention after a sucking stab wound is to dress the wound and tape it on three sides which allows air to escape. Do not use an occlusive dressing, which could convert the wound from open pneumo to closed one, and a tension pneumothorax is worse situation. After that get your chest tube tray, labs, iv.
678.
What to do if your patients chest tube accidently getes removed?
An occulsive dressing is used
679.
Labs in DKA>?
Serum acetone and serum ketones rise in DKA. As you treat the acidosis and dehydration expect the potassium to drop rapidly, so be ready, with potassium replacement. Fluids are the most important intervention with HHNS as well as DKA, so get fluids going first. With HHNS there is no ketosis, and no acidosis. Potassium is low in HHNS (d/t diuresis).
680.
Decorticate and Decerebrate?
Decorticate positioning in response to pain = Cortex involvement. Decerebrate in response to pain = Cerebellar, brain stem involvement
681.
Other S/S of MS?
Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, vision changes, fatigue and spasticity are all symptoms of MS
682.
After removal of the pituitary gland what should you watch for?
After removal of the pituitary gland you must watch for hypocortisolism and temporary diabetes insipidus.
683.
After appendectomy?
position on the RIGHT side with legs flexed
684.
Hirschsprungs is dx how?
Hirschsprung's diagnosed with rectal biopsy looking for absence of ganglionic cells. Cardinal sign in infants is failure to meconium, and later the classic ribbon-like and foul smelling stools.
685.
More info on intussception?
Intussusception common in kids with CF. Obstruction may cause fecal emesis, currant jellylike stools (blood and mucus). A barium enema may be used to hydrostatically reduce the telescoping. Resolution is obvious, with onset of bowel movements.
686.
Omphalocele?
With omphalocele and gastroschisis (herniation of abdominal contents) dress with loose saline dressing covered with plastic wrap, and keep eye on temp. Kid can lose heat quickly.
687.
Hydrocele?
After a hydrocele repair provide ice bags and scrotal .
688.
PKU ?
No phenylalanine with a kid positive for PKU (no meat no dairy no aspartme
689.
When to test urine for ketones and glucose?
Second voided urine most accurate when testing for ketones and glucose.
690.
Nepphrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria (looks dark and frothy) caused by glomerular damage. Corticosteroids are the mainstay. Generalized edema common.
691.
Western blot test?
A positive Western blot in a child <18 months (presence of HIV antibodies) indicates only that the mother is infected. Two or more positive p24 antigen tests will confirm HIV in kids <18 months. The p24 can be used at any age.
692.
Kids with HIV?
For HIV kids avoid OPV and Varicella vaccinations (live), but give Pneumococcal and influenza. MMR is avoided only if the kid is severely immunocompromised. Parents should wear gloves for care, not kiss kids on the mouth, and not share eating utensils.
693.
What will alter the accuracy of o2 sats?
Hypotension and vasoconstricting meds
694.
Room air is?
Ambient air (room air) contains 21 % o2
695.
The first s/s of ards?
The first sign of ARDS is increased respirations. Later comes dyspnea, retractions, air hunger, cyanosis.
696.
PCWP
Normal PCWP (pulm capillary wedge pressure) is 8-13. Readings of 18-20 are considered high.
697.
First sign of pe?
First sign of PE is sudden chest pain, followed by dyspnea and tachypnea.
698.
Carbon dioxide narcosis?
High potassium is expected with carbon dioxide narcosis (hydrogen floods the cell forcing potassium out). Carbon dioxide narcosis causes increased intracranial pressure.
699.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis?
Pulmonary sarcoidosis leads to right sided heart failure..Sarcidosis is basically scar tissue build up
700.
NG tube rules?
An NG tube can be irrigated with cola, and should be taught to family when a client is going home with an NG tube.
701.
If your patient starts seeing bugs?
If your normally lucid patient starts seeing bugs you better check his respiratory status first. The first sign of hypoxia is restlessness, followed by agitation, and things go downhill from there all the way to delirium, hallucinations, and coma. So check the o2 stat, and get abg's if possible.
702.
Cold stress in a newborn?
The biggest concern with cold stress and the newborn is respiratory distress.
703.
A preggo in a minus station?
If your laboring mom's water breaks and she is any minus station you better know there is a risk of prolapsed cord.
704.
R in a five year old?
In a five-year old breathe once for every 5 compressions doing r.
705.
After Gtube placement?
After g-tube placement the stomach contents are drained by gravity for 24 hours before it can be used for feedings.
706.
Cephalhematoma (caput succinidanium)?
Cephalhematoma (caput succinidanium) resolves on its own in a few days. This is the type of edema that crosses the suture lines.
707.
Hep A precautions?
During the acute stage of Hep-A gown and gloves are required. In the convalescent stage it is no longer contagious.
708.
More labs suggestive of renal failure?
Low magnesium and high creatinine signal renal failure.
709.
Hightest priority for RA?
Pain is usually the highest priority with RA
710.
TB health risk?
If a TB patient is unable/unwilling to comply with tx they may need supervision (direct observation). TB is a public health risk.
711.
Highest priortiy in status elipticus?
Level of consciousness is the most important assessment parameter with status epilepticus.
712.
Crackles most likely are?
Crackles suggest pneumonia, which is likely to be accompanied by hypoxia, which would manifest itself as mental confusion, etc.
713.
Anorexia sucks because?
Absence of menstruation leads to osteoporosis in the anorexic.
714.
Low crit/hemoglobin?
A patient with a low hemoglobin and/or hematocrit should be evaluated for signs of bleeding, such as dark stools.
715.
More IVP info?
A laxative is given the night before an IVP in order to better visualize the organs.
716.
Pt with edema and walking?
A patient with liver cirrhosis and edema may ambulate, then sit with legs elevated to try to mobilize the edema.
717.
High priority in Addisons?
Managing stress in a patient with adrenal insufficiency (Addison's) is paramount, because if the adrenal glands are stressed further it could result in Addisonian crisis. While we're on Addison's, blood pressure is the most important assessment parameter, as it causes severe hypotension.
718.
Pancreatitis prioritys?
After pain relief, cough and deep breathe is important in pancreatitis, because of fluid pushing up in the diaphragm.
719.
Likely cause of cardiac arrest in child?
Prolonged hypoxemia is a likely cause of cardiac arrest in a child.
720.
What can also cause an s3 heart sound?
Fluid volume overload caused by IVC fluids infusing too quickly (or whatever reason) and CHF can cause an S3
721.
coarctation of the aaorta causes?
Coarctation of the aorta causes increased blood flow and bounding pulses in the arms
722.
If you THINK a patient has new HTN?
A newly diagnosed hypertension patient should have BP assessed in both arms
723.
Depression manifests itself?
Depression often manifests itself in somatic ways, such as psychomotor retardation, gi complaints, and pain.
724.
Chief concern in CF
Respiratory problems!
725.
More info on TB testing a positive result?
speaking of TB... PPD is positive if area of induration is: >5 mm in an immunocompromised patient >10 mm in a normal patient >15 mm in a patient who lives in an area where TB is very rare.
726.
Hba1c?
HbA1c - test to assess how well blood sugars have been controlled over the past 90-120 days. 46 corresponds to a blood sugar of 70-110; 7 is ideal for a diabetic and corresponds to a blood sugar of 130.
727.
Most accurate way to test kids for medication accuracy?
BSA is considered the most accurate method for medication dosing with kids. (I though it was weight, but apparently not)
728.
Placement of a wheelchair?
Place a wheelchair parallel to the bed on the side of weakness
729.
If you see a nurse make a mistake? Chain of command?
If one nurse discovers another nurse has made a mistake it is always appropriate to speak to her before going to management. If the situation persists, then take it higher.
730.
Besides meds and congenital problems .. what can lead to decreased preload ?
Sepsis and anaphylaxis (along with the obvious hemorrhaging) reduce circulating volume by way of increased capillary permeability, which leads to reduced preload (volume in the left ventricle at the end of diastole). This is a toughie...think about it.
731.
Nitrazine paper?
Amniotic fluid is alkaline, and turns nitrazine paper blue. Urine and normal vaginal discharge are acidic, and turn it pink.
732.
STD= gonnorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a reportable disease
733.
Crutch use?
the phrase "step up" when picturing a person going up stairs with crutches. The good leg goes up first, followed by the crutches and the bad leg. The opposite happens going down. The crutches go first, followed by the good leg.
734.
MORE info on DKA? ugh!
While treating DKA, bringing the glucose down too far and too fast can result in increased intracranial pressure d/t water being pulled into the CSF. Polyuria is common with the hypercalcemia caused by hyperparathyroidism.
735.
Nonfat milk?
Nonfat milk reduces reflux by increasing lower esophageal sphincter pressure
736.
Gerd again?
Patients with GERD should lay on their left side with the HOB elevated 30 degrees.
737.
To prevent dumping syndrome?
Unusual positional tip - Low-fowlers recommended during meals to prevent dumping syndrome. Limit fluids while eating.
738.
Emphysema?
In emphysema the stimulus to breathe is low PO2, not increased PCO2 like the rest of us, so don't slam them with oxygen. Encourage pursed-lip breathing which promotes CO2 elimination, encourage up to 3000mL/day fluids, high-fowlers and leaning forward.
739.
Kernigs sign?
One of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis is Kernig's sign. Severe stiffness of the hamstrings causes an inability to straighten the leg when the hip is flexed to 90 degrees.
740.
Brudzinski's sign?
One of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis is Brudzinski's sign. Severe neck stiffness causes a patient's hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed ( The kid knees will fly up and he lift his bum off the table cause it hurts his neck)
741.
Phenalalanine?
It is an amino acid that is BAD for people with PKU. It is found in food only and is also found in aspartame
742.
Vertical C section?
Used in plus sized women or risky or emergency c sections. less chance of harm for the baby
743.
Dystocia?
Just means a difficult or abnormal delivery or birth... example.. shoulder dystocia
744.
Peritoneal dialysis?
On the other hand, peritoneal dialysis does not require that the patient's blood be pumped outside of his body. Instead, the blood is cleaned while still inside the body. The organs in the abdomen are surrounded by the peritoneum, which is a membrane that allows waste products to through it. Peritoneal dialysis uses a Tenckhoff catheter to run the dialysis fluid, a sugar solution with some salts, into the abdominal, or peritoneal, cavity. This allows the patient's blood to be filtered without pumping it through a dialysis machine. A Tenkhoff catheter is usually used in peritoneal dialysis
745.
Why would somone who is allergic to latex be allergic to food too?
CROSS REACTION! People who have a latex allergy may be allergic to some foods, as well. This is called a cross reaction. When this happens, your body responds with the same allergic symptoms that you would have if you were exposed to latex. Cross reactions differ from one person to another. Someone may have a reaction to all the foods noted to cause cross reaction while another may have no reaction at all. Likewise, if you are allergic to any of these foods, you may also be allergic to latex: •apples, bananas, kiwi, peaches, plums, figs, grapes, melons, papaya, ion fruit, cherries, nectarines, pears, pineapple and strawberries; •carrots, celery, raw potatoes, avocados and tomatoes; •chestnuts and hazelnuts; •wheat and rye.
746.
Acid/ ASH diet?
