33-hour Chick Reviewer 1b2w3e
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 2z6p3t
Overview 5o1f4z
& View 33-hour Chick Reviewer as PDF for free.
More details 6z3438
- Words: 1,254
- Pages: 5
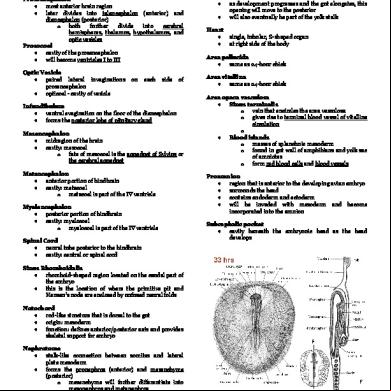
33-hour Chick: Whole Mount
primary brain vesicles are already present fundamental regions of the heart have already formed
Prosencephalon most anterior brain region later divides into telencephalon (anterior) and diencephalon (posterior) o both further divide into cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, hypothalamus, and optic vesicles Prosocoel cavity of the prosencephalon will become ventricles I to III Optic Vesicle paired lateral invaginations prosencephalon opticoel - cavity of vesicle
on
each
side
of
Infundibulum ventral evagination on the floor of the diencephalon forms the posterior lobe of pituitary gland Mesencephalon midregion of the brain cavity: mesocoel o fate of mesocoel is the aqueduct of Sylvius or the cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon anterior portion of hindbrain cavity: metacoel o metacoel is part of the IV ventricle Myelencephalon posterior portion of hindbrain cavity: myelocoel o myelocoel is part of the IV ventricle Spinal Cord neural tube posterior to the hindbrain cavity: central or spinal cord
Somites 11-12 pairs are present Anterior Intestinal Portal opening of the foregut as development progresses and the gut elongates, this opening will move to the posterior will also eventually be part of the yolk stalk Heart
single, tubular, S-shaped organ at right side of the body
Area pellucida same as 24-hour chick Area vitellina same as 24-hour chick Area opaca vasculosa Sinus terminalis o vein that encircles the area vasculosa o gives rise to terminal blood vessel of vitelline circulation o Blood islands o masses of splanchnic mesoderm o found in gut wall of amphibians and yolk sac of amniotes o form red blood cells and blood vessels Proamnion region that is anterior to the developing avian embryo surrounds the head contains endoderm and ectoderm will be invaded with mesoderm and become incorporated into the amnion Subcephalic pocket cavity beneath the embryonic head as the head develops
Sinus Rhomboidalis rhomboid-shaped region located on the caudal part of the embryo this is the location of where the primitive pit and Hensen’s node are enclosed by unfused neural folds Notochord rod-like structure that is dorsal to the gut origin: mesoderm function: defines anterior/posterior axis and provides skeletal for embryo Nephrotome stalk-like connection between somites and lateral plate mesoderm forms the pronephros (anterior) and mesenchyme (posterior) o mesenchyme will further differentiate into mesonephros and metanephros
1
33-hour Chick: Transverse Section Level of Optic Nerve Optic Vesicles lateral bulges of prosencephalon forerunners of the portions of the eyes will induce the head ectoderm to thicken, invaginate, and form the lens vesicles cavity: opticoel Proamnion region below the head fold consists of ectoderm underlain with a layer of endoderm will eventually be overgrown and disappear
Section through Oral Plate
Prosencephalon forebrain that consists of median vesicle and a lateral outpocket on each side cavity: prosocoel
Foregut smile-shaped cavity ventral to notochord walls are derived from endoderm middle portion of the foregut’s floor is slightly thickened
Anterior neuropore median cleft at anterior tip of neural tube presence of this opening means the neural folds have not fused yet Lens Placode thickening of head ectoderm that surrounds the optic vessel forerunner of eye lenses Infundibulum shallow depression of prosencephalic floor located at posterior border of optic vessels Amniotic fold fold of somatopleure arise at the head region, the sides, and the caudal end fusion of amniotic folds will give rise to amnion (inner) and chorion (outer) Yolk sac extra embryonic membrane encloses and absorbs yolk of amniote embryos endoderm + splanchnic mesoderm (splanchnopleure) Other structures to be noted (description in 24-hour chick) Head ectoderm Mesenchyme Neural Crest Subcephalic pocket Area pellucida Coelom Area Vasculosa
Notochord ventral to mesencephalon mesoderm derived
Oral Plate thickened area formed by the ventral ectoderm and the adjacent endodermal evagination of pharynx ventral to the foregut will form the mouth when it perforates Subcephalic Space Extraembryonic germ layers
below the head fold
Mesencephalon oval-shaped brain vesicle posterior to prosencephalon Anterior cardinal veins paired blood vessels at the lateral sides of the mesencephalon Pharynx region of foregut at this level Dorsal Aorta large, paired blood vessels dorsal to the pharynx Stomodeum shallow midventral depression in the ectoderm forerunner of buccal cavity Ventra Aorta small paired blood vessels located below the pharynx one is at each side of a median depression in the floor of the foregut First Aortic Arches connects the dorsal aorta with the ventral aorta can be seen at the anterolateral region of the foregut
2
