Anatomy - The Nervous System Powerpoint c24
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View Anatomy - The Nervous System Powerpoint as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 1,122
- Pages: 47
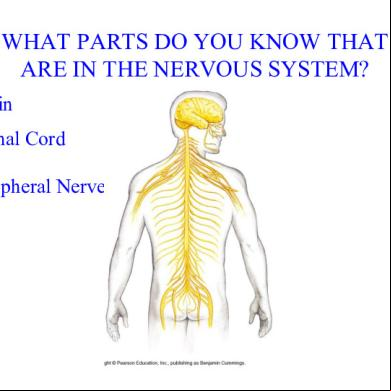
WHAT PARTS DO YOU KNOW THAT ARE IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? • Brain • Spinal Cord • Peripheral Nerves
Classification of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS): Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input – gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body
Integration - To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed
Motor output A response to stimuli Activates muscles or glands
The Peripheral Nervous System Sensory (afferent) division - Nerve fibers that carry information to the central nervous system
Motor (efferent) division - Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system.
Somatic system: voluntary
Autonomic system: involuntary
Autonomic Nervous System The involuntary branch of the nervous system Consists of only motor nerves Divided into two divisions Sympathetic division – “fight or flight” response Parasympathetic division – “housekeeping”
The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord.
The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body.
Nervous System Histology Neurons = nerve cells Cells specialized to transmit electrochemical messages
Major regions of neurons Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body
Neuron Anatomy Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body Cell body (soma): contains organelles & Nissl substance (specialized rough ER) Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body
Schwann cells – produce myelin sheaths in jelly-roll like fashion Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
Classification of Neurons Sensory (afferent) neurons Carry impulses from the sensory receptors Cutaneous sense organs
Receptors – detect stretch or tension
Interneurons (association): “connector”
Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from the central nervous system
What makes up the brain, the spinal cord or your peripheral nerves? • • • • •
Neurons are “the cell” Cell body Nucleus Axon Dendrite
QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Un compressed) decompressor are neede d to see this picture.
Key Note Neurons perform all of the communication, information processing, and control functions of the nervous system.
Someone getting on your nerves?
How are neurons connected? • Synapses!!
Why are neurons connected?
More neuron connections!
General Organization of the nervous system Brain & spinal cord
How does the Synapse carry the signal? 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane - what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to to the next cell -
The synapse carries a signal from cell to cell
1
2
3
4
Are all neurons equal in size? • Brain vs spinal cord vs peripheral nerves?
About how many neurons are in the human brain?
100 billion
About how many neurons are in the spinal cord?
1 billion
How long do you think the longest axon in the world is?
around 15 feet
How many synapses are in one neuron? 1,000 to 10,000!!
This science is called Neurobiology • • • • • •
Looking at the actual cells - how do they work? Looking at the connections - how and when do they work? Looking at what can change normal cells and connections Looking at diseases that occur in the brain One of the largest areas still unknown Neurons connecting!
What do you think can change neurons and their connections? • • • •
Accidents Drugs Alcohol Disease
Accidents • Physical injury of your neurons
Drugs and alcohol bind important receptors on neurons
Repeated binding causes the neuron to die
Drugs = neuron death
•Parkinson's Disease •ALS - Lou Gehrig’s Disease •Huntington’s Disease •Multiple Sclerosis •Alzheimer's •Cerebral Palsy •Epilepsy
100 Billion or so neurons - what’s the problem with some of them dying? •Cells multiply all the time - will your neurons? •Does everyone react the same way to accidents, or drugs and alcohol? •Do all organisms react the same to all stimulus? •Which of your activities use your neurons?
Specialized Area of the Cerebrum
Figure 7.13c
Cranial Nerves 12 pairs of nerves that mostly serve the head and neck
Numbered in order, front to back Most are mixed nerves, but three are sensory only
* The outer nervous system carries messages between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
* The Outer Nervous System’s job is to connect the Central Nervous System to the rest of the body.
* The outer nervous system is made of the nerves and the sense organs.
Eye
Ear
Skin
Nerves Tongue
* An automatic reaction that happens without thinking about it.
* A reflex happens quickly in less than a second.
* The outer nervous system controls the body’s activities that you don’t think about.
* The outer nervous system controls activities in your small intestine, your breathing, and your heartbeat.
controls
Sense organs carry messages about the environment to the central nervous system. The eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin are examples of sense organs. The sense organs gather information (light, sound, heat, and pressure) from the environment.
The environment is everything outside the body. The sense organs gather information from outside the body, then send the messages to the brain.
Vision is your ability to see.
Vision involves the eye and the brain.
The eye is one of your sense organs.
The eye is made of the iris and the pupil.
The eye gathers pictures and sends them to the brain.
The colored part of the eye is the iris.
The black part of the eye is the pupil.
Pupil
Iris
The pupil becomes larger and smaller as it controls the light coming into the eye.
When a sound is made, the air around the sound vibrates.
Hearing starts when some of the sound waves go into the ear.
The sense of touch is located in the skin.