The acid ash diet has nothing to do with weight loss. It is a diet intended for health and may be prescribed by your physician to control illness or disease. Once your liver has metabolized the food you ingest, it leaves a mineral deposit, known as ash, which can be acidic or alkaline depending on its effect on the pH of your urine. Eating foods that create an acid ash may help to balance your system or create a hostile environment to inhibit bacterial growth. .... Acid/ ash diet is used to BALANCE the acid/alkaline ash in the body... Ash wiill affect the urinary system and even the nervous system. Imbalance will be diet modified
747.
PTB means?
Pumonary tuberculosis
748.
Psuedomembrane in DIptheria?
Diptheria is an upper respiratory tract infection. It is characterized by sore throat, low fever and the psuedomembrane! Which is just a capsule around the tonsils that you can see with your penlight... It just looks like a whiteish yellow capsule around the tonisils
749.
SLE?
Systemic Lupus Ethramoutus.... (Lupus)
750.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Hermans sign= flushes and redness of skin with lighter color at the center of the rash.... It is a disease that comes from tropical and subtropical areas that are spread by misquotos
751.
Risus Sardonicus?
Risus sardonicus is a highly characteristic, abnormal, sustained spasm of the facial muscles that appears to produce grinning--- From Tetany! Sad and scary looking! Never Google image it again, Megan! Nightmares!
752.
Grey Turners sign?
Purple bruises around the belly button... Pancreatitis!
753.
PDA?
patent ductuous arteriousus in infants! Valve doesn't close!
754.
Dance Sign?
Dance's sign: RUQ mass (intussusception) with RLQ empty space (movement of cecum out of normal position).
755.
Charcots sign?
A. Charcot's triad for multiple sclerosis 1. Nystagmus 2. Intention tremor 3. Scanning or staccato speech
756.
MG and Guillian Barre?
Opposites! Nursing connection! Think about it!
757.
Chvostek and Trosseaus sign
Chvostek= Tapping on the face above the cheek bone will cause spams! Trosseaus= using a BP cuff and inflating it, and it will cause spasms of the wrist
758.
VRSA?
Staph infection that is resistant to Vancomycin treatement! Worse than MRSA
759.
Tet spells?
Children with tetralogy of Fallot may develop "tet spells". The precise mechanism of these episodes is in doubt, but presumably results from a transient increase in resistance to blood flow to the lungs with increased preferential flow of desaturated blood to the body. Tet spells are characterized by a sudden, marked increase in cyanosis followed by syncope, and may result in hypoxic brain injury and death. Older children will often squat during a tet spell, which increases systemic vascular resistance and allows for a temporary reversal of the shunt.
760.
HHNS Vs DKA
· Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a condition of DKA=insulin deficiency resulting in acidemia due to altered metabolism. · Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) is primarily a disorder of dehydration due to hyperglycemia
761.
Pancreatitis
NPO, TPN May be used
762.
Diverticulitis
Clear liquids to high fiber
763.
Cholecystis
Low-fat diet
764.
Liver disease
Decreased protein intake
765.
Celiac disease
Avoid glutens
766.
Nausea and vomiting
Clear liquids
767.
Gout
Avoid purines
768.
Dumping syndrome
Small frequent meals
769.
GERD
Avoid large meals, eating late, alcohol caffeine
770.
Monitor for digoxin
Potassium
771.
Monitor for acetaminophen
Temperature
772.
Monitor for glipizide
Blood glucose
773.
Monitor for morphine
Respiratory rate
774.
Monitor for prednisone
Delayed wound healing
775.
Monitor for warfarin
INR
776.
Monitor for zolpidem
Sleep patterens
777.
Monitor for Olanzapine
Mood
778.
Monitor for Levoflaxacin
Culture and sensitivity
779.
Erikson stage 0-1, posterior fontanelle closes at 2 to 3 months, 1 to 5 m grasp rattle 6 m transfer between hands, 8-9 m uses pincer grasps, nine months bangs toys together, 3 m holds head, 5-6 m rolls, 9m sits up on own, 12 m stands alone
Trust vs mistrust, meet social and developemental needs
780.
Erikson stage 1-3, feeds self, anterior fentanyl closes, steady gait, draw stick figure, potty train, need routines and rituals
Autonomy vs shame and doubt, provide acceptable options
781.
Erikson stage 3-6, hopping, draws shapes, walking heel to toe
Initiative vs. guilt, provide age appropriate activities, stranger danger
782.
Erikson stage 6-12 or games, rides bicycle, build models, organize sports, puzzles games, video games
Industry vs inferiority, encourage participation in care
783.
Erikson stage 12-20 pure activities, music interest, career training, sexual maturiation, STI's, pregnancy, substance abuse
Identity vs role confusion, Provide groups of same age
784.
Erikson stage 20-35 leaves families and seeks relationships, growth ends childbearing, established career,
Intimacy vs isolation, provide private time with partner
785.
Erikson stage 35-65 bouncing life, aging parent, adult children, grandchildren, career transition, retirement, menopause, osteoporosis, decrease in visual and hearing
Generativity vs stagnation
786.
Erikson stage 65+, decreased skin elasticity, decreased cough reflects, lower cardiac output, peridontal disease
Integrity vs despair, use personal items were not home
787.
Antidote for opoids
Naloxone
788.
Antidote for warfarin
Vitamin K
789.
Antidote for acetaminophen
Acetylcystiene
790.
Antidote for heparin
Protamine sulfate
791.
Antidote for benzodiazepine
Flumaxenil
792.
Antidote for digitalis
Digoxin immune fab
793.
Antidote for lead
Succimer
794.
Antidote for magnesium
Calcium gluconate
795.
When mixed with regular insulin draw this medication up last, 4-6 hr peak time
NPH
796.
Have client eat as soon as this medication is given
Lispro
797.
Hold this medication 48 hours before and after use of contrast dye
Metformin
798.
Given subcutaneously and has no peak time
Glargine
799.
May be used to lower potassium levels, can be given IV, also for DKA
Regular insulin
800.
Type of solution for TPN
Hypertonic
801.
Routes TPN can be given
Picc line, tunneled catheter
802.
TPN is prepared how often
Daily
803.
TPN is hung every_ hours
24
804.
Standard precaution requirements
Nothing, gloves prn
805.
precaution requirements (body fluids)
Gloves and gown
806.
Droplet precaution requirements (air)
Mask
807.
Airborne precaution requirements (air)
Mask
808.
Normal sodium level
135-145
809.
Normal potassium level
3.5-5
810.
Normal calcium level
9-10.5
811.
Normal carbon dioxide level
35-45
812.
Normal hydrochloride level
21-28
813.
Normal hemoglobin level
14-18
814.
Normal Hct level
37-52%
815.
Normal WBC level
5,000-10,000
816.
Normal cholesterol level
<200
817.
Normal platelets
150,000-400,000 (enoxaparin sodium)
818.
Normal P T
11-12.5 sec, rx: 1.5-2x (Coumadin)
819.
normal aptt
30-40 sec rx 1.5-2x (heparin)
820.
Normal INR
0.7-1.8, rx 2-3x (Coumadin)
821.
Normal glucose fasting
70-105
822.
Normal HbA1c (glycosylated hgb)
4-6%
823.
Normal BUN level
10-20
824.
Normal creatinine level
0.5-1.2
825.
Arterial supply
Goes down in legs
826.
Venous supply
Goes up in legs
827.
Red tag
Emergent
828.
Yellow tag
Urgent within 1 to 2 hours
829.
Green tag
Non-urgent 2 to 4 hours
830.
Black tag
Not seen don't have survival potential
831.
LPNs cannot what
Evaluate Assess teach, can reinforce or reteach, iv therapy, blood therapy rhogam
832.
Medication to hold prior to ECT
Dilantin or other medications that alter brain activity
833.
How long post surgery to be on blood thinners
30 days
834.
Priority if chest tube comes out
Cover with Vaseline soaked gauze
835.
Ebola
Hemorrhagic fever, w/ out symptoms quarenteen for 21 days
836.
System affected by methotrexate (steroid)
Immune system, decreased white blood cells and decreased platelets
837.
System affected by sodium levels
Neurological system, seizures occur with low levels
838.
Anti-cholinergic drugs side effects
No see no Pee no stool no drool
839.
Versed
Pt cannot sign for anything after recieving
840.
16 y.o can be a majority if
Married, emancipated, or has child
841.
ED triage
Treat most severe injury first
842.
Mass casualty triage
Do the greatest good for the greatest number
843.
Magnesium
drip needs to have one-to-one, due to side effects (absent deep tendon reflexes), monitor BP, resp, DTR, used for preclampsia
844.
Meningitis
symptoms: Headache, Stiff neck and photosynthesis, Diagnostics: spinal fluid (lumbar puncture) blood cultures, Prevention: Hand washing, immunization, Assessments: Brudzinski (pain with Head to breast bone) Kernigs (Pain with knee up to chest) Living in close spaces can cause this.
845.
Priority for MI
Apply oxygen first
846.
2 pt gait
Partial weight-bearing on extremity walking with crutches right leg left crutch as if they were skiing
847.
3 pt gait
Nonweightbearing swing through crutches
848.
4 pt gait
Stability partial weight-bearing on both extremities right leg right crutch
849.
Walker
Step into it, arm's-length away, don't pull self up with device
850.
Cane
Always on the strong side
851.
Up stairs
Strong leg first
852.
Down stairs
Weak leg first
853.
Yogurt
Form of calcium for lactose intolerant patients
854.
Diet for Christianity
Don't eat meat on ash Wednesday or Fridays of light may have days of fasting
855.
Diet for Buddhism
Avoid beef pork seafood
856.
Judaism diet (Muslims)
Kosher- can't mix milk and meat no pork avoid fish that don't have scales
857.
Hinduism diet
No beef, may fast, many are vegetarian
858.
Interventions for dumping syndrome
Lay down after eating, avoid drinking one hour before and one hour after eating, avoid sugar and milk
859.
Interventions for eternal nutrition
Start slow increase rate every 8 to 12 hours, greater than 100 residue fluid hold fluid, head of bed 30° or higher, assess for signs of intolerance, first feeding have x-ray every other check pH.
860.
Lithium toxicity
Can occur if greater than two
861.
Zolpidem
(Ambien) sleepwalk and cannot
862.
Side affects of anti-psychotics (typical)
Sedation, EPS, and anti-cholinergic effects
863.
Adverse affects of antipsychotics
Tardive dyskinesia,such as thumb rolling And eye emovements, Agranulocytosis, neuroleptic malignment syndrome, siezures
864.
Risedronate
Don't lay down right away
865.
Fentanyl patch
Remove with temperature, one for three days, don't put heating pad over it
866.
Gentamicin
Don't use if damage to kidneys when used with furosemide can cause hearing loss at high doses
867.
Amoxicillin
Be aware with cephalosporins allergy
868.
Ceftriaxone
Can create C diff
869.
Adverse effects
Life-threatening
870.
varenicline
Only use up to 12 weeks for smoking cessation
871.
Calcium channel blocker's, beta blockers, ARBs, ace inhibitors
Blood-pressure medications
872.
Calcium channel blocker's side effects
Bradycardia, decreased contractility, peripheral edema
873.
Ace inhibitor side effects
Dry hacking cough, angioedema
874.
20 gauge catheter
Can be used for packed RBCs, dextrose 5%, 9% sodium chloride, not used for TPN, amirodone, vancomycin
875.