Neural Crest cells found at the edges of the neural plate and above the neural tube will form ganglia, pigment cells, and parts of the gills Thyroid Gland endocrine gland that functions for control of metabolism and growth from ventral endoderm of pharynx seen as a thickened shallow depression of the foregut at the region of the dorsal mesocardium Section at the level of the Heart: Posterior Sections Atrium posterior level of the heart located now at the middle of the pericardial cavity becomes the future auricles Sinus venosus caudal continuation of the atrium dorsoventrally flattened tube in the midline Section at the level of the Heart: Anterior Section Ventral Aortae fusion of ventral aorta from earlier now a median, unpaired vessel Bulbus arteriosus anterior chamber of heart embryo connects ventricle to the ventral aorta Epimyocardium outer, thicker layer of heart rudiment arises from splanchnic mesoderm fuses with the endocardium to form the heart’s wall will give rise to: epicardium (outer covering of the heart) and myocardium (cardiac musculature)
Anterior Intestinal Portal ventral opening of the gut into the yolk future midgut Vitelline veins paired, large vessels that enter the atrium via sinus venosus at the caudal sections, these vessels will rise at the lateral part of the blastoderm Anterior cardinal veins pair of small blood vessels above the dorsal aortae also lies adjacent to the rhombencephalon
Isthmus broad connection between heart and foregut synonymous to dorsal mesocardium rhombencephalon by the time na mag-heart na
Section at the level of the Heart: Through the Ventricle Ventricle bends to one side of the coelom narrower dorsal mesocardium Rhombencephalon posterior part of brain level of future ventricle possesses a thick wall Auditory Pits ectodermal thickenings at hindbrain level forerunners to the inner ears syn: auditory placodes
3
Section through the Sinus Rhomboidalis Neural Tube neural groove has opened Hensen’s node large mass of compactly arranged cells displaces the notochordal tissue
Section through the Somites
Unsegmented mesoderm somites are not yet divided at this section Omphalomesenteric vein it is located far out in the splanchnopleure
Spinal Cord elongated with elliptical cavity Notochord Somites Nephrotome
refer to the 24-hour chick description for these structures
Hypomere Dorsal Aortae pair of large vessels between the endoderm and the somites at more caudal sections, they continue laterally into the plexus of vessels -- emphalomesenteric arteries
4
pictures are from: http://www.vcbio.science.ru.nl/images/embryology/c hicken-33hrs-dorsal-longitudinal-patten.gif http://nte-serveur.univlyon1.fr/nte/embryon/www.uoguelph.ca/zoology/devobio/33h rchck/33ckintr.htm https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/i mages/thumb/7/72/Patten028.jpg/600px-Patten028.jpg
5
primary brain vesicles are already present fundamental regions of the heart have already formed
Prosencephalon most anterior brain region later divides into telencephalon (anterior) and diencephalon (posterior) o both further divide into cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, hypothalamus, and optic vesicles Prosocoel cavity of the prosencephalon will become ventricles I to III Optic Vesicle paired lateral invaginations prosencephalon opticoel - cavity of vesicle
on
each
side
of
Infundibulum ventral evagination on the floor of the diencephalon forms the posterior lobe of pituitary gland Mesencephalon midregion of the brain cavity: mesocoel o fate of mesocoel is the aqueduct of Sylvius or the cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon anterior portion of hindbrain cavity: metacoel o metacoel is part of the IV ventricle Myelencephalon posterior portion of hindbrain cavity: myelocoel o myelocoel is part of the IV ventricle Spinal Cord neural tube posterior to the hindbrain cavity: central or spinal cord
Somites 11-12 pairs are present Anterior Intestinal Portal opening of the foregut as development progresses and the gut elongates, this opening will move to the posterior will also eventually be part of the yolk stalk Heart
single, tubular, S-shaped organ at right side of the body
Area pellucida same as 24-hour chick Area vitellina same as 24-hour chick Area opaca vasculosa Sinus terminalis o vein that encircles the area vasculosa o gives rise to terminal blood vessel of vitelline circulation o Blood islands o masses of splanchnic mesoderm o found in gut wall of amphibians and yolk sac of amniotes o form red blood cells and blood vessels Proamnion region that is anterior to the developing avian embryo surrounds the head contains endoderm and ectoderm will be invaded with mesoderm and become incorporated into the amnion Subcephalic pocket cavity beneath the embryonic head as the head develops
Sinus Rhomboidalis rhomboid-shaped region located on the caudal part of the embryo this is the location of where the primitive pit and Hensen’s node are enclosed by unfused neural folds Notochord rod-like structure that is dorsal to the gut origin: mesoderm function: defines anterior/posterior axis and provides skeletal for embryo Nephrotome stalk-like connection between somites and lateral plate mesoderm forms the pronephros (anterior) and mesenchyme (posterior) o mesenchyme will further differentiate into mesonephros and metanephros