The nerves in the skin allow us to feel texture, pressure, heat, cold, and pain.
Texture is how something feels.
The nose controls your sense of smell.
The nose is able to smell 80 different kinds of smells.
Your sense of taste comes from the taste buds in the tongue.
Taste buds are the parts on the tongue that allow us to taste. The four kinds of taste buds are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty.
Tastes and smells work together to make flavors.
Flavors are the tastes of food and drinks.
Classification of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS): Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input – gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body
Integration - To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed
Motor output A response to stimuli Activates muscles or glands
The Peripheral Nervous System Sensory (afferent) division - Nerve fibers that carry information to the central nervous system
Motor (efferent) division - Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system.
Somatic system: voluntary
Autonomic system: involuntary
Autonomic Nervous System The involuntary branch of the nervous system Consists of only motor nerves Divided into two divisions Sympathetic division – “fight or flight” response Parasympathetic division – “housekeeping”
The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord.
The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body.
Nervous System Histology Neurons = nerve cells Cells specialized to transmit electrochemical messages
Major regions of neurons Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body
Neuron Anatomy Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body Cell body (soma): contains organelles & Nissl substance (specialized rough ER) Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body
Schwann cells – produce myelin sheaths in jelly-roll like fashion Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
Classification of Neurons Sensory (afferent) neurons Carry impulses from the sensory receptors Cutaneous sense organs
Receptors – detect stretch or tension
Interneurons (association): “connector”
Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from the central nervous system
What makes up the brain, the spinal cord or your peripheral nerves? • • • • •
Neurons are “the cell” Cell body Nucleus Axon Dendrite
QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Un compressed) decompressor are neede d to see this picture.
Key Note Neurons perform all of the communication, information processing, and control functions of the nervous system.
Someone getting on your nerves?
How are neurons connected? • Synapses!!
Why are neurons connected?
More neuron connections!
General Organization of the nervous system Brain & spinal cord
How does the Synapse carry the signal? 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane - what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to to the next cell -
The synapse carries a signal from cell to cell
1
2
3
4
Are all neurons equal in size? • Brain vs spinal cord vs peripheral nerves?
About how many neurons are in the human brain?
100 billion
About how many neurons are in the spinal cord?
1 billion
How long do you think the longest axon in the world is?
around 15 feet
How many synapses are in one neuron? 1,000 to 10,000!!
This science is called Neurobiology • • • • • •
Looking at the actual cells - how do they work? Looking at the connections - how and when do they work? Looking at what can change normal cells and connections Looking at diseases that occur in the brain One of the largest areas still unknown Neurons connecting!
What do you think can change neurons and their connections? • • • •
Accidents Drugs Alcohol Disease
Accidents • Physical injury of your neurons
Drugs and alcohol bind important receptors on neurons
Repeated binding causes the neuron to die
Drugs = neuron death
•Parkinson's Disease •ALS - Lou Gehrig’s Disease •Huntington’s Disease •Multiple Sclerosis •Alzheimer's •Cerebral Palsy •Epilepsy
100 Billion or so neurons - what’s the problem with some of them dying? •Cells multiply all the time - will your neurons? •Does everyone react the same way to accidents, or drugs and alcohol? •Do all organisms react the same to all stimulus? •Which of your activities use your neurons?
Specialized Area of the Cerebrum
Figure 7.13c
Cranial Nerves 12 pairs of nerves that mostly serve the head and neck
Numbered in order, front to back Most are mixed nerves, but three are sensory only
* The outer nervous system carries messages between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
* The Outer Nervous System’s job is to connect the Central Nervous System to the rest of the body.
* The outer nervous system is made of the nerves and the sense organs.
Eye
Ear
Skin
Nerves Tongue
* An automatic reaction that happens without thinking about it.
* A reflex happens quickly in less than a second.
* The outer nervous system controls the body’s activities that you don’t think about.
* The outer nervous system controls activities in your small intestine, your breathing, and your heartbeat.
controls
Sense organs carry messages about the environment to the central nervous system. The eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin are examples of sense organs. The sense organs gather information (light, sound, heat, and pressure) from the environment.
The environment is everything outside the body. The sense organs gather information from outside the body, then send the messages to the brain.
Vision is your ability to see.
Vision involves the eye and the brain.
The eye is one of your sense organs.
The eye is made of the iris and the pupil.
The eye gathers pictures and sends them to the brain.
The colored part of the eye is the iris.
The black part of the eye is the pupil.
Pupil
Iris
The pupil becomes larger and smaller as it controls the light coming into the eye.
When a sound is made, the air around the sound vibrates.
Hearing starts when some of the sound waves go into the ear.
The sense of touch is located in the skin.
The nerves in the skin allow us to feel texture, pressure, heat, cold, and pain.
Texture is how something feels.
The nose controls your sense of smell.
The nose is able to smell 80 different kinds of smells.
Your sense of taste comes from the taste buds in the tongue.
Taste buds are the parts on the tongue that allow us to taste. The four kinds of taste buds are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty.
Tastes and smells work together to make flavors.
Flavors are the tastes of food and drinks.