Clean wound with _ before getting culture
Saline or sterile water
876.
V tach
First action drug Amerodone then lidocaine then prepare for cardioversion
877.
CAGE
Screening tool for alcoholism, cutdown use of alcohol, ever felt anger when people tell you to cut down, ever feel guilty about how much you drink, eye-opener to quit
878.
Wilms tumor
On adrenal gland needs to be removed prior to bursting
879.
1 pound
3500 calories
880.
Intropic agents
Increases myocardial contraction, and cardiac output, digoxin, dopamine, dubotamine
881.
Digoxin toxicity
Halos around everything, <6
882.
Dopamine and dubotamine
Monitor heart rate urine output and blood pressure
883.
BNP
Diagnostic test for CHF, normal is lower than 100, 100 to 300 heart failure is possible, 300 to 600 heart failure is mild, 600-900 moderate heart failure, severe hf > 900
884.
Packed RBCs
Treat anemia, monitor hemoglobin
885.
Platelets
Treats thrombocytopenia, monitor platelets
886.
Plasma
Treats Burns, monitor albumin, 3.5-5
887.
Factor 8
Treats hemophilia, monitor ptt
888.
1 unit of blood
Expect 1g/dl increase in hgb ex. 7.8-8.8
889.
Kidneys
Monitor I&O, electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, Hgb, BP (BUN & creatinine increases with kidney failure)
890.
Complications with central lines
Pneumothorax, air embolism, occlusion, infection, with air embolism lay on left side and Trendelenburg position with insertion
891.
Hyperthyroidism
PTU & Tapazole, or remove thyroid (calcium at bedside) Think of Tigger orange and hyper
892.
Hypothyroidism
Levothyroxine, Think of eeyore, slow moving, depressed
893.
Affected system of potassium
Cardiac, cardiac arrest with severe levels
894.
Insulin withdrawal when mixing
Clear to cloudy (regular-NPH)
895.
Oxytocin
Monitor fhr, contractions, BP, hr, rr
896.
Quetiaphine fulmarate
Bipolar, monitor for suicidal thinking, dizziness, leukopenia
897.
Risperidone
Bipolar, monitor for sedation insomnia pseudoparkinsonism,
898.
Lithium carbonate
Bipolar, no levels of lithium,
899.
SSRI
Antidepressant that blocks reuptake of serotonin
900.
SNRI and tricyclics
Antidepressant that box reuptake of serotonin and norepinepherine
901.
MAOI
Focus on diet
902.
Atypical antidepressants
Selectively inhibits dopamine and stimulates CNS, side effects: seizures psychotic symptoms, Buproprion
903.
Developing cancer with birth control
Only with smoking
904.
Naegeles rule
1st day menstrual cycle-3 months, +7 days
905.
First stage of labor
Latent 0 to 3 cm, active 4 to 7, transition 8 to 10,
906.
Second stage of labor
Pushing stage
907.
Third stage of labor
Delivery of placenta
908.
Fourth stage of labor
Bonding with newborn
909.
Taking in phase
It's all about me
910.
Taking hold phase
It's all about the baby
911.
Letting go phase
Getting back to the new normal
912.
Anemia side effects
Weakness paler fatigue
913.
Anemia interventions
Food sources that contain red meat, organ meat, egg yolks, leafy green vegetables, use z track method for Iran dextran
914.
Blood compatibility
this by what factor they have a or B or both AB or neither o patient doesn't have that factor they can't receive the blood,
915.
Hemophilia signs and symptoms
Risk for bleeding, Hematomas, G.I. and G you bleeding, brain hemorrhage, and bleeding mucous membranes
916.
Hemophilia nursing interventions
Assess for t pain, monitor vitals, onister factor replacement, avoid injections and NSAIDs, assess LOC and bleeding
917.
MI diagnostic labs
Troponins
918.
Sickle cell anemia and crisis
Most common in African Americans, blood comes and causes severe pain, oxygen is limited to the cells of the body because cells cannot carry oxygen as well, don't do well in cold weather or high altitude
919.
Signs and symptoms of sickle cell anemia
Anemia, hypoxic damaged tissue, dehydration, susceptibility to infection, knowledge deficit and powerlessness
920.
Nursing interventions for sickle cell anemia
Oxygen as needed, manage pain, and her vitals, monitor H&H, Mr. fluids as needed, assess for signs and symptoms of infection, teach self-care, causes and prevention of crisis
921.
Cervical cancer
Contributing factors: HPV/ multiple partners, manifestations: abnormal bleeding, Dianosing: pap/DNA test, prevention: Gardisil
922.
Breast cancer
Contributing factors: family history, lifestyle, Manifestations: Lumps, thickening, Diagnosing: mammogram, Prevention: Diet, weight, excercise
923.
When is a colposcopy used?
abnormal pap test
924.
Stable angina
pt is awake and doing something when having chest pain. Pain is able to be treated with first nitro
925.
Unstable angina/ preinfarction
Moving around but not relieved with nitro.
926.
Prinemetal/ Coronary spasm
Sound asleep and woken up by pain in chest
927.
Protocol for American Heart Association regarding MI
Sit down take a nitro, wait 5 min, call 911, take another nitro, wait 5 min and take final nitro.
928.
Nursing interventions for MI
Morphine (decreases preload & afterload) Oxygen (First, treats ischemic myocardium) Nitro (increases coronary perfusion) Aspirin- (decreases clot formation) MONA
929.
Aortic femoral By (restoring blood supply to blocked area) interventions
peripheral pulses, skin temp, anticoags, avoid crossing legs, monitor site, KEEP BP LOW
930.
Heart sounds mnemonic
Ape to man Aortic, pulmonic, erbs point, tricuspid, mitral
931.
Where do I listen to S2?
aortic and pulmonic
932.
Where do I listen to S1?
tricuspid and mitral
933.
S3 and S4 sounds
kentucky (going into CHF) Tennessee (Angina)
934.
Angioplasty
NI: cardiac diet, check vitals every 15 min, cardiac monitor, pressure @ site. Complications: dysrhithmias, bleeding, hypovolemia
935.
P wave
atrium are contracting
936.
QRS
ventricles contract
937.
T wave
ventricles relax, Don't want PVC's to hit T wave
938.
Cardioversion
Use with unstable v tach, machine synchronizes with the heart rhythm because you do not want to hit the t wave
939.
v fib
whole ventricles are shaking like jello and not firing
940.
Common heart rhythm with anemia
Sinus tachycardia
941.
Left sided heart failure
Fluid backs up into lungs, crackles in lungs, dyspnea
942.
Right sided heart failure
Fluid backs up into heart, S3 gallop, peripheral edema
943.
Normal pulmonary wedge pressure
4-12
944.
Heart failure
NI: O2, fowlers, lung sounds, I&O, fluid restriction, daily weights, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, digitalis
945.
DKA
Symptoms include: kussmaul respirations, fruity breath
946.
Thyroidectomy
Check for positive Chvotesek sign
947.
Hyponatremia
Causes: Diuretics, renal disease, Treatment: SIADH, Symptoms: confusion-> seizures, muscle weakness, cramping
948.
Hypernatremia
Causes: Water deficit, Cushings, Symptoms: Confusion->siezures, muscle weakness
949.
Hypokalemia
Causes: Diuretics, corticosteriods, suctioning, diarhea. Symptoms: muscle weakness, shallow respirations, Dysrrhithmias
950.
Hyperkalemia
Causes: salt substitutes, renal failure, packed RBCs, Addisons Symptoms: Dysrhythmias, peaked T waves
951.
Addisons
Low cortisol
952.
Cushings
High cortisol (steroid symptoms)
953.
Kayexalate enema
pulls off potassium
954.
Hypocalcemia
Causes: hypoparathyroidism, renal failure, malabsorption Symptoms: Changes in HR, prolonged ST, tetany, changes in LOC, siezures
955.
Hypercalcemia
Causes: Hyperthyroidism, Excessive intake Symptoms: Dysrhithmias, cardiac arrest
956.
Isotonic
No fluid crosses the cell membrane 0.9%NS
957.
Hypotonic
fluid moves into the cell 0.45% NS
958.
Hypertonic
fluid moves out of the cell D5 NS
959.
Cirrhoises
Symptoms: hypertension, esophageal carices, clotting abnormalities, hepate encephalopathy, ascites, peritonitis. NI: Assess fluid balance, assess bleeding, safety precaustions, high calorie diet, fluid restrictions, low protien
960.
Rule of 9's
Each arm= 9%, Anterior leg=9%, Posterior leg=9% Head=9%, Back=18% Chest=18%, Perineum=1%
961.
Parkland formula
used for determining amount of lactated ringersfor burn patient. Begin time at time of burn. ister through central line and have foley cath. 4mL x kg x %TBSA= 1/2 total in first 8 hrs, 1/2 in remaining 16 hours
962.
Head injury
Signs: Changes in LOC, Increased I, Brady, tachypnea, hypo/hypertension, hyperthermia, bradycardia, posturing. Interventions: Assess neurostatus w/ glascow coma scale (higher the better), I & O, Elevate HOB, monitor electrolytes, decrease stimulation, monitor I, vitals, nutritional .
963.
Spinal shock
occurs right away, hypotension,
964.
Autnomic dyreflexia
Spinal injury, can occur after several weeks only in T6 or higher, hypertension, flushing, headache Treatment: lower BP and treat cause.
965.
Cervical spine
Top 8, worry about breathing
966.
Thoracic spine
Middle 12, quadroplegic
967.
Lumbar spine
Bottom 5, paraplegic
968.
Spinal cord injury
Intervention: Immobilization, assess respiratory status, assess vital signs, institue bowel sounds and bladder program, prevent DVT, urinary retention, constipation, skin break down.
969.
VEAL CHOP MINE
Menomic for decelerations Variable Cord compression Move patient Early Head compression Identify labor progress Accelearate Okay No action Late Placental insufficiency Execute STAT
970.
Precalampsia
NI: Monitor BP, protein in urine, weight, watch edema eclampsia occurs with seixures
971.
Uncompensated
pH is off and 1 other is off
972.
Partially compensated
pH is off as well as other two are off
973.
fully compensated
pH is normal other two are off
974.
Metabolic alkalosis
Vomiting loose acid and left with base
975.
Metabolic acidosis
Diarrhea loose base and left with acid
976.
High pressure with mechanical ventilation
NI: assess for need to suction, pt needs tomlet machine breath for them.
977.
Low pressure with mechanical ventilation
check tubes for leaks
978.
Cancer internal radiation
NI: visitors should maintain 6 feet away and visit no longer then 30 min, staff needs a dosimeter badge.
979.
Carseat
Middle of backseat for 2 years or 20 lbs
980.
Donning order
Gown-Mask- goggles-gloves-enter
981.
Doffing order
gloves- gown- goggles-mask
982.
Nasal Cannula
1-6 L/min over 2 needs humidifyer
983.
Simple face mask
6-8L/ min
984.
Venturi face mask
4-8L/min
985.
Non- Rebreather
12L/min
986.
RSV
contagious for 1 week after antibiotic
987.
C-Diff and VRE
use soap and water
988.
Droplet (infections)
measles, influenza, can cohort
989.
Airborne(infections)
chicken pox, TB, cant cohort
990.