1
33-hour Chick: Transverse Section Level of Optic Nerve Optic Vesicles lateral bulges of prosencephalon forerunners of the portions of the eyes will induce the head ectoderm to thicken, invaginate, and form the lens vesicles cavity: opticoel Proamnion region below the head fold consists of ectoderm underlain with a layer of endoderm will eventually be overgrown and disappear
Section through Oral Plate
Prosencephalon forebrain that consists of median vesicle and a lateral outpocket on each side cavity: prosocoel
Foregut smile-shaped cavity ventral to notochord walls are derived from endoderm middle portion of the foregut’s floor is slightly thickened
Anterior neuropore median cleft at anterior tip of neural tube presence of this opening means the neural folds have not fused yet Lens Placode thickening of head ectoderm that surrounds the optic vessel forerunner of eye lenses Infundibulum shallow depression of prosencephalic floor located at posterior border of optic vessels Amniotic fold fold of somatopleure arise at the head region, the sides, and the caudal end fusion of amniotic folds will give rise to amnion (inner) and chorion (outer) Yolk sac extra embryonic membrane encloses and absorbs yolk of amniote embryos endoderm + splanchnic mesoderm (splanchnopleure) Other structures to be noted (description in 24-hour chick) Head ectoderm Mesenchyme Neural Crest Subcephalic pocket Area pellucida Coelom Area Vasculosa
Notochord ventral to mesencephalon mesoderm derived
Oral Plate thickened area formed by the ventral ectoderm and the adjacent endodermal evagination of pharynx ventral to the foregut will form the mouth when it perforates Subcephalic Space Extraembryonic germ layers
below the head fold
Mesencephalon oval-shaped brain vesicle posterior to prosencephalon Anterior cardinal veins paired blood vessels at the lateral sides of the mesencephalon Pharynx region of foregut at this level Dorsal Aorta large, paired blood vessels dorsal to the pharynx Stomodeum shallow midventral depression in the ectoderm forerunner of buccal cavity Ventra Aorta small paired blood vessels located below the pharynx one is at each side of a median depression in the floor of the foregut First Aortic Arches connects the dorsal aorta with the ventral aorta can be seen at the anterolateral region of the foregut
2
Neural Crest cells found at the edges of the neural plate and above the neural tube will form ganglia, pigment cells, and parts of the gills Thyroid Gland endocrine gland that functions for control of metabolism and growth from ventral endoderm of pharynx seen as a thickened shallow depression of the foregut at the region of the dorsal mesocardium Section at the level of the Heart: Posterior Sections Atrium posterior level of the heart located now at the middle of the pericardial cavity becomes the future auricles Sinus venosus caudal continuation of the atrium dorsoventrally flattened tube in the midline Section at the level of the Heart: Anterior Section Ventral Aortae fusion of ventral aorta from earlier now a median, unpaired vessel Bulbus arteriosus anterior chamber of heart embryo connects ventricle to the ventral aorta Epimyocardium outer, thicker layer of heart rudiment arises from splanchnic mesoderm fuses with the endocardium to form the heart’s wall will give rise to: epicardium (outer covering of the heart) and myocardium (cardiac musculature)
Anterior Intestinal Portal ventral opening of the gut into the yolk future midgut Vitelline veins paired, large vessels that enter the atrium via sinus venosus at the caudal sections, these vessels will rise at the lateral part of the blastoderm Anterior cardinal veins pair of small blood vessels above the dorsal aortae also lies adjacent to the rhombencephalon
Isthmus broad connection between heart and foregut synonymous to dorsal mesocardium rhombencephalon by the time na mag-heart na
Section at the level of the Heart: Through the Ventricle Ventricle bends to one side of the coelom narrower dorsal mesocardium Rhombencephalon posterior part of brain level of future ventricle possesses a thick wall Auditory Pits ectodermal thickenings at hindbrain level forerunners to the inner ears syn: auditory placodes
3
Section through the Sinus Rhomboidalis Neural Tube neural groove has opened Hensen’s node large mass of compactly arranged cells displaces the notochordal tissue
Section through the Somites
Unsegmented mesoderm somites are not yet divided at this section Omphalomesenteric vein it is located far out in the splanchnopleure
Spinal Cord elongated with elliptical cavity Notochord Somites Nephrotome
refer to the 24-hour chick description for these structures
Hypomere Dorsal Aortae pair of large vessels between the endoderm and the somites at more caudal sections, they continue laterally into the plexus of vessels -- emphalomesenteric arteries
4
pictures are from: http://www.vcbio.science.ru.nl/images/embryology/c hicken-33hrs-dorsal-longitudinal-patten.gif http://nte-serveur.univlyon1.fr/nte/embryon/www.uoguelph.ca/zoology/devobio/33h rchck/33ckintr.htm https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/i mages/thumb/7/72/Patten028.jpg/600px-Patten028.jpg
5