(infections)
MRSA, C-diff can cohort
991.
Abuse phases
Tension building-> battering-> honeymoon-> tension building
992.
PTSD
symptoms are delayed, assess for irritibility, difficulty sleeping and concentration, decrease excessive stimulus, help evaluate coping mechanisms
993.
Bipolar disorder
Depression and mania, inflated self esteem, flight of ideas, buying sprees, decreased needs for sleep, coexist with substance abuse.
994.
Borderline personality disorder
Manipulative behavior
995.
Depression
R/f: female, unmarried, low socialeconomic class, postpartum period, medical illness, early child hood trauma. Symptoms: Insomnia, anergia, feelings of worthlessness decreased concentration.
996.
Grief
Denial-> Anger-> Bargaining-> Depression-> Acceptance
997.
Cluster A
Paranoid, schizoid, Schizotypal
998.
Cluster B
Antisocial, Borderline, Histronic, Narcissistic
999.
Cluster C
Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive Compulsive
1000.
When patient hears voices
"What are the voices saying to your?"
1001.
What does clubbing of the fingers mean?
chronic hypoxia
1002.
Cap refill reveals what?
end-organ perfusion
1003.
#1 thing to do with edema
elevate
1004.
Where to check for skin turgor?
Adult - chest child - abdomen/thigh
1005.
HR over what is tachycardic
100
1006.
In acid/base balance, poop is? vomit is?
Poop is base Vomit is acid
1007.
Where is apex of heart found
6th intercostal space mid-axillary
1008.
Where is PMI found
4th intercostal space mid-clavicular
1009.
Where is 6 month fetal heart rate found
halfway between umbilicus and symphysis pubis
1010.
What cannot be taken with CCBs
Grapefruit juice
1011.
What does digoxin do
Makes the heart pump harder
1012.
How many cc's is 1 ounce
30 cc (30 ml)
1013.
LPN ramifications
No vents, can't do initial assessment, can't do initial teaching, can't discharge Can take phone orders, can do f/u assessment, can do reinforcement teaching, can do dry dressings
1014.
Hurts with eating/feels better with eating
Hurts with eating = gastritis Feels better with eating = PUD
1015.
Zantac and -dines are what?
H2 blocker
1016.
Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, and Protonix are what?
PPI
1017.
What to do with metabolic acidosis
...
1018.
What to do with metabolic alkalosis
...
1019.
What to do with respiratory acidosis
...
1020.
What to do with respiratory alkalosis
...
1021.
Aquamephytin
vitamin K
1022.
secretes vitamin K
liver
1023.
secretes bile
liver
1024.
bile stores
gallbladder
1025.
S/S of hepatitis
jaundice, foamy-tea colored urine (bile in urine - bile is soap), clay colored stool (no bile in stool)
1026.
Hepatitis needs in diet
increased protein and decreased fat
1027.
ESLD is caused by..
Liver dying, has lots of scar tissue, closing off biliary tree (same symptoms as hepatitis, but will not regenerate)
1028.
ESLD needs in diet
decreased protein (this creates more ammonia)
1029.
Secretes amylase/lipase
Pancrease
1030.
Crohn's
diarrhea inflammation of entire colon tx = anti-inflammatory drugs (steroids) malnourished
1031.
Ulcerative colitis
bloody diarrhea No steroids tx = complete removal of lg bowel w/ ileostomy malnourished
1032.
Why no morphine with bowel surgery or biliary pain
morphine can cause spasm at sphincter of Odi Give Demerol
1033.
RA
inflammatory response red, hot, swollen, bad deformities anti-inflammatories (NSAID, steroids) Rest t when inflamed
1034.
OA
t is wearing out - DJD Pain meds (tylenol, NSAIDS, narcotics) likes temp extremes (hot better) Keep t moving even when painful or will freeze
1035.
weight bearing for hip replacement
TOUCH weight bearing
1036.
weight bearing for hip fracture
NON weight bearing
1037.
Instructions when taking Fosamax
Empty stomach sit up for 30 minutes
1038.
Anterior pituitary gland
Growth hormone Too much = acromegaly Too little = Dwarfism
1039.
Posterior pituitary gland
ADH Too much = SIADH Too little = DI (DDAVP)
1040.
Thyroid gland
T3/T4 Too much = Increased metabolism (Graves) Too little = Decreased metabolism (thick nails, course hair, myxedema coma)
1041.
Parathyroid gland
Calcium Too much = hypercalcemia (somnolent) - tx diuretics/dialysis Too little = hypocalcemia (jittery, seizure, mouth tetany)
1042.
Adrenal gland
glucocorticoids Too much = like too many steroids (weight gain, increase infection, increase glucose, skinny limbs, moon face, buffalo hump) Too little = Addison's disease - tx is life long steroids (which causes Cushings)
1043.
Addisonian crisis
Not enough steroids Bronze pigment to skin d/t mineral corticoid steroids
1044.
Pancreas
Insulin Too much = hyperglycemia (dry, hot) Too little = hypoglycemia (pale, cold, clammy)
1045.
Diet for renal patient
Low protein, fluid restriction, low potassium, low phosphorus Phosphate binder given with meals
1046.
Bronchodilators
increased oxygen demand-myocardial
1047.
Intermittent claudication
think arterial vs venous-this is arterial-position leg dependently
1048.
arterial
skin shines
1049.
arterial issues
put your legs down-so blood flows down-like an A (artery)
1050.
venous issues
like a V-put them up-so blood can go up
1051.
Heart Failure
-pumping issue; give Lasix and Digoxin (help with pumping)
1052.
V tach
electrical conduction system issue
1053.
INFILTRATION
IV site painful and swollen
1054.
blood reaction
send blood and tubing to the lab
1055.
New Trach
DO NOT remove the ties before cleaning the tracheostomy-wrong-stoma is not formed yetrisk of stoma closing and airway impacted
1056.
all tracheostomies
dont cut the gauze; need a pre cut gauze
1057.
C3 spinal fracture
airway is your issue
1058.
if you see a presenting part for a baby for a labor pt in ER
prepare delivery room-priority
1059.
pt found on the floor
assess vital signs and LOC first, not injuries assessment first (if pt was conscious before the fall-vitals will tell us the most about the client; unconscious pt would not have been found on the floor-they cannot get up-most likely they rails are up)
1060.
NCLEX wont test
chemo drugs
1061.
NCLEX will test
Eriksson but not Piaget, high pressure alarms
1062.
obese client that vomits after surgery-will increase pressure in the abdomen, at more risk for
Adhehicence
1063.
Disaster prioritization
Priority pt-pt with burns on the face, with respiratory stridor; fixed pupil and agonal respirations-will not live, so not a priority
1064.
LPN
can give report during a transfer can take VS in a transfusion client, after RN has stayed with client for first 15 min or the necessary initial time
1065.
pt after MVA on balanced suspension traction
disorientation is a priority; not shallow respirations
1066.
ECT
before: withhold Dilantin; Atropine IS given- for its anticholinergic effects-will lower the secretions in the mouth; ECT causes seizures-we don't want them to have fluids in mouth-risk for aspiration; Methohexital- possible given for amesthesia; also Succinylcholine-possible given
1067.
knee arthroplasty-1 week ago
post op-for 4 to 6 weeks blood thinners are given throughout the recovery; also if pt was on blood thinners prior to arthroplasty, he won't be taken off these meds, because they are lying down (postop) so they are at risk for cloths; they won't be taking NSAIDs-they are on blood thinners; Motrin vs Lortab?
1068.
pt that had a catheter in before, now catheter is out and pt cannot peeintervention
assessment FIRST-so do a bladder scan first; (full bladder-dull sounds when you percuss); anesthesia can cause decreases ability to urinate
1069.
if chest tube is disconnected
immerse the end of chest tube in a bottle of sterile water-this will prevent the air going into the chestcreates a water sill
1070.
new dx of RA-Methotrexate order
this drug is used in CA patients as well-but its not a chemo drug associated with this drug: WBC low- possible 1200, stomatitis-sores and difficulty in the mouth-hard to eat, fever above 101 can be caused (fever is only above 101 F), increased urine specific gravity-they are not eating or drinking-dehydration occurs; low platelets; also pts are advised to take Folic Acid with this drug-it causes a depletion of dolic acid
1071.
three point crutches
unaffected leg first, then crutches 6 inches forward
1072.
2 point leg
R foot and the L crutch go first together; L foot and the R crutch after at same time-m0ve the other ones
1073.
swing through gait
crutches forward, lift both feet and swing forward
1074.
Tetralogy of Fallot
4 issues here: ventricular septal defect, right ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonic stenosis, overriding aorta, there is a whole in the septum; this will impact blood getting around the body
1075.
TPN pt- to prevent fluid volume deficit
monitor glucose q 4-6 hrs-if the glucose is up-dehydration (osmotic diuresis)
1076.
incident reports
risk management investigates these, they are not shared with non involved staff, include description of incidents in the reports
1077.
medication reconciliation
contains documented meds taken by client, comparrison of current and past meds list; this list is done at any change in care..not only at ission and discharge; the purpose is to avoid errors of duplication, missing some meds etc; also the pharmacy has a role in this, not only the RN
1078.
Autocratic manager
"do this, don't ask any questions"; employees have little to say; these managers are good in critical situations
1079.
Laissez Faire manager
disorganized floor, chaotic environment, employees make the decisions
1080.
Democratic manager
decisions are made as a group , employees ARE asked their opinions
1081.
UAP
CANNOT encourage to share feelings-this requires therapeutic communications-RN has the skills to do this CANNOT get a urine specimen from a indwelling catheter-this is sterile CAN assist with ambulating the client; CAN empty the suction container, but RN has to assess the fluid collected
1082.
LPN
CANNOT ister Rogham-its a blood product; they CAN hang the second bag for TPN, not the first one-RN they CANNOT do anything with titration they CANNOT stick the pt-no IV's start CAN hang a piggy pag as long as its not a titration and as long as its a second bag; always RN has to hang the first bag; LPN CAN give IM injections, they CAN hang the bag of fluid; when LPN hangs the second bag, she does not need the RN there CAN do wound care-dressing changes, irrigations, sterile techniques CAN listen for the lung sounds-for data collection only-not as an assessment-RN will go in there and listen to those heart sounds
1083.
UAP
new ission or post of fresh pt-RN has to do the vitals, not the UAP CAN do specimen collection but not something that require sterile specimens
1084.
IV antibiotics
30 min window
1085.
antidiarrheals
always PRN
1086.
acute glomerulonephritis
can lead to acute kidney failure-watch for decreased urine output
1087.
these CAN be disclosed/reported to DMV
uncontrolled seizure disorder of a school bus driver, if it is not controlled dx of TB or HIV someone with a gun in the hospital can be called to the cups right away
1088.
nonmaleficence
do not insert a contaminated catheter in after not sterile anymore
1089.
implied consent
unless you have a DNR, you do everything for them
1090.
living will WITHOUT a DNR order
you have resuccitate in a code
1091.
in an outbreak for STD's
tell sexually active students to trace outbreaks-in a high school (when addressing the community outbreak)
1092.
phone triage for a client exposed to EBOLA-client has no symptoms
tell client: "we will have to notify the health dept, HIPPA does not apply in this case"
1093.
Fire disaster
evacuate the ones can ambulate first-smoke kills before fire
1094.
NCLEX
increased number of questions about religions and cultures practices
1095.
when you need a translator
call a certified one; no family member should translate-HIPPA
1096.
Ebola
report immediately-fever, epistaxis, vomiting
1097.
AMA client
no need to call security but DO inform about possible complications if they leave
1098.
Amiodarone
should be given through a central line, not peripherally- because ph < 5
1099.
Vacomyocin
ph is <5-not given peripherally but PICC line ok
1100.
TPN
not given peripherally
1101.
narcotics (eg. Morphine)
can be taken out without a witness signature BUT needs second nurse when wasting it never take out a narcotic if drower count is incorrect LPN CAN sign a waste for narcotics
1102.
SEIZURES (precautions before a seizure, after an aura)
roll them on their side only if they lost consciousness; if not they CAN maintain their airway time it during a seizure-needs to be documented after: report it, document, determine LOC postdictal state: drowsy; ok for them to sleep on their side
1103.
chemo treatment
if it spills you call the biohazard, not the housekeeping-you put them at danger (not the housekeeping, not the laundry department) incident report done as well
1104.
smoking client on non smoking campus
give hime a patch
1105.
cane use left side weakness
cane opposite affected leg (COLL)-move cane and the bad leg forward first
1106.
crutches
arms flexed; 2-3 inches to underarmed cannot rest on crutches (underarm)
1107.
Parkinson client
walker with wheels-not ok for this client-safety problem should use the walker with tennis balls-he is shuffling he needs smooth sole shoes- not the non skid ones-he will fall
1108.
Shingles and TB
cannot share room
1109.
neutropenic pt
needs private room
1110.
DONT isolate
an HIV pt UNLESS he is neutropenic or he has an opportunistic infections
1111.
private room
productive cough and possible TB rash with possible varicella only airborne needs private room C-dif is -does not need private room but its recommended (its only in the stool-only way to get it-if you touch the stool)
1112.
Laryngectomy client with fresh trach, Hep C and HIV
need gloves, gown, mask, googles-all of these needed because the new tracheostomy
1113.
client with MRSA + client who's post op total knee replacement
you dont want them in the same room-knee rejection risk-MRSA might get in the knee
1114.
mammogram
after 40 annually
1115.
colorectal exam
should start at age of 50
1116.
prostate
discuss with p at 50
1117.
pap test
every 3 years starting at 21 if there is an abnormal pap->annual exam recommended
1118.
vaginal exam
has to be done annual in all patients
1119.
analgesia
cold and hot
1120.
hot
relaxes
1121.
emergency numbers
should be next to the phone, not the exit door
1122.
progressive macular degeneration
room free of clutter call light within rich
1123.
fall history
have bed alarm for client
1124.
purulent exudate drainage from wound
clean site first with sterile saline and water place specimen in biohazard bag
1125.
who is at risk for falls
over 65 yrs old bifocal glasses pt on Lasix
1126.
hypotonic pulls fluid INTO the cell
hypertonic pulls it OUT of the cell
1127.
to check for JVD
place in semi fowler
1128.
if you see JVD when client is standing
CHF R side
1129.
Calculate output
Assume-0.5 ml per kg output per hour if we dont know the weight then is 30 ml per hr
1130.
the lower the Na it goes
the higher the risk for seizures it is
1131.
kidney function decreased
creatinine increased
1132.
hyperventilation
blowing out CO2-give rebreather bag-client is in respiratory alkalosis
1133.
Atropine
metabolic acidosis
1134.
Narcan
risk for respiratory acidosis-they are not breathing
1135.
pt on Zofran
risk for metabolic alkalosis-they are vomiting
1136.
Insulin
metabolic acidosis-K is high
1137.
Dilaudid
respiratory acidosis or alkalosis
1138.
sputum specimen
collect in the morning- also provide oral care for this pt
1139.
bronchoscopy
they are looking for lung cancer assess gag reflex asks client if he has night sweats-lung CA pts has this particular symptom
1140.
Quantiferon Gold-TB
blood test definitive for TB results within 24 hrs ask for night sweats
1141.
Thoracentesis
place a chest tube in the room- pt at risk for pneumothorax during procedure check lung sounds on that side
1142.
pulmonary hygiene
T turn and cough bronchodilators steroids use bronchodilator first
1143.
suctioning
3 rounds before you hyper oxygenate again, max 15 secs rounds suction on exiting
1144.
TB
mucopurulent sputum, low grade fever, chest tightness, decreased appetite
1145.
chronic bronchitis
copious sputum cough for few months
1146.
emphysema
pursed lip breathing
1147.
asthma
bronchospasms careful with beta blockers
1148.
lung cancer
non specific s/s
1149.
pneumonia
pleuritic chest pain-that does not go down when you sit/lay down, movement hurts
1150.
anginal pain
pain goes away when you lay down
1151.
pneumothorax
O2 decreases, put pt on O2, semi high fowler position; give anxiolytics- if anxious they won't be breathing ok; give analgesics- because it hurts chest tube placed as well
1152.
Chest tubes components
right container-this is the drainage water seal-middle-red suction bubbles on the left if no bubbling- possible kick in the tube if drainage becomes purulent-check for fever, check when CBC was done last time, look at the insertion side for infection in case of crackles-these are in the pleural space-crackles mean fluid; check to see if a chest xray was done this morning 1153.
intubated client
nurse should do frequent hand wash provide oral decontamination clean oral suction device turn client q 2 hrs high fowler
1154.
preop clients
might take half of insulin
1155.
post op
respiratory, circulation, neuro, GU, GI, pain-these are all impaired by the surgery
1156.
dehisscence
put some stitches on high fowler
1157.
evisceration
lay pt down, bend knees, call for help, cover with sterile dressing 1158.
acute cholecystitis
low fat diet have rich in HDL food sources
1159.
NG tube
with x-ray first, gastric ph later empty when 1.5 to 3/4 full check residual in continuous feeding-check in q 4 hrs; if less than 100 ml-put it back; if more than 200-call provider; if more than 200 is taken out-metabolic alkalosis risk meds through NG tube are given liquid, if crushed you give the meds 1 at a time-you don't know how they interact when crushed and mixed in all together-also flush in between you don't give extended release meds through ng tube-they need liquid or non extended released
1160.
GERD
prokinetic agents- Reglan
1161.
Peptic ulcer
...
1162.
IBS
diarrhea and constipation LLQ pain cramps
1163.
Inflammatory bowel disorders (UC and Crohn's)
give immune modulators with the Ulcerative colitis-stool gets into the tissues?
1164.
Diverticulitis
they always have diverticulosis, but if something gets in a diverticula-then it becomes diverticulitis fluids only, rest the bowel later-low fiber and after, transition to high fiber
1165.
Dumping syndrome
dizziness, sweating, tachicardia post bariatric surgery-avoid lactose and high concentrated sugar, high fat and protein foods, turn to the L side not supine
1166.
Bariatric clients
they are obese- so high risk clients
1167.
Colostomy care teaching
include cranberry juice and yogurt to the diet-this will help with the odor empty bag when one third full clip hair surrounding the peristomal site
1168.
post up stoma care
pink and red is good the further in the colon the stoma is, the more solid the stool is emotional , lots of teaching required they will have an NG tube initially in for feeding stoma care and assessment-priorities
1169.
pancreatitis
need for intervention: 1.042 Urine specific gravity-severe dehydration (osmotic diuresis-started on TPN, sugar elevates) amylase, lipase, related to the exocrine function of the endocrine system
1170.
acute pancreatitis
possible hypocalcemia (Tressou sign)-hand spasms occurs during blood pressure monitoring with the auto digestion-Ca ends up in the bloodstream
1171.
Cirrhosis
low protein diet bleeding-esophageal varices they are breaking down protein-so they have high ammonia-this is toxic to neuro system
1172.
Hepatitis
liver impairment
1173.
Pancreatitis-malnutrition
put them far away from nurses station-so when food comes the smell wont create pancreatic enzymes
1174.
pancreatic cancer
immunosuppression present treatment: Whipple procedure and chemo many times its mehtastazied
1175.
OA
weather changes-barometric pressure chronic unilateral pain pain worsen after activity
1176.
Rheumatoid A
bilateral t inflammation morning stiffness and pain
1177.
Gout
men usually get it cannot put pressure on foot during acute episode multiple tophi excruciating pain with acute episode bed rest, avoid touch, increase fluids Allopurinol
1178.
SIADH
low sodium level seizure precautions
1179.
Arterial line
...
1180.
Clonidine
change position slowly, this is a BP drug take at night in case of a cough->don't stop the med, just call the dr
1181.
VTac
obtain VS don't defibrillate but cardiovert (if hemodynamically stable don't cardiovert) check carotid pulse give Amiodarone
1182.
Progressive MS
get rest and avoid stress major personality changes need speech therapist might lose ability to empty bladder eye patch given
1183.
Palliative care
improve quality of life meet physical and emotional needs
1184.
mental health pts to
treat based on developmental age, not chronologic age
1185.
amputation
first reaction-many times denial
1186.
Olanzepine/Zyprexa for Anxiety
antipsychotic-causes hyperglycemia and weight gain they can't eat whatever they want for the first two months-risk for agranulocytosis
1187.
Agoraphobia
intervention-desensitation-this is a slow process
1188.
OCD
intervention-allow the ritual-we are not allow to stop it without a physician order-we will send them into a panic attack
1189.
PTSD
intervention- groups
1190.
Hypochondriasis
intervention-limit rumination-will help them not thinking of it
1191.
Social Phobia
Intervention-GAD? intervention-reinforce coping
1192.
Schizophrenia
Paranoid-auditory hallucinations-know what the voices are telling them Disorganized-flat affect, disorganized behavior and speech Catatonic-stupor or extreme agitation, bizarre body posture-they can be in same position for a long timealteration of skin break down can happen
1193.
Prolixin
targets dyskenisia-repetitive involuntary facial and tongue motion
1194.
Aripiprazole
reduce daily delusional thoughts
1195.
Aricept
increase mental cognition
1196.
Haloperidol/Haldol
highest risk of EPS
1197.
Clozapine
agranulocytosis
1198.
Seroquel (for depression)
slipineess
1199.
Congentin
manages EPS
1200.
Risperdal
lowest risks gynecomastia is a major risk in young boys
1201.
Olanzapine/Zyprexa
hyperglicemia
1202.
Autism-alterations in
social skills-interventions-structured routines language-might talk late-interventions-foster independence behaviors-anger, frustration; intervention-safety cognition-depends where they fall-intervention-family health-frequent GI disorders-advised to be on gluten free diet-intervention-offer community resources
1203.
Niacin
flushing-normal
1204.
Rifampin (TB drug)
orange body fluids
1205.
Adenosine
flushing and chest pain, iv push
1206.
Protonix (PPI class)
antiulcer med
1207.
Pitocin
decreases bleeding uterine stimulant
1208.
Fentanyl (narcotic)
reversible agent is Nalaxone
1209.
Metothrexate
...
1210.
Palivizunab
prevents RSV
1211.
Methylprednisolone sodium succinate
given orally or IV IV push
1212.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (Evista)
given for postmenapausal osteoporosis
1213.
Lipitor
no grapefruit
1214.
Prostaglandin-Xalatan-Lantanoprost
...
1215.
Geodon
...
1216.
Indocin
ister with food, milk
1217.
Singulair, montelukast
bronchodilator
1218.
anti inflamatory-Nasonex
dont ister in clients with milk allergy
1219.
Flagyl-no alcohol first 3 days
...
1220.
Viagra-dont give with nitrates
...
1221.
slows osteoporosis-Premarin
...
1222.
avoid foods with tyramine-antibiotic-ZyvoxNeurontin-partial seizure and neuralgia given for these
...
1223.
-Methadone-monitor respiratory
...
1224.
-ster sq with evening meal or HS-Levemir; dont mix with other insulins (long acting insulin); doses must be 12 hrs apart
...
1225.
-antimicrobial-Zocyn-check allergy for penicillin
...
1226.
-for ADHD-available in po form only, taken once daily-Vyvanse-Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
...
1227.
Coumadin
anticoagulant, intake of greens important for vitamin K
1228.
Ariprippazole
avoid grapefruit, alcohol, overheating, dehydration
1229.
Nemanda/Nemantine
avoid diet in fruits and vegetables
1230.
antibiotic
caution in colitis
1231.
Hydrochloride
ister po-moderate to severe dementia such as Alzheimer fresh fruits will cause alkalinity-low excretion of drug
1232.
Actonel
CI with esophageal disorder remain uprights for 30 min take with a full glass of water
1233.
Cardizem
...
1234.
Avodart
BPH drug females of age that might have kids should not handle this
1235.
Chantix-
nicotinic blocker
1236.
Paxil
antidepressant don't take St John Worth take at night time
1237.
Depression
Anhedonia-maintain ADLs sleep alteration-bedtime routine anergia-encourage exercise worthlessness-monitor safety poor concentration-clear directions suicidal ideation-giving away things
1238.
Severe Mania
Anorexia-provide finger foods Accelerated speech-calm demeanor Fragmented thoughts-redirect no impulse control-monitor safety
1239.
SSRI
weight gain therapeutic effect after 1 week
1240.
Lithium
AE with diuretics therapeutic effect after 1 week
1241.
MAOI-
therapeutic effect after 1 week
1242.
TCA
therapeutic effect after 1 week monitor for dysrhythmias
1243.
detoxification of cocaine
s/s several hrs later-poor concentrations
1244.
hypertention crisis
hrs after opiods
1245.
alcohol withdrawal
dont leave them alone Diaphoresis—fluid replacement hallucinations-decrease stimuli Wernicke-Korsakoff-Infuse IV Thiamine
1246.
Oxazepam (Serax)
Delirium Tremens Tachycardia-monitor VS
1247.
stages of Alzeimer
4 only, not 6 stage 2 is moderate-cannot balance checkbook, decline in daily basic hygiene needs,; leave the stove after cooking; stage 1 (mild)-discuss meaning of client's framed photo: integrity vs dispair stage; you want them to have personal things around
1248.
Dementia
decrease in cognition-safety is major problem they need their routine provide education to the whole team taking care of this pt dont rationalize with them
1249.
Anorexia
we don't focus on their weight, they do prepare fluid therapy and enteral feeding for them
1250.
Clozapine
...
1251.
mental health miscellaneous
pt can leave facility if at will involuntary ission occurs if people are deemed a threat to themselves or others clients can communicate with their attorney nurse cannot open postal packages prior to giving to client
1252.
Hcg test-why is important before surgery
a positive pregnancy test may require canceling surgery
1253.
Hcg
rises during pregnancy and maintains the pregnancy raises until about 12 weeks of pregnancy, then body recognizes it and then it drops again
1254.
prenatal examination
report if pt is on a vegetarian diet; usually they are pseudo anemic until 32 weeks, then the iron should become normal again
1255.
first semester
nausea, vomiting, nutrition
1256.
2nd semester
dyspnea, heartburn
1257.
3rd trimester
make sure she know how to recognize false vs true labor signs
1258.
prenatal care
assess at each exam-VS, weight, fundal height...
1259.
Mag Sufate IV
resp 10-priority
1260.
Chronic HTN
mom had HTN prior to pregnancy this pt may develop preeclampsia
1261.
Gestational HTN
mom gets HTN after 20th week of gestation NO protenuria
1262.
STI
higher risk for ectopic pregnancy
1263.
Placenta previa
no vaginal exam painless, bright red bleeding
1264.
abruption placenta
painful dark red bleeding
1265.
hyperemesis
whatch the weight and electrolytes
1266.
hydatidiform mole
avoid pregnancy until hCG returns to normal she can a grape like structure... ideally avoid pregnancy for 4 years ? she is at risk for cancer as well usually this only happens once
1267.
Cerclage
cervical insufficiency
1268.
ectopic pregnancy
unilateral, stabbing, abdominal pain ectopic pregnancy is never a livable pregnancy
1269.
danger signs during pregnancy
fever and chills (infection) decreased or absent fetal movement sudden weight gain (preeclampsia) severe HA ROM prior to 37 weeks gestation vaginal bleeding
1270.
Isotonic IV fluids
...
1271.
If contractions frequency is 90 secs
stop Pitocin check FHR assess pain and fatigue
1272.
severe back pain labor
give back massage place on all fours (legs and nands)
1273.
If baby has a longitudinal lie, with FHR above the umbilicus
prepare for US need to evaluate for breech
1274.
pain
associated with labor
1275.
stage 1 of labor
keep her active after 3-7 cm-help her breath assess FHR and UC comfort
1276.
stage 2 of labor
check FHR q 15 min assist pushing
1277.
stage 3 stage of labor
placenta delivered do newborn care
1278.
stage 4 of labor
priority-prevent bleeding
1279.
fetal monitoring late deceleration
reposition first on L side
1280.
fetal monitoring
VEAL CHOP (what causes it) MINE (what you do about it)-make sure you know where they are in the process
1281.
Late decels
uteroplacental insufficiency
1282.
Lenght of contractions
maximum length of contraction should be 90 secs if 90 secs or longer or FHR is lower than 11-stop Pitocin if a mom is on it
1283.
L&D meds tocolytics-Indomethacin and Terbutaline
stops labor
1284.
Pitocin
used to augment labor/assist labor
1285.
Beamethasone
2 doses 24 hrs apart help to mature fetal lungs
1286.
breastfeeding
don't feed if discomfort is present schedule feeding for breastfeeding q 2-3 hrs meds might transfer to milk if mom is breastfeeding
1287.
Rhogham istration
monitor labs: Indirect Coomb's for baby Direct Coomb's for mom
1288.
PP hemorrhage
priority
1289.
mom breastfeeding on heparin therapy
breast milk will not be affected, after breast feeding is over she can go back to Coumadin
1290.
Initial Newborn Care
at 1 and 5 min check Apgar after drying him off put him skin to skin with mom for thermoregulation evaporation when baby is wet when baby is dry-heat is loss through..
1291.
baby assessment
reflexes check-premie will not demonstrate all the reflexes
1292.
fetal alcohol syndrome
high pitch cry hard to console cognitive disabilities
1293.
tobacco/nicotine
vasoconstricor decreased O2 for baby-increased SIDS risk, asthma
1294.
hypoglycemia in babies
check glucose w/o an order; it takes some time for the baby to get used with the insulin production
1295.
phototerapy
cover eye with mask reposition newborn q 2 hrs cover scrotum take them off light only for feeding
1296.
Kernisterus
yellow baby, we only take the baby out of the light for feeding
1297.
Womens Health
...
1298.
cancers
...
1299.
menopause
hot flashes night sweats palpitations vaginal atrophy osteoporosis
1300.
over 35
increased risk of DVT with oral contraception
1301.
all these matter when choosing oral contraception
history of hypertension severe PMS hist of DVT
1302.
Diflucan
...
1303.
Rocephin
...
1304.
Flagyl
...
1305.
postmenaupausal- 57 yrs old- (on Climara)monitor BP, yearly mammogram, take with food, call provider if bleeding occurs
...
1306.
Methergine
CI in HTN and cardiac disease promotes uterine contractions
1307.
lyrics (Pregabalin)
dont stop abruptly, monitor for edema
1308.
Plavix
Prilosec and Nexium will decrease the effects of this
1309.
Synthroid
give in the morning increases HR
1310.
complicated UTI
give antibiotics CI with sensitivity to cephalosporins-Maxipime
1311.
Gentamicin
antibiotic for bacterial infections monitor UO and renal function
1312.
Antipshychotic-Risperdal
dont mix oral solution with cola or tea
1313.
Aricept
monitor for bradicardia, dont interupt abrutptly
1314.
Lidocaine
not effective against SVT, given IV
1315.
Bystolic
don't stop abrupt, weight daily, can impair thinking and reaction time
1316.
Oxycontin
highly abused-should not be taken within 2 weeks of istration of an MAOI
1317.
Dilaudid
causes spasms of sphincter of odi
1318.
Levaquin
can alter glucose level in diabetic client
1319.
Vancomycin
antibiotic for MRSA risk for Red man syndrome
1320.
Digoxin
assess AP for one min hypokalemia can lead to toxicity
1321.
Inderal
check BP and pulse before istration
1322.
PPI-Nexium (GERD)
don't crush or chew
1323.
Effexor
can increase ptinr, don't discontinue abruptly
1324.
Lithium
mantain Na levels normal
1325.
Lovenox
hold if platelets are less than 100,000 ister sq
1326.
Pradaxa
avoid use with drugs that prolong bleeding keep dry and in a dark bottle
1327.
Varivax vaccine
prevents chicken pox
1328.
Lasix
Diuretic monitor HR, BP monitor weight
1329.
Amiodarone
first line drug for...
1330.
Dilantin
therapeutic level 10-20
1331.
Novolog
...
1332.
Advair (Fluticasone)
long term for asthma
1333.
Concerta
contra with MAOI
1334.
Simvastatin and Zetia-Vytorin
its a combination drug
1335.
Gardasil
prevents HPV istered to both male and female-
1336.
Nitro
onset 1-3 min sublingual
1337.
regular Insulin
the only one istered IV
1338.
Haldol
monitor for EPS causes dry mouth
1339.
Ambien
rapid onset given for short term insomnia
1340.
PEDS-know
infants and children-common causes of death incorrect car seat placement or not being in the seat
1341.
Ritalin
side effects-Tics, nervousness, increased BP; can cause insomnia, don't give in the evening
1342.
pt that is on radiation
no lotion on the side, no scrubbing, just warm water
1343.
know back/spine safety for nurse
upper bod mechanics, position client in the correct way
1344.
1hr oral glucose tolerance test
positive results 145mg/dl, report to provider, adv. pt to avoid caffeine the morning of test because it can increase glucose levels
1345.
Abstract Thinking
Asking questions about similarities between objects or to explain a common proverb or saying
1346.
Acarbose
oral antidiabetic agent that postpones the absorption of glucose
1347.
Acute hemolytic reaction
low back pain due to age of hemolyzed blood cell through kidneys, increased respirations, tachycardia
1348.
ister regular and NPH insulin steps
swab top of both insulin bottles with alcohol wipe, insert air into NPH insulin equal to dose, remove and insert air in regular insulin equal to dose, then withdraw dose from regular insulin and ister then withdraw correct dose from NPH insulin and subcutaneously
1349.
Advance directives
allow client to make decisions and provide written instructions regarding end of life care
1350.
Agoraphobia
behavioral therapy technique pt teaching includes modeling, systematic desensitization, flooding...
1351.
Air travel
2nd trimester, airplane cabin humidity is low (approx.. 8%), which can result in water loss, teach pt to maintain increased hydration with water to compensate for loss
1352.
Akathisia
responds to anti-parkinsonian medication
1353.
Albuterol (Proventil)
activates beta2-adrenergic receptors in the heart, increase in heart rate is a side effect
1354.
Alcohol anonymous (AA)
helps abstinence and sobriety
1355.
Alcoholism
causes CNS depression, drowsiness, slurred speech, and impaired coordination, s/s withdrawal elevated BP/HTN
1356.
Alendronate (Fosamax)
on empty stomach with 8oz water, may cause esophageal ulcerations if lodged in esophagus, remain upright for 30min after
1357.
Altruism
helping meet the needs of others who have experienced similar loss
1358.
Amitriptyline (Elavil)
tricyclic antidepressant must be taken within 3hr of missed dose if not wait til next dose,
1359.
Amniocentesis
evaluate fetal lung maturity
1360.
Amphetamine intoxication
stimulant use, adv. Effect; paranoia
1361.
Amphotericin B
adverse reaction is ototoxicity (vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss)
1362.
Ampicillin (Principen)
signs of allergic reaction hypotension, pruritus, flushing, wheezing
1363.
Anabolic steroids
in adolescence can lead to premature epiphyseal closure thus reducing height potential
1364.
Anaphylaxis Behavioral signs
apprehension, uneasiness, restlessness and anxiety
1365.
Anti-Hypertensives meds
contraindications caffeine
1366.
Antisocial personality disorder
impulse control, reminding client about expectations and providing clear boundaries and consequences of action will help promote client adherence
1367.
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) and fenofibrate (TriCor)
treats hypercholesterolemia, both meds may cause myopathy, pt has increased risk for myopathy than if either taken alone
1368.
Aversion therapy
uses punishment techniques to reduce inappropriate behaviors (alcoholism, aggression)
1369.
Avolition
lack of motivation
1370.
Baclofen (Lioresal)
antispasmodic, decreased muscle spasticity in client w/ MS, can cause urinary retention, drowsiness in early phase of therapy, hypotension
1371.
Benzodiazepine (Lorazepam)
withdrawal causes tremors and dizziness making ADL's difficult to perform
1372.
Bethanechol
muscarinic agonist that increases GI motility leading to abdominal cramps and diarrhea
1373.
Bi-Polar Disorder
increased energy and pressured speech, manic phase is treated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) if a course of medication is ineffective
1374.
Bladder distention
pushes uterus out of pelvis, can palpate fundus above umbilicus and to the right of midline,
1375.
Borderline personality disorder
development of manipulative behaviors that make establishing a meaningful relationship difficult
1376.
Boundary violation
when nurse engage in social relationship with client
1377.
Breastfeeding
baby should have at least 2 stools/day, may eat 8-12 times/ day, milk can be stored in freezer for up to 6mths, should have at least 6wet diapers per day, pt teaching; wake baby Q4hr at night for first 24-48 hr after birth
1378.
Bronchoscopy
post op; check for gag reflex,
1379.
Bulimia Nervosa
s/s tooth erosion, hand calluses, parotid swelling
1380.
Buprenorphrine
prevents withdrawal associated with opiate use, taking during pregnancy can improve maternal and neonatal outcomes
1381.
Bupropion
for nicotine use disorder
1382.
Caffeine (pregnancy)
consuming more than 200mg of caffeine/day increases risk of miscarriage and intrauterine growth restriction
1383.
Calcium carbonate (Tums)
...
1384.
Captopril (Capoten)
treat HTN, greatest risk to pt is infection r/t neutropenia therefore unexplained fever, sore throat, and fatigue can indicate and infection and provider should be notified, avoid ibuprofen or any other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication as it can reduce anti-hypertensive effects of medication
1385.
Carboprost
adv. effect fever
1386.
CD4 T-cell count
indicates the status of the pts immune system, a rise indicates return of immune function for HIV pt
1387.
CD4-T cell count
indicates the status of clients immune system, rise in cd4 counts indicates return of immune function of client w/ HIV
1388.
Cefotetan (Cefotan)
a cephalosporin, group of antibiotics hat are similar to penicillins (PCN), should be avoided in pt who is allergic to PCN
1389.
Celecoxib Celebrex
cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) inhibitors act by suppressing inflammation and relieving pain, will allow pt to move more easily, increases risk of MI because of increased vasoconstriction and unimpeded platelet aggregation
1390.
Cervical laceration
is a slow, oozing trickle of blood, during which fundus can remain firm
1391.
Chest tube drainage device
may ambulate, keep collection device below the level of the pt chest to ensure drainage, only clamp device when checking for air leaks or changing drainage system
1392.
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
for alcohol use disorder, avoid getting pregnant, teratogenic to developing fetus
1393.
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
increases skins sensitivity to UV light pt should apply sunblock to counteract adverse effect
1394.
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
orthostatic hypotension risk for falls, treats schizophrenia
1395.
Chorionic villus sampling
involves removal of small amount of tissure from the fetal section of the placenta to detect genetic conditions
1396.
Cimetidine (Tagamet)
should be taken 1hr before or 2hr after antacid
1397.
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
pt should avoid products with cations such as antacids, iron salts, milk and other dairy products because they reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin, in allergic reaction check for wheezing, diphenhydramine (Benadryl), possibly prep for IV catheter insertion, collect VS to determine pt status
1398.
Clang association
use of rhyming words
1399.
Clozapine (Clozaril)
can cause agranulocytosis, pt should have WBC evaluation
1400.
Cocaine intoxication
tachycardia, elevated BP, dilated pupils, display grandiosity and euphoria
1401.
Cocaine
CNS stimulant, may cause vomiting, dilated pupils and tachycardia
1402.
Coughing
incision with interlocked hands, pillow, towel or blanket to prevent excess stress on the incision when coughing
1403.
C-section
ambulate several times/day to increase circulation in lower extremities and prevent thrombophlebitis
1404.
Cystic Fibrosis
can have constipation should eat diet high in fiber, high calorie diet due to decreased intestinal absorption and increased work of breathing
1405.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
bed rest with affected limb elevated to reduce swelling, fit with elastic stockings, to prevent venous congestion once pt can ambulate
1406.
Delusions
belief that one's thoughts can be heard by someone else, common w/schizophrenia
1407.
Dementia
memory impairment and loss of speech
1408.
Depression
lethargy and slowed speech
1409.
Digoxin and chlorothiazide
increase pt risk of developing digoxin toxicity due to chance of developing hypokalemia
1410.
Digoxin toxicity
nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and fatigue
1411.
Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
an antihistamine, has anticholinergic properties, anticholinergic meds can cause urinary retention thus compounding urinary tract symptoms associated with prostatic hypertrophy, is contraindicated in pt with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
1412.
Displacement
defense mechanism, emotionally transferring anger for one person to innocent victim
1413.
Disulfiram
for alcohol use disorder
1414.
Doxycycline (Vibramycin)
should be taken with a full glass of water to ensure it es into the stomach which will prevent esophageal ulcerations
1415.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
pt awake 15min after ECT, likely to be confused and disoriented, reorient frequently
1416.
Eplerenone
treat HTN, adverse effects; diarrhea, decreased sodium levels, vaginal bleeding, increased potassium levels cause of potassium retention effect
1417.
Erythromycin
apply medication starting from inner canthus to outer canthus, instill 1cm ribbon of medication in lower conjunctiva to ensure proper delivery of medication, medication prophylactically to protect newborn from ophthalmia neonatorum
1418.
Exenatide
treat DM, monitor for abd pain pt at risk for pancreatitis
1419.
Expected anticipatory grieving
statements indicating shock and disbelief, needing to get away from situation, anger against dying person or caregivers,
1420.
Eyedrop instillation
advise pt to look up during to protect cornea and decrease change of blinking, clean eyes starting from inner canthus moving outward,
1421.
Felodipine (Plendil)
grapefruit juice can inhibit metabolism raising level of medication in blood increasing risk of toxicity
1422.
Ferrous sulfate
treat iron deficiency anemia, improvement in hemoglobin levels increases oxygen transport to the tissues and increases activity tolerance
1423.
Fine crackles
continuous, musical sounds which are caused by narrowing of airways
1424.
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
monitor sleeping patterns, insomnia common side effect,
1425.
Fluoxetine
contraindicated with sumatriptan put pt at risk for serotonin syndrome causing tremors, confusion, hallucinations
1426.
Fluphenazine (Prolixin)
avoid sun exposure causes photosensitivity
1427.
Fundal Height
in pregnancy should be approximately the same as the number of weeks gestation plus or minus 2cm
1428.
Furosemide (Lasix)
loop diuretic, can lead to hypokalemia, can cause BP to drop, medication should be withheld if BP 85/60,
1429.
Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
myopathy is an adverse effect, report muscle weakness or tenderness
1430.
Gentamicin (Garamycin)
is nephrotoxic, monitor BUN and serum creatinine levels
1431.
Ginkgo Biloba
herbal supplement to treat a variety of conditions (dementia, vascular disease), may interfere with platelet production and increase the risk of bleeding in clients on anticoagulation therapy (warfarin/antiplatelet medications)
1432.
Glipizide
oral antidiabetic agent that stimulates insulin secretion
1433.
Gonorrhea
STI, can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and tubal scarring which can result in infertility
1434.
Grief
community bereavement group may help cope with feelings of grief
1435.
Haloperidol (Haldol)
typical antipsychotic that decreases symptoms of psychosis and anxiety, adverse reactions tremors, shuffling gait, drooling pseudoparkinsonism
1436.
Heel stick in newborn
1st warm newborns heel
1437.
Heroin
causes CNS depression, drowsiness and slurred speech, pupillary constriction, effective treatment strategy is participation in a methadone maintenance program
1438.
Histrionic personality disorder
impulsive behavior, inappropriate sexual behavior
1439.
Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV2)
3 doses of immunization over 6mths,
1440.
Hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril)
can cause hypokalemia from excessive potassium excretion, other adverse effects are hyperchloremia, hypernatremia, hypercalcemia.
1441.
Hyperemesis gravidarum
S/S persistent vomiting and ketonuria
1442.
Hypoglycemia (newborn)
hypothermia, twitching, tachypnea (respiratory distress)
1443.
Inhalants intoxication
s/s incoordination, nystagmus, blurred vision
1444.
Ipratropium (Atrovent)
an anticholinergic, contraindicated in pt who is allergic to peanuts or soybeans because medication may contain peanut oil and soy lecithin
1445.
Iron (foods)
beef liver, lentils, oysters
1446.
Isoniazid (INH)
can cause liver damage, important for nurse to determing the clients daily alcohol intake because alcohol use increase risk, pt should reduce or avoid all use of alcohol
1447.
Isotretinoin
pt teaching will need to have triglyceride levels monitored, may cause nosebleeds, due to nature of severe birth defects pt will need 2 negative pregnancy test prior to starting medication
1448.
IV Meds
medication that are water soluble can only be istered intravenously
1449.
Jaundice
should be reported within first 24hrs of life, physiologic jaundice can lead to severe cognitive disorders
1450.
Ketorolac (Toradol)
is nephrotoxic and can cause renal impairment, monitor serum creatinine level
1451.
Kosher dietary laws
avoid eating meat and dairy product together
1452.
Lactation suppression
frequent application of cold cabbage leaves to breast can prevent engorgement
1453.
Levodopa/carbidopa (Sinemet)
dopaminergic medication, works by activating dopamine receptors, restoring nerve transmission in the basal ganglia for pt with Parkinsons disease, allows client to move freely and resume ADL's
1454.
Lisinopril (Zestril)
ACE inhibitor, can result in buildup in bradykinin, resulting in nonproductive cough, pt should withhold medication and follup with provider for further evaluation, contraindicated w/ ibuprofen can decrease antihypertensive effect
1455.
Lithium Carbonate (Eskalith)
monitor lithium levels if dosage is changed
1456.
Lower extremity amputee
anchor residual limb dressing at the nearest t proximal to the amputation, cleanse residual limb with mild soap and carefully rinse and dry, maintain compression dressing following amputation in order to promote proper fit of prosthesis and reduce edema, wrap 3x day and prn
1457.
Lumbar laminectomy
pt teaching; involves removing a portion of vertebra to expose spinal cord which produces a sense of instability in spine, avoid twisting and bending, sit in straight back chair, sleep on firm mattress
1458.
Magnesium sulfate
depresses neuromuscular activity, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis
1459.
Magnesium toxicity
bradycardia, hyporeflexia, oliguria (urine output 30ml or less), respirations less than 12/min, increased BUN indicating renal impairment which can decrease excretion and cause magnesium to accumulate to toxic levels
1460.
Major Depression
monitor elevated mood, may be indication the pt plan to commit suicide
1461.
Maladaptive grieving
statements indicating shame and guilt, feelings of being overwhelmed
1462.
Manic behavior
unable to focus on a solitary activity w/o direction from another person, impacts other clients negatively,
1463.
MAOI
contraindications aged cheese
1464.
Marijuana
a hallucinogen, has depressant properties, euphoria, relaxation and paranoia
1465.
Maslow's Hierarchy
Physiological (hunger, thirst, bodily comforts, etc.), Safety/security (out of danger), Belongingness and Love ( with others, be accepted, loved), Esteem (to achieve, be competent, gain approval and recognition), Self-Actualization (morality, creativity, problem solving)
1466.
Mastitis
pump affected breast frequently
1467.
Meconium
develops in utero, first stool ed by newborn w/I first 24 hr, dark green and viscous, contains components of amniotic fluid, cells, intestinal secretions, occult blood
1468.
Medroxyprogesterone
adv effect; loss of bone mineral density advise pt to increase calcium intake while on medication
1469.
Mesalamine (Asacol)
maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease and pt should take daily for at least 3-6 weeks
1470.
Metformin (Glucophage)
oral antidiabetic agent, used to treat DM II by decreasing glucose production in the liver, facilitates decreased glucose production; monitor for adverse effects muscle pain, agitation, GI manifestation such as bitter or metallic taste
1471.
Methamphetamine
expect high fever with overdose of CNS stimulant
1472.
Methotrexates (Rheumatrex)
pt should avoid alcohol due to risk for hepatic fibrosis and liver toxicity
1473.
Metoprolol (Lopressor)
slows the conduction through AV node therefore is contraindicated in pt who have AV block that is greater than first degree, caution in pt with diabetes mellitus because it can mask the manifestations of hypoglycemia
1474.
Milieu therapy
creates therapeutic community in which client has opportunities for learning and healing, inpatient therapy
1475.
Nasogastric tube (NG)
place pt in high fowlers position, determine which naris has greatest airflow, measure appropriate tube length, lubricate 3-4inches of end of tube, instruct client to hyperextend neck
1476.
Negligence
failing to respond to escalating behavior and prevent harm from others
1477.
Neologisms
words made up by the client
1478.
Nephrotic syndrome
with peripheral edema, low sodium diet to assist with diuresis of extracellular fluid
1479.
Nifedipine
causes vasodilation, resulting in decreased BP, can increase orthostatic hypotension and dizziness, change position slowly
1480.
Nitrates
cause relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, resulting in pooling of blood in veins and decreased venous return to heart, decreases cardiac output which causes blood pressure to fall and orthostatic hypotension to occur with change in position
1481.
Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat)
sublingual tablets, treat angina, can take up to 3doses 5min apart if chest pain persist
1482.
Nitroglycerin (TransdermNitro)
advise pt to place patch on different site for each application to prevent skin irritation, medication may cause orthostatic hypotension/dizziness should change position slowly to avoid injury
1483.
NonMaleficence
ethical concept of avoiding harm
1484.
Nonstress test (NST)
orange juice to increase the clients blood sugar and stimulate fetal movement, 2 FHR acceleration of 15/min over 20min period lasting at leatst 15 seconds indicate reactive non-stress test
1485.
Ondansetron (Zofran)
side effects headache and dizziness, pt should avoid driving or using heavy machinery
1486.
Operant conditioning
type of behavior modification that use positive reinforcement to promote a desired behavior
1487.
Oral contraceptives
contraindicated in pt who experience frequent headaches w/vision changes (can indicate cardiovascular condition) because combination can increase risk of CVA, MI, and thromboembolism
1488.
Orientation/preorientation relationship
plan for interactions with the pt
1489.
Oxycodone (OxyContin)
opioid analgesic, pain reliever, can cause CNS depression, contraindicated with diphenhydramine (Benadryl) put pt at risk for sedation, respiratory depression and injury
1490.
Paranoid schizophrenia
dominant symptoms hallucinations and delusions
1491.
Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
may cause tachycardia and other cardiac arrhythmias
1492.
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
stimulates synthesis of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes, can decrease effects of warfarin, providers (titration of medication) base dosage on therapeutic blood levels
1493.
Phytonadione
is ister via IM to newborn,
1494.
Pioglitazone (Actos)
oral antidiabetic agent, works by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, 8-12wks to experience full therapeutic effects of medication
1495.
Pleural rub sounds
loud grating sound caused by pleurisy
1496.
Postpartum diuresis
should begin 12hr after delivery, expected urine output of 3000ml/24hr
1497.
Prednisone (glucocorticoids)
suppress the body's immune response increasing risk of infections, pt should notify provider if they experience the following symptoms sore throat, black tarry stools (indicates GI bleed) due to the increased risk GI ulcers, white patches on tongue (increased risk for candida infections due to immunosuppression), hyperglycemia, weight gain
1498.
Propranolol (Inderal)
beta blocker, bradycardia is a common adverse effect, advice pt to withhold med if pulse rate less than 60bpm, can suppress tachycardia a warning sign of hypoglycemia in pt with DM, advise to rely on other signs
1499.
Propylthiouracil (Propyl-Thyracil)
desired effect HR WNL, reduction in serum T4 level, improved sleep patterns, increased attention span
1500.
PTSD
experience disrupted sleep
1501.
Quetiapine
pt at risk for abnormal glucose metabolism which may result in DM, serum glucose testing regularly
1502.
Reflection
communication technique that lets the client know that their concerns and feeling are heard and understood
1503.
Regular Insulin
clear in appearance, discard if appear cloudy
1504.
Religiosity
obsession with religious ideas and actions
1505.
Repaglinide (Prandin)
HbA1c lab test should be review to obtain information about long term therapeutic, measures blood glucose levels over past 2-3mths; glycosylated HbA1c
1506.
Repression
pt excludes unwanted ideas from conscious awareness
1507.
Respiratory distress (newborn)
S/S; nasal flaring, tachypnea, substernal retractions, grunting
1508.
Retention of placental fragments:
...
1509.
Rho(D) immunoglobin
given to Rh neg. mother who has Rh pos. newborn to prevent mother from developing antigens against the Rh factor
1510.
Risperidone
treat schizophrenia, atypical antipsychotic help to improve/minimize pt w/schizophrenia with difficulty interacting with others/maintaining relationships, put client at risk for developing diabetes due to metabolic effects of medication, obtain fasting glucose baseline prior to istration of first dose, and again, 12wks later, then annually
1511.
Schizophrenia
multiple pos & neg symptoms, flat affect & tangential speech, delusions (delusions of grandeur), appears stuporous, little to no movement at all, pt/family teaching; manage client stress to help control symptoms of illness
1512.
Schizotypal personality disorder
suspicious attitude
1513.
Scopolamine patch
treat motion sickness, should be placed behind the ear
1514.
Signs of Allergic reaction
hypotension, pruritus, flushing, wheezing
1515.
Simvastatin
notify provider if muscle pain or tenderness develops could indicate rhabdomyolysis
1516.
Social worker
help client build a structure to help promote and preserve mental health, including arrangements for employers, day treatments, financial and other community resources
1517.
Spironolactone (aldactone)
potassium sparing diuretic, salt substitutes are high in potassium can place pt at risk for hyperkalemia
1518.
Sumatriptan
contraindicated with use of fluoxetine can lead to excessive stimulation of serotonin receptor putting pt at risk for serotonin syndrome s/s tremor, confusion, hallucinations
1519.
Systematic desensitization
form of behavior modification that employs relaxation techniques in response to specific phobias
1520.
Tardive dyskinesia
lip smacking, tongue rolling, spastic facial expressions
1521.
Tetanus
booster recommended every 10yrs or sooner if injury occurs from a potentially contaminated object
1522.
Tetracycline hydrochloride (Sumycin)
causes photosensitivity and increased severity of sunburn
1523.
Therapeutic lithium level
1.2 meq/L serum lithium level
1524.
Therapeutic relationship:
...
1525.
Timolol eyedrops
treat glaucoma, press the nasolacrimal duct to prevent the medication from absorbing into systemic circulation
1526.
Tolbutamide (Orinase)
treat DM, contraindicated in pt with hypersensitivity to sulfonamide antibiotics that might also be allergic to sulfonylureas
1527.
Tonsillectomy
pt/child can chew gum to prevent throat and ear pain post-op
1528.
Topical decongestants
rebound congestion can occur with prolonged use congestion can become progressively severe
1529.
Tracheostomy child care
allow child to rest for 30-60 seconds after each aspiration to allow oxygen saturation to return to expected levels, suction as needed when there is indication of excessive secretion in airway, suction for no more than 5 sec w/each , hyperventilate w/100% oxygen before and after suctioning
1530.
Triamterene (Dyrenium)
inhibits exchange of (Na) and (K) in the distal nephron retaining (K) and excreting (Na) leading to hyperkalemia
1531.
Triple marker screening
done at 16-18wks gestation, identify chromosomal abnormalities
1532.
Uterine bleeding
relaxed, distended uterus with presence of blood and clots,
1533.
Vancomycin (Vancocin)
adverse reaction ototoxicity
1534.
Varicella (chickenpox vaccine)
hypersensitivity to neomycin is contraindicated for receiving vaccine
1535.
Veracity
duty to tell the truth
1536.
Vesicular sounds
soft, rustling sounds that occur as normal breath sounds
1537.
Vitamin K
needs to be at least 2hr after birth to prevent risk for hemorrhagic disease
1538.
Wheezes
continuous, musical sounds which are caused by narrowing of the